This document discusses various narrative theories including:
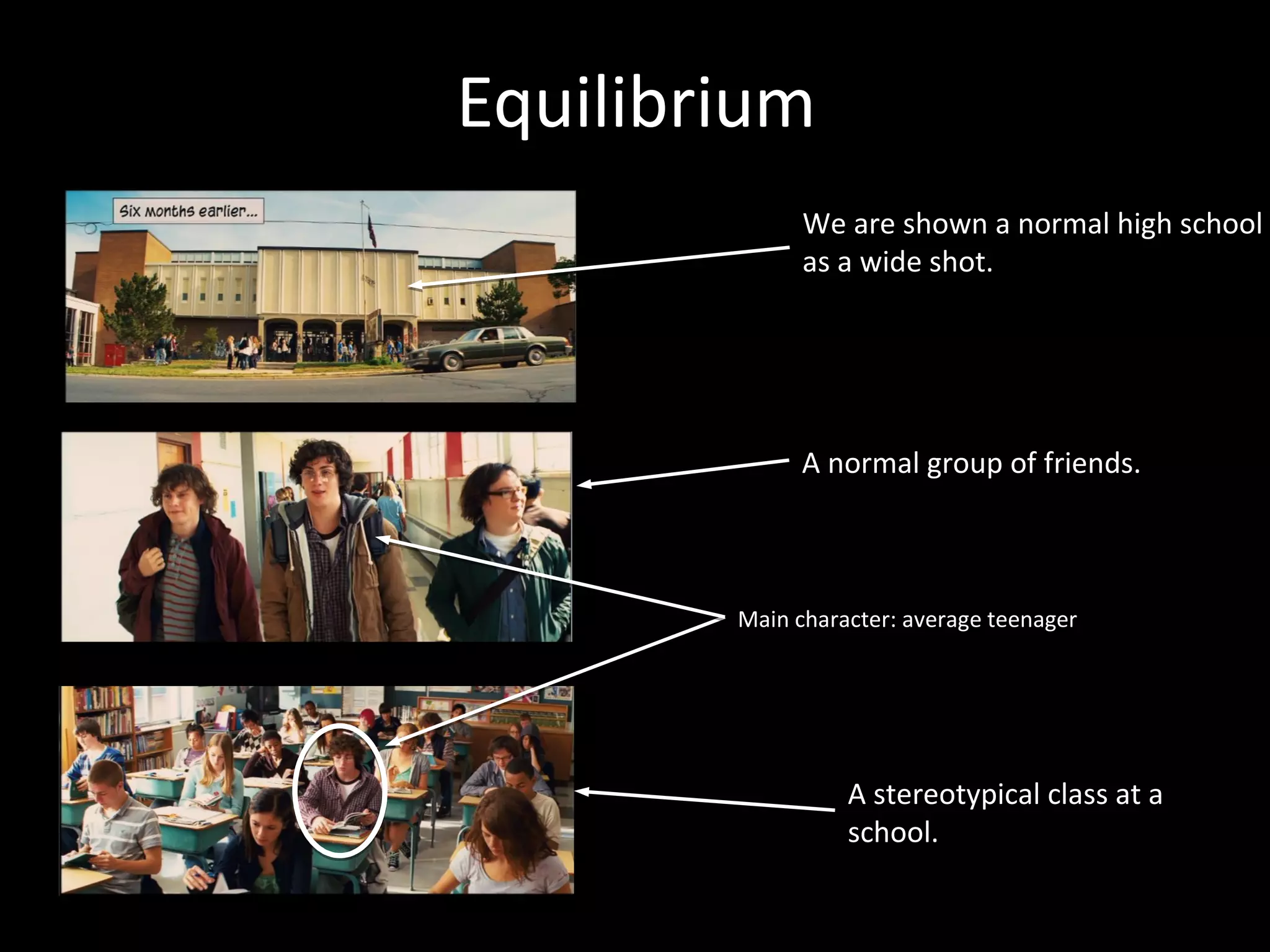
