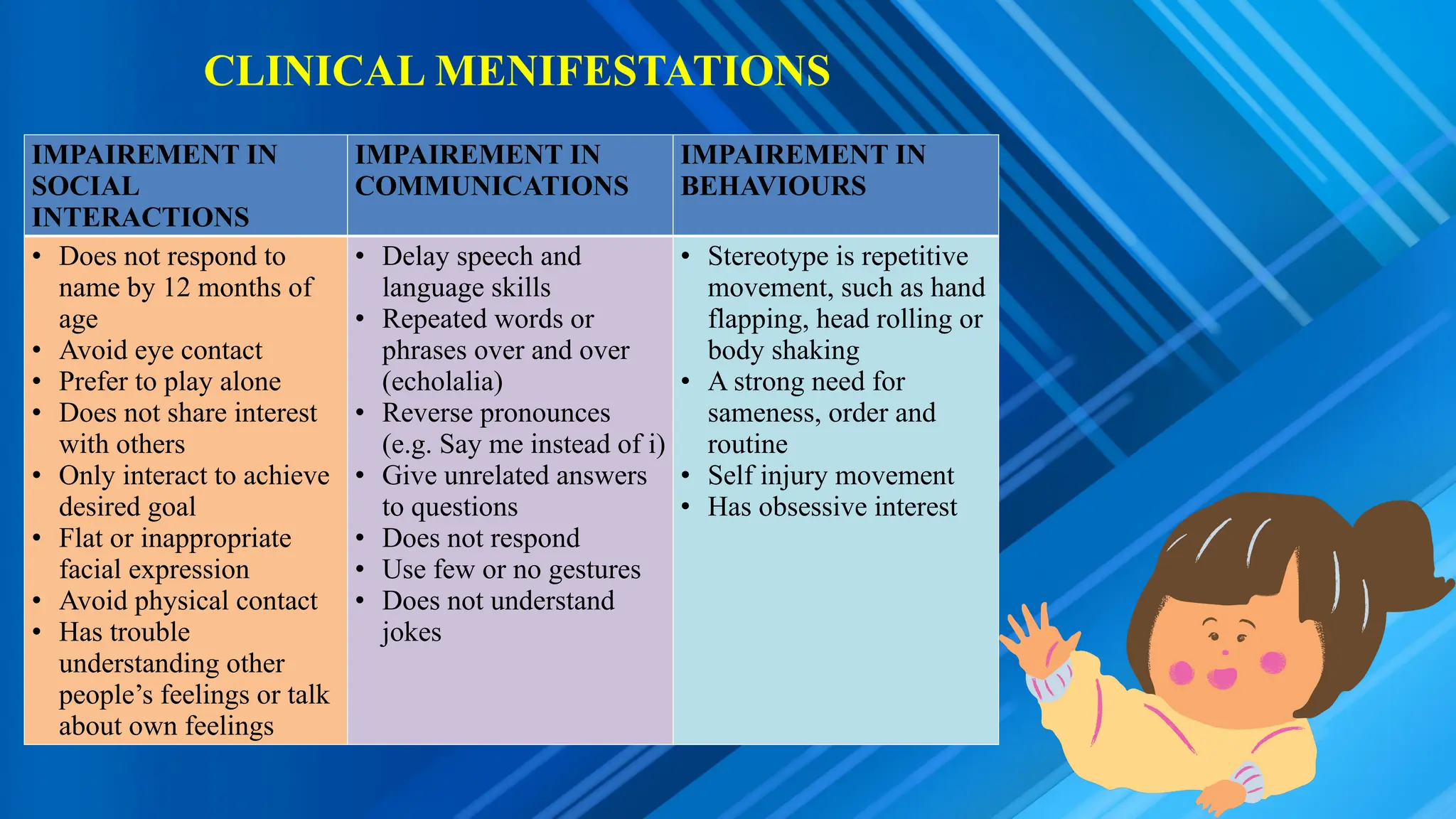
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder characterized by impaired social interactions, communication issues, and repetitive behaviors. Prevalence is approximately 1-2 per 1000, with a higher risk in boys, and potential causes include neurological, biochemical, genetic, and environmental factors. Management strategies involve special education, behavioral management, family therapy, and various medications.