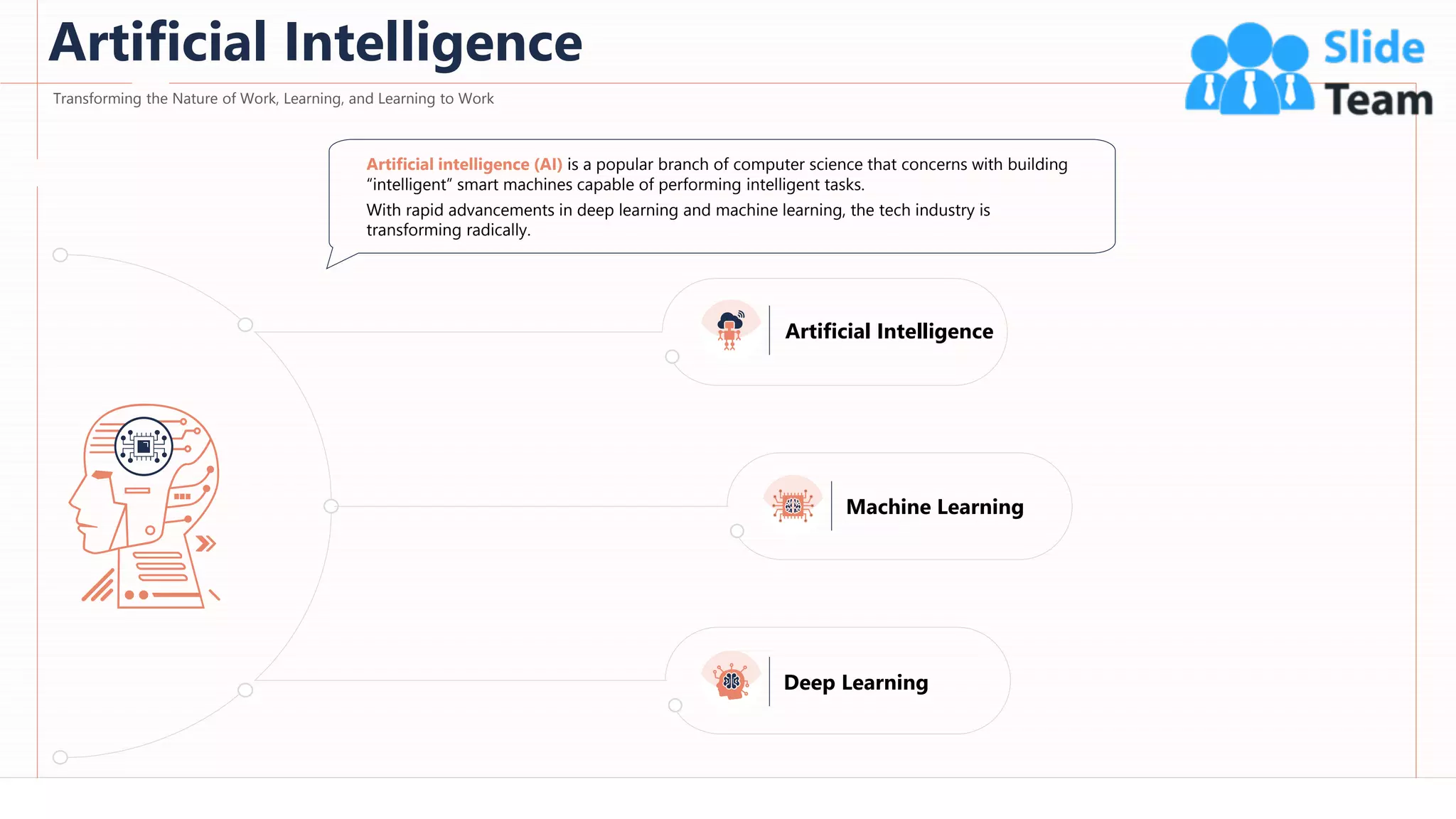