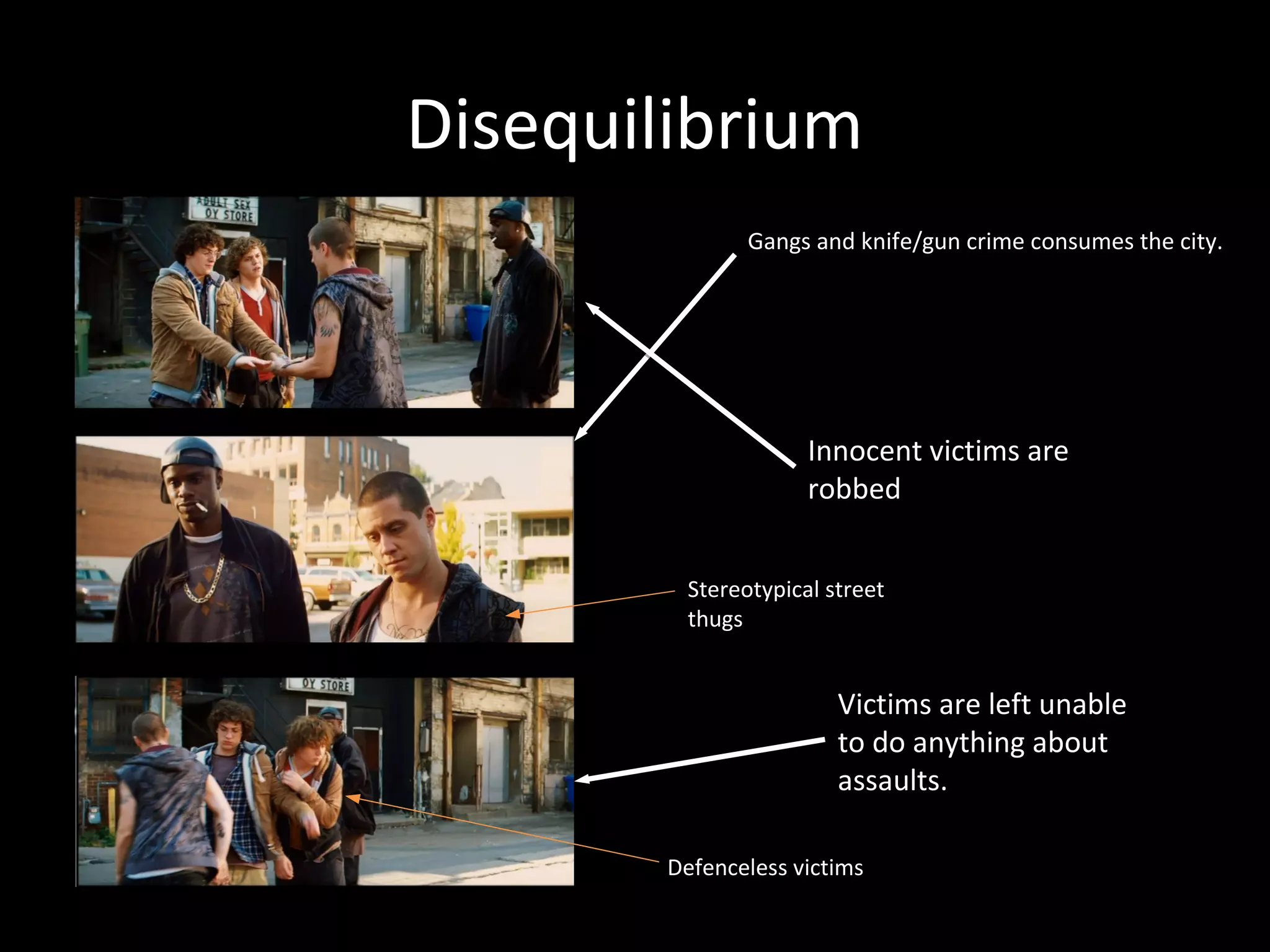
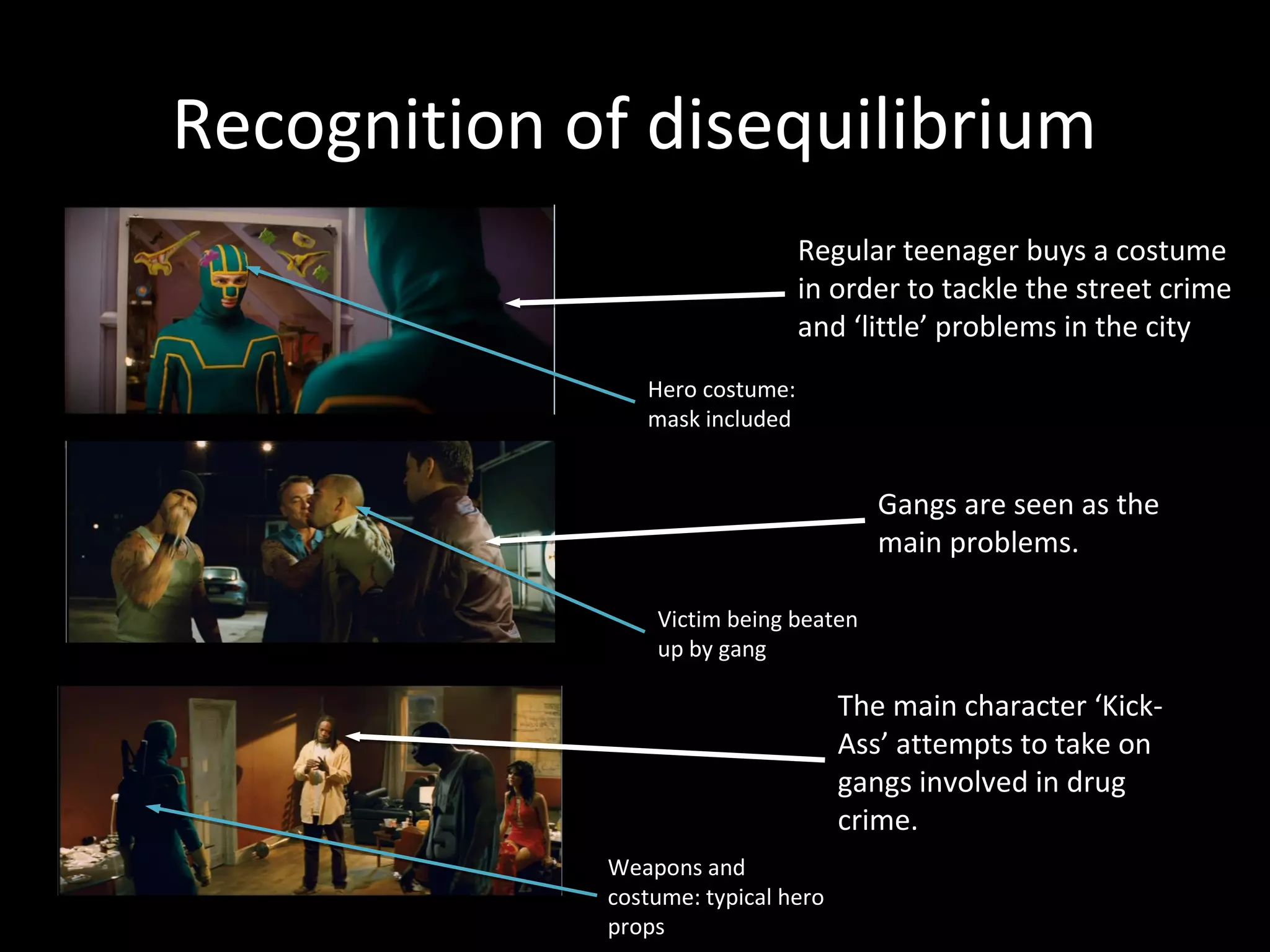
1. Todorov's theory of 5 stages of narrative: equilibrium, disequilibrium, recognition, attempt to repair, new equilibrium. This is applied to the film Kick-Ass.
2. Levi-Strauss' theory that the world is described through binary opposites like good/bad.
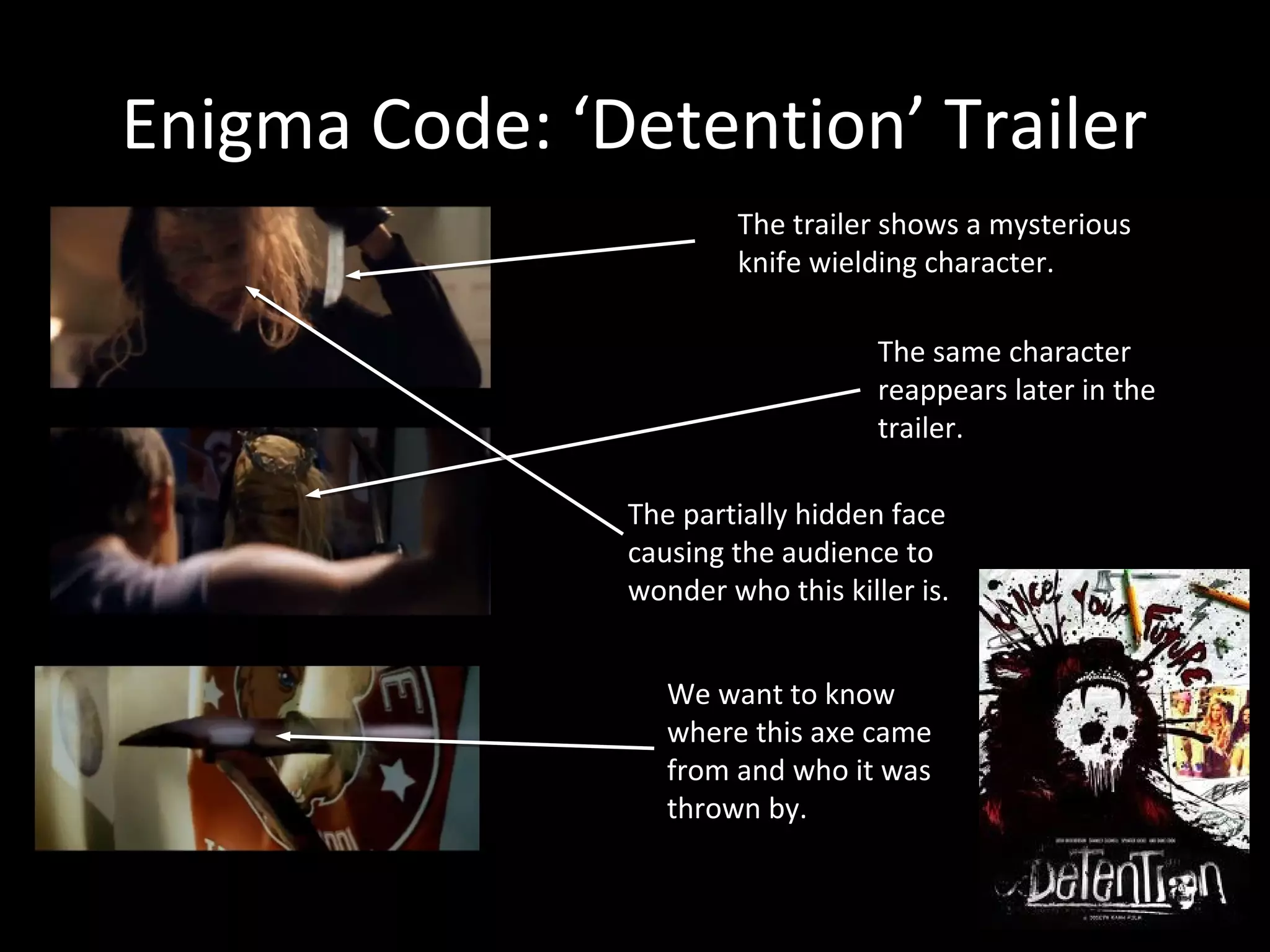
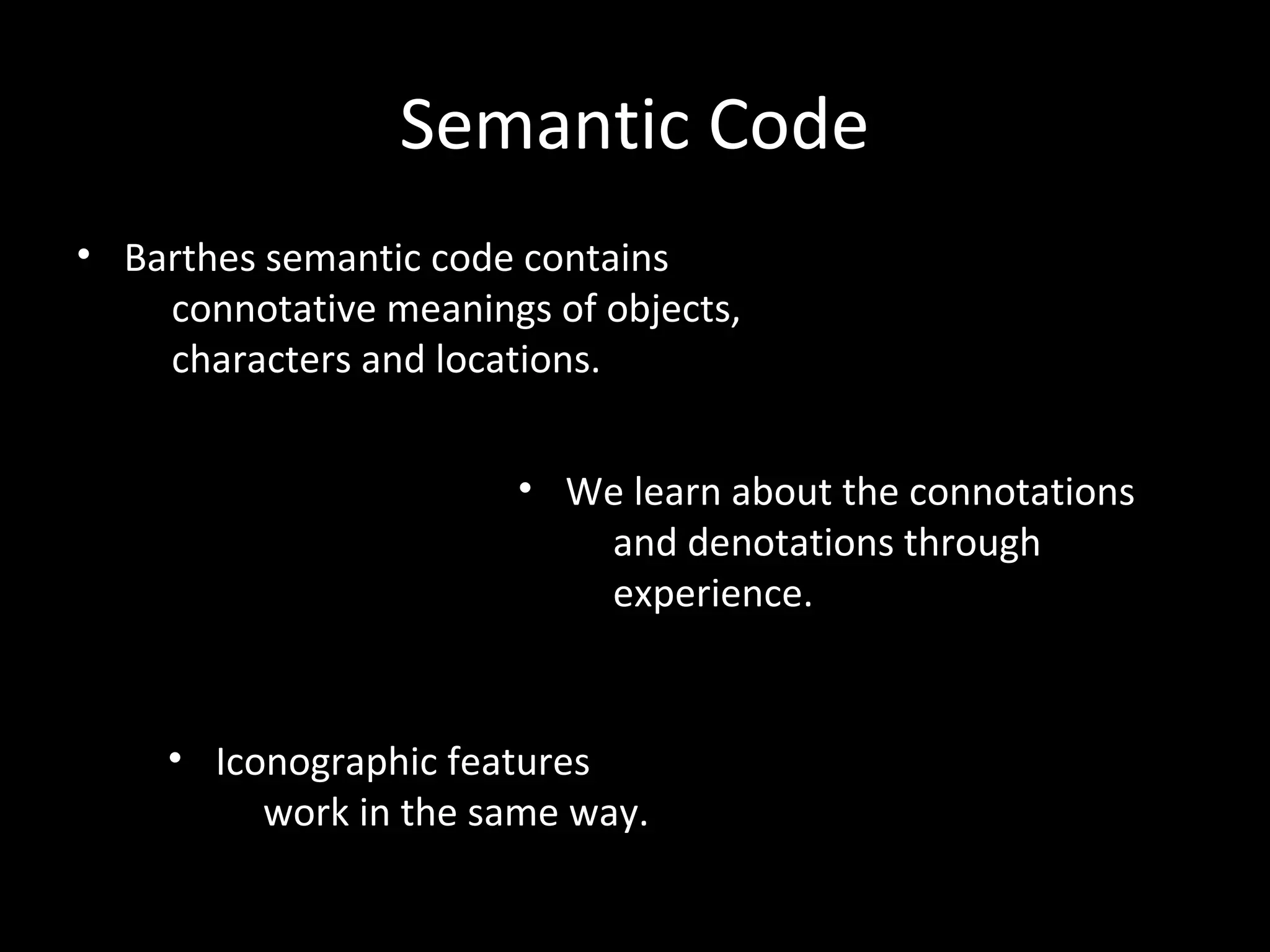
3. Barthes' theory of codes including enigma, action, semantic, symbolic, and cultural codes which provide clues and encourage audience anticipation. Various film examples are discussed.
4. Propp's theory of 7 character types in folktales and legends.
5. Other terms discussed include diegesis, narrative range (restricted