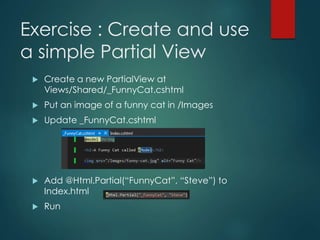
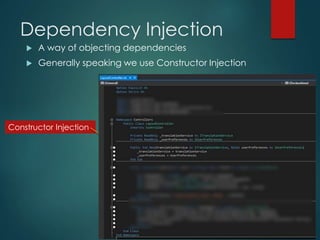
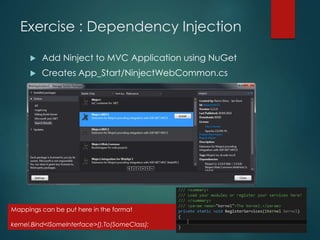
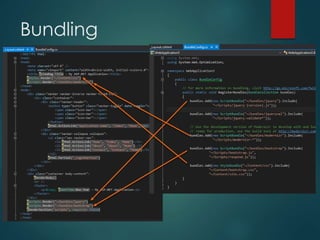
This document discusses several key concepts in ASP.NET MVC including areas, HTML helpers, partial views, dependency injection, model validation, and asynchronous controller actions. It provides code examples for creating an area, partial view, unit tests, and using model attributes for validation. The document is intended to be part of an ASP.NET MVC training and covers important topics like routing, generating HTML, reusing views, testing, and asynchronous programming.











![Scaffolding Views
It is possible to auto-generate the input fields for a
Views Model properties
@Html.EditorForModel()
May have to ignore unwanted Model properties
with [ScaffoldColumn(false)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-part2-150501084750-conversion-gate02/85/MVC-Training-Part-2-16-320.jpg)
![Exercise : Scaffolding View
using Model Change the save form on
the Index View to use
@Html.EditorForModel() and
run
You should see most of the
properties are provided
with relevant inputs
To tell the ‘auto-scaffolder’
to ignore certain properties,
give the properties the
[ScaffoldColumn(false)]
attribute](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-part2-150501084750-conversion-gate02/85/MVC-Training-Part-2-17-320.jpg)
![Model Attributes
Model properties can be given attributes to provide
additional information about them
This is especially useful in validation
Attributes include
[Required]
Marks the property as non-optional
[DisplayName]
Overrides the default label of a property in the view
[StringLength(50), MinimumLength=3]
Sets a max length for a string property
[Range(0,5]
Provided value must be within a range](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mvctraining-part2-150501084750-conversion-gate02/85/MVC-Training-Part-2-18-320.jpg)