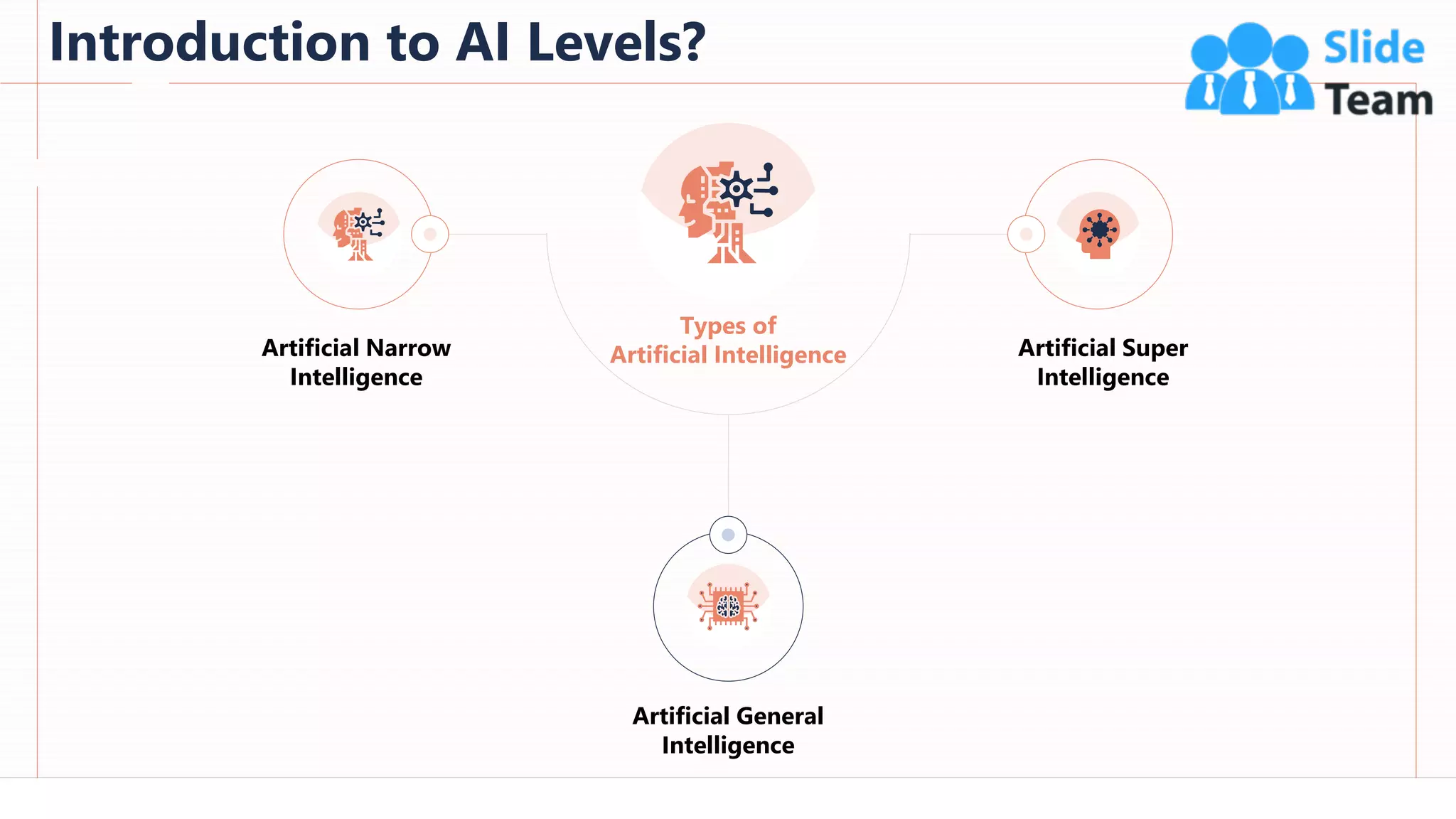
