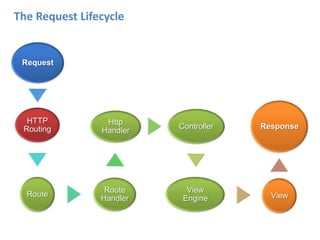
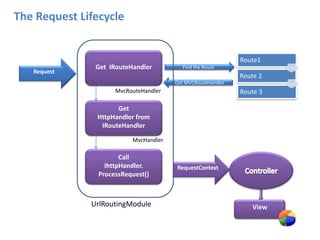
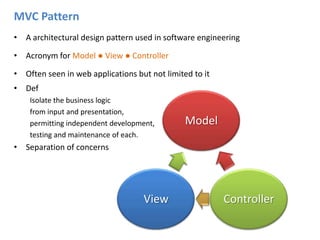
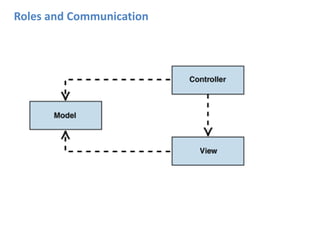
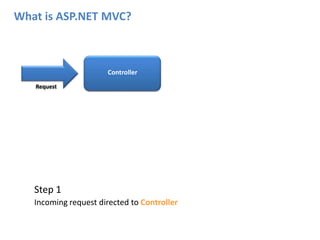
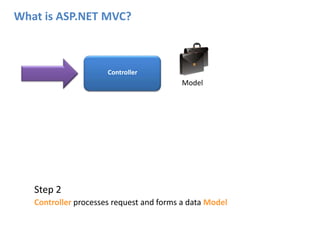
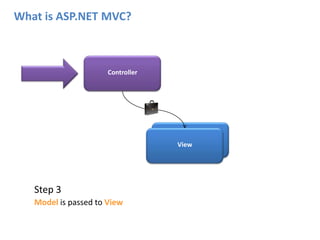
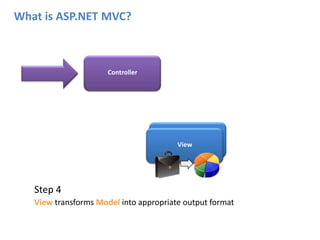
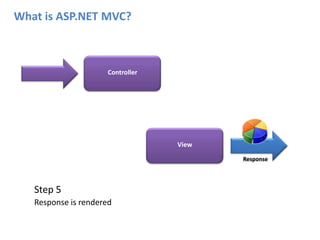
ASP.NET MVC is an architectural pattern that separates an application into three main components: the model, the view, and the controller. The MVC pattern decouples these components to allow for independent development and testing. ASP.NET MVC uses this pattern and introduces features like testability, loose coupling, separation of concerns, and clean URL structures. The core components include models for the data, controllers to handle requests and interface with models, and views for generating output. Requests are routed and then handled by the controller, which works with models and returns an action result to the view for output.











![Model BindersThese are user defined classes Used to define the strongly typed views of model objectsTo make easy of handling HTTP Post requests and helps in populating the parameters in action methods.Models are passed betweenAction method Strongly Typed ViewsUse attribute to override model binding Bind(Exclude:="Id")How?Incoming data is automatically parsed and used to populate action method parameters by matching incoming key/value pairs of the http request with the names of properties on the desiredSo what can we do In view you can use the Model.propertyname(or)ViewData[“propertyname “]In action method for post you can have model object as parameter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-101012062748-phpapp01/85/ASP-MVC-Training-20-320.jpg)

![FiltersFilters handovers extra framework level responsibility to Controller/Action methodsAuthorize: This filter is used to restrict access to a Controller or Controller action.Authorize(Roles=”Admins, SuperAdmins”)]HandleError: This filter is used to specify an action that will handle an exception that is thrown from inside an action method.[HandleError(Order=1, ExceptionType=typeof(ArgumentException), View=”ArgError”)]OutputCache: This filter is used to provide output caching for action methods.[OutputCache(Duration=60, VaryByParam=”none”)]ValidateInput:Bind: Attribute used to provide details on how model binding to a parameter should occur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-101012062748-phpapp01/85/ASP-MVC-Training-23-320.jpg)

![ErrorsHandleError Attribute Mark methods with this attribute if you require to handle a special exception [HandleError(Order=1, ExceptionType=typeof(ArgumentException), View=”ArgError”)]By default no need to mention Exception type . It returns Error view in shared folderThis attribute will create and populate the System.Web.Mvc.HandleErrorInfoError.aspx is a strongly typed view of HandleErrorInfoEnable CustomErrors in web.configHow do you handle errors if the user tries to request a wrong URL??ApproachCreate a controller by name ErrorCreate a Action method with some error number/error/404Enable custom errors and specify redirect the url to Create a views to show the error messageRetrieve the user requested url with Request.QueryString["aspxerrorpath"]Configure the Route in global.aspx(optional depends upon the existing routes)routes.MapRoute("Error“, "Error/404/{aspxerrorpath}", new { controller = "Error", action = "404", aspxerrorpath = "" });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-101012062748-phpapp01/85/ASP-MVC-Training-25-320.jpg)