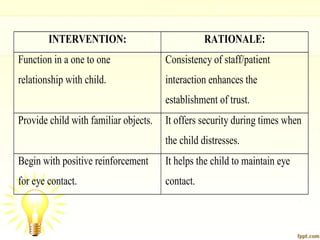
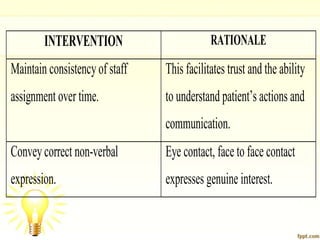
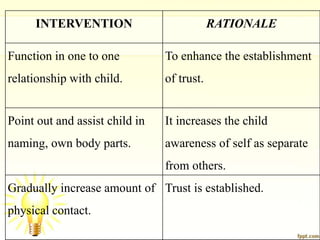
Autism is a developmental disorder characterized by impaired communication, social interaction, and behavior, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. The condition generally has its onset before the age of 2.5 years, and while its exact causes involve genetic and environmental factors, effective treatment typically includes behavioral therapies and medication to manage specific symptoms.























![• 3. Screening test for autism (such as the
Checklist for Autism in Toddlers [CHAT] or
the Autism Screening Questionnaire).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/autism-180204084513/85/Autism-MSc-MENTAL-HEALTH-NURSING-25-320.jpg)