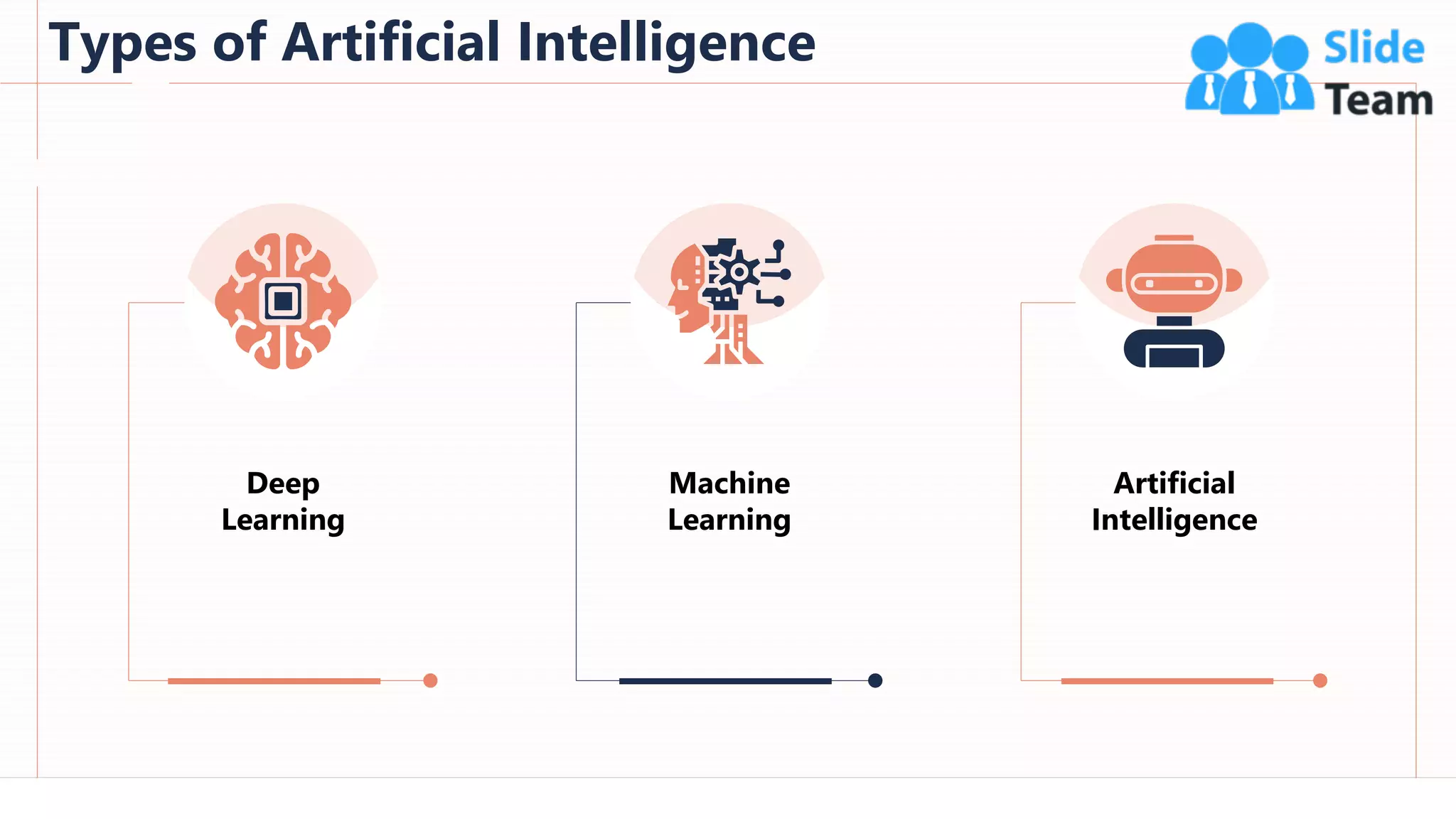
