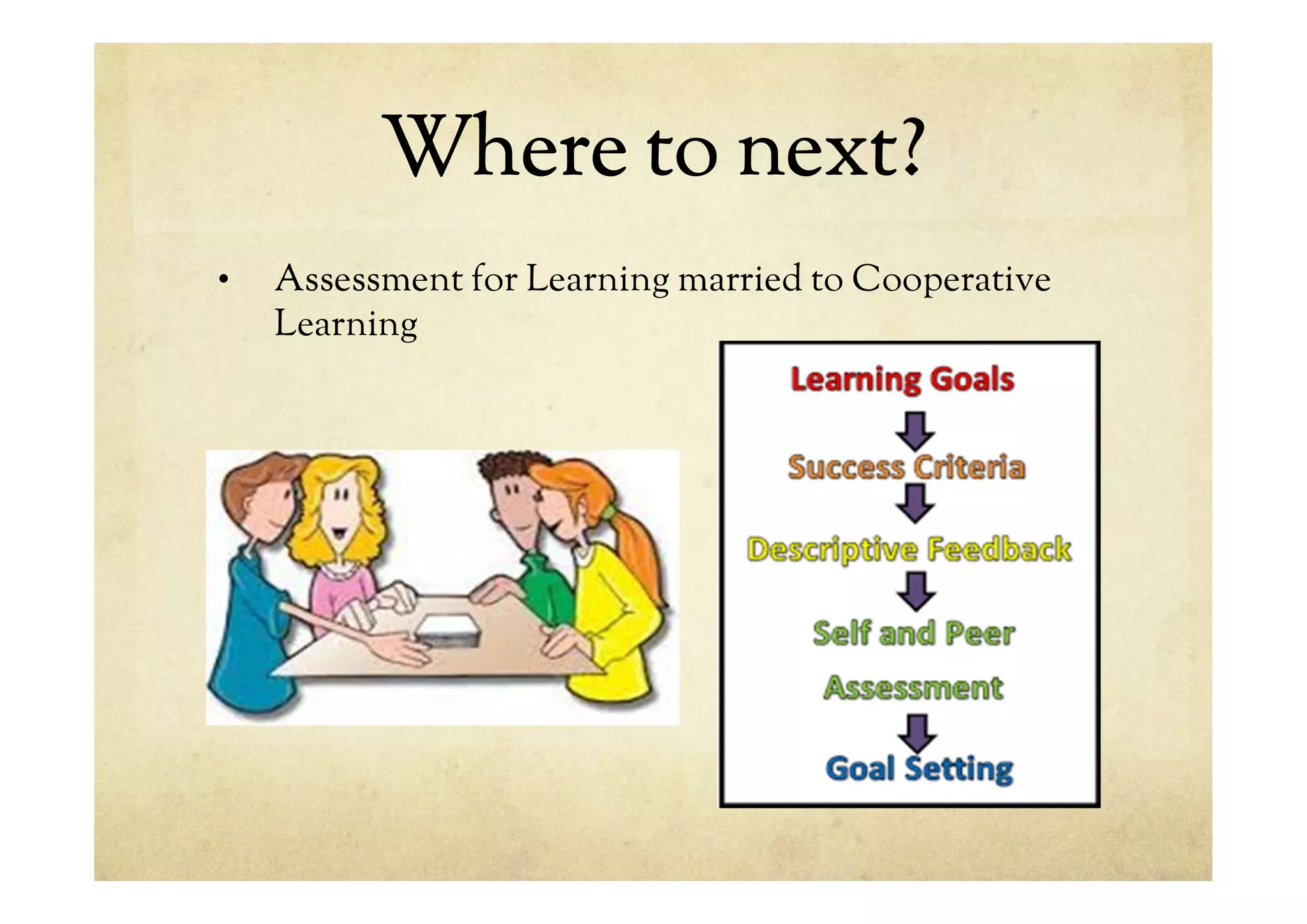
The document discusses assessment for learning (AfL). It defines AfL as being part of everyday practice by students, teachers, and peers that seeks, reflects upon, and responds to information from dialogue, demonstration, and observation to enhance ongoing learning. The key elements of AfL are knowing the goals of learning, comparing actual performance to desired performance, and taking action to close gaps. The teacher's role is to get alongside learners, notice and respond to learning, promote dialogue, and establish an environment where learners take responsibility for their learning. The learner must know the goals, standards, their current achievement, and how to improve.










![The Teacher’s Role is to:
• Get ‘alongside’ the learner(s), noticing, recognising and
responding to learning, during learning [importance of
knowledge bases];
• Promote dialogue between learners, and between the teacher
and learner(s) so they can co-construct understandings, ask
questions …
• Establish an environment and program that encourages
learners to take responsibility for and ownership of their learning
(to become self-regulating learners )
eg: provide authentic opportunities to set goals, generate
feedback, review peers’ work, self-monitor, reflect on learning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assessmentforlearning-190324125221/75/Assessment-for-learning-11-2048.jpg)