The document discusses balanced and unbalanced assignment problems and the Hungarian method for solving them. It provides the following key points:
- Assignment problems involve assigning jobs to workers or machines to minimize costs or maximize output. The Hungarian method is commonly used to solve them.
- Balanced problems have an equal number of jobs and workers, while unbalanced problems have different numbers.
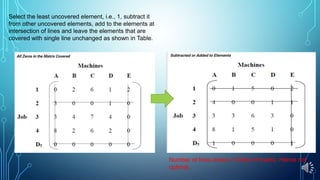
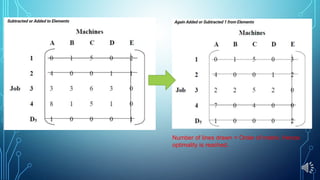
- The Hungarian method uses a matrix and steps of row/column reduction, finding minimum uncovered values, and covering zeros with lines to find an optimal assignment.
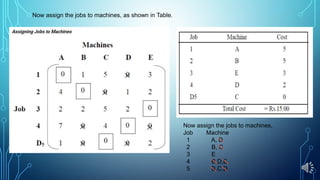
- An example shows applying the method to assign four jobs to four machines and minimizing costs in the assignment matrix.