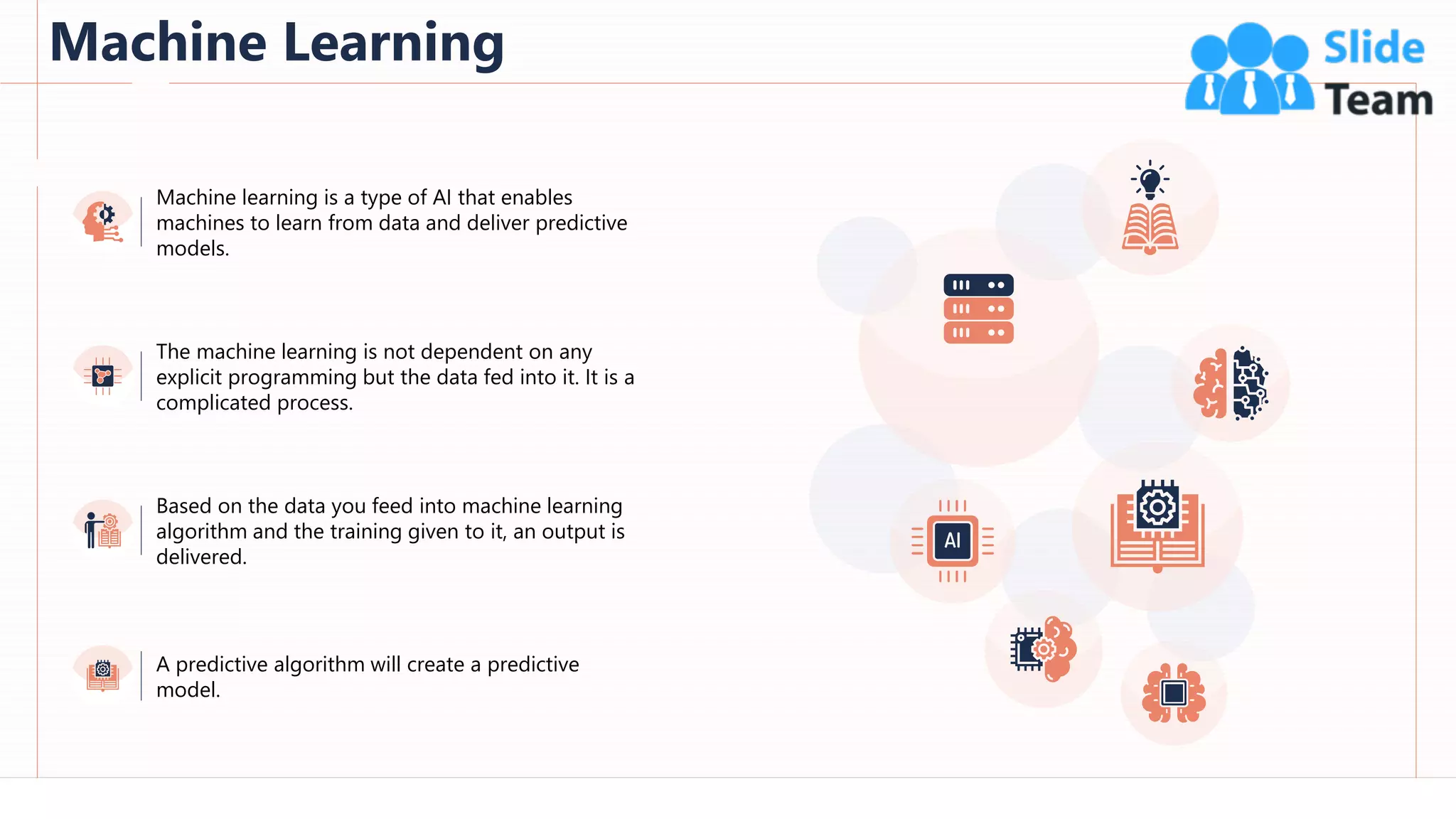
