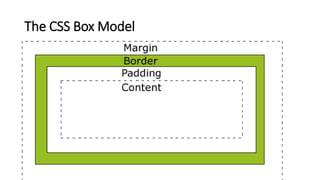
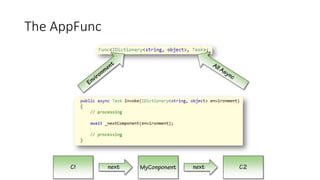
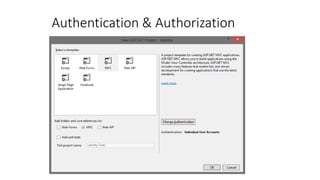
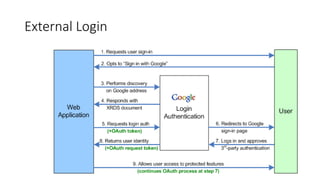
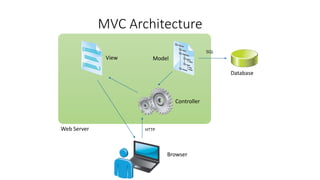
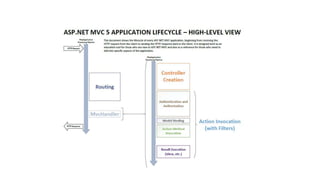
The document outlines a comprehensive course on ASP.NET MVC 5, detailing important concepts such as models, views, controllers, routing, authentication, and integration with JavaScript and SignalR. It covers practical implementation aspects, including creating projects, using Entity Framework, implementing AJAX, and building Web APIs. Additionally, it discusses architectural components like OWIN and Katana for building scalable applications.








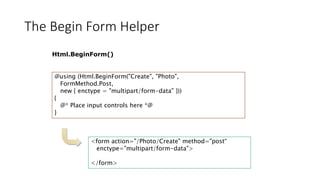
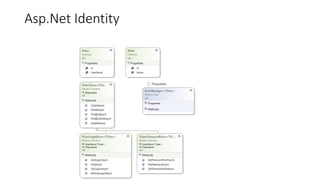
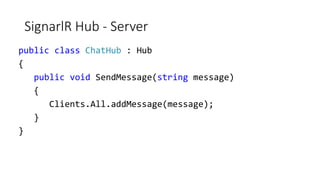
![Developing Models
public class Photo
{
public int PhotoID { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public byte[] PhotoFile { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public DateTime CreatedDate { get; set; }
public string Owner { get; set; }
public virtual List<Comment> Comments { get; set; }
}
-PhotoID : int
-Title : string
-PhotoFile : byte
-Description : string
-CreatedDate : object
-Owner : string
Photo
-CommentID : int
-User : string
-Subject : string
-Body : string
-PhotoID : int
Comment
1 0..*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvc5presentation-181223062352/85/Asp-Net-MVC-5-in-Arabic-12-320.jpg)
![Display and Edit Data Annotations
public class Photo
{
// other properties excluded
[DisplayName("Picture")]
public byte[] PhotoFile { get; set; }
[DataType(DataType.MultilineText)]
public string Description { get; set; }
[DataType(DataType.DateTime)]
[DisplayName("Created Date")]
[DisplayFormat(DataFormatString = "{0:dd/MM/yy}"]
public DateTime CreatedDate { get; set; }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvc5presentation-181223062352/85/Asp-Net-MVC-5-in-Arabic-13-320.jpg)
![Validating User Input with Data Annotations
public class Person
{
public int PersonID { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage="Please enter a name.")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Range(0, 400)]
public int Height { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.EmailAddress)]
public string EmailAddress { get; set; }
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvc5presentation-181223062352/85/Asp-Net-MVC-5-in-Arabic-14-320.jpg)