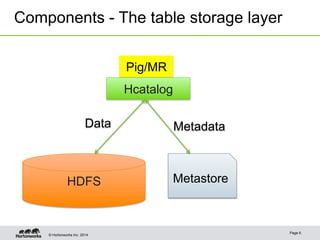
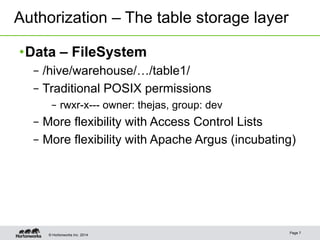
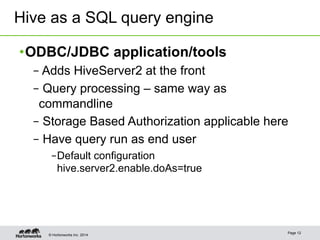
The document discusses security concepts and authorization solutions for Apache Hive. It introduces key security concepts like authentication and authorization. It then describes different authorization solutions for Hive including storage-based authorization using HDFS permissions, SQL standard-based authorization using grant/revoke statements in HiveServer2, and extending Hive authorization using plugins. It concludes by discussing use cases implemented at Yahoo, including row and column level access controls using HiveServer2 and views, and limited authorization for the Hive CLI.