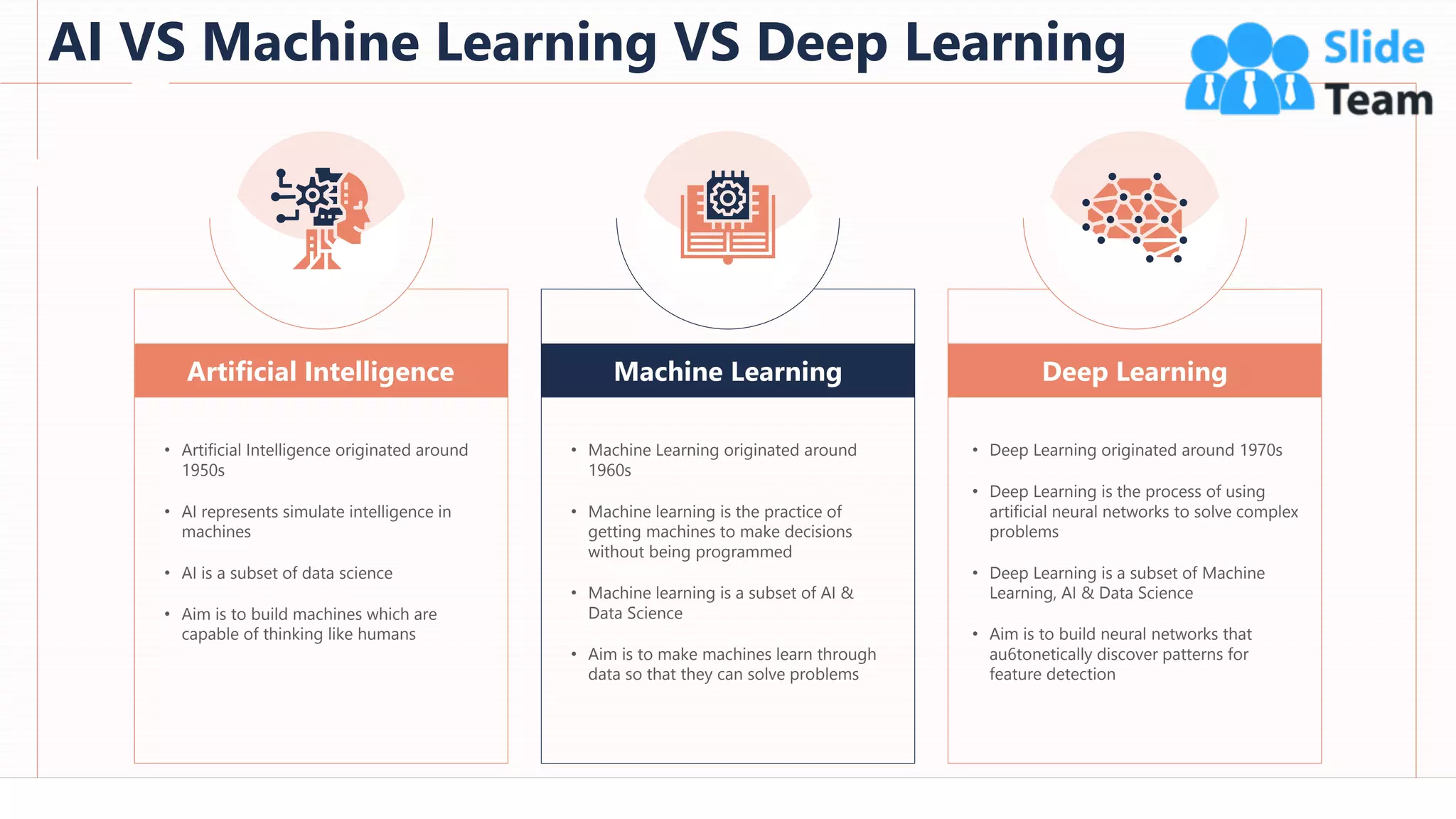
