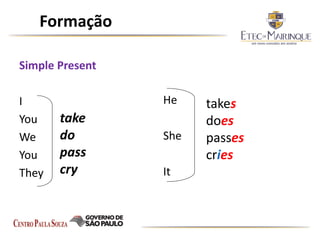
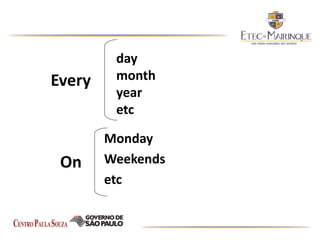
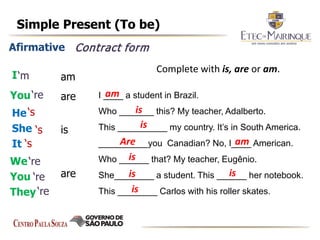
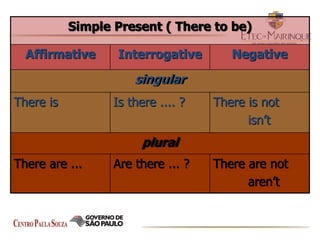
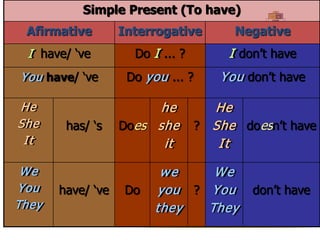
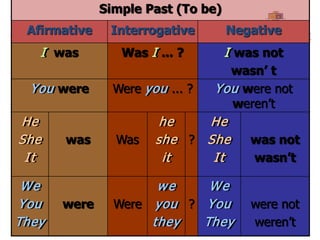
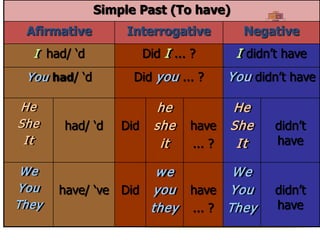
The document explains the formation and usage of the simple present tense in English, including affirmative, negative, and interrogative forms. It details the rules for verb conjugation, especially for third-person singular, and discusses common adverbs of frequency and their placement in sentences. Additionally, it provides examples and exercises for practicing the simple present tense.