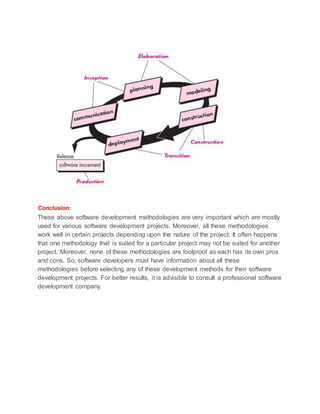
The document discusses and compares several software development life cycle (SDLC) models:
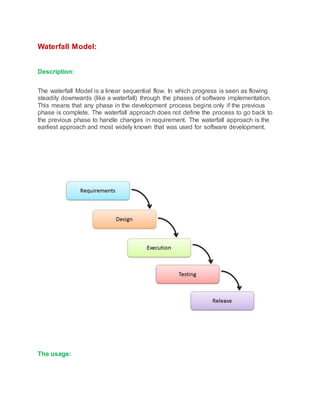
1) The waterfall model is a linear sequential flow where progress flows steadily through phases without backtracking. It is best for projects with clearly defined requirements.
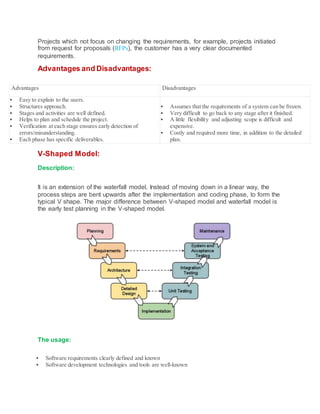
2) The V-shaped model extends the waterfall model with early testing. It works well when requirements are easily understood.
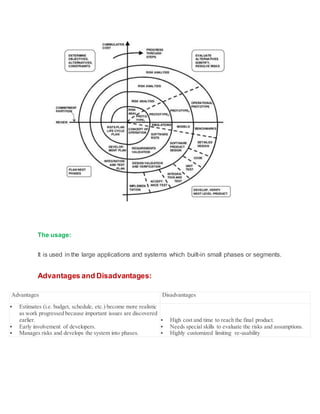
3) The spiral model combines prototyping and risk assessment in cycles. It is favored for large, expensive projects built in phases.
4) The iterative model develops a system through repeated cycles and smaller portions, allowing learning from earlier versions. It produces value early and accommodates some changes.
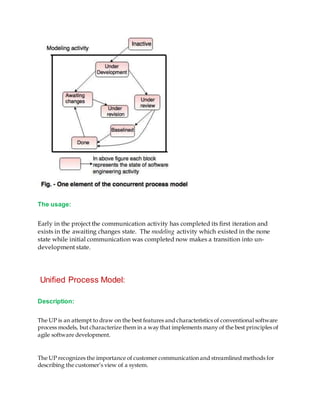
5) The concurrent model develops tasks and states concurrently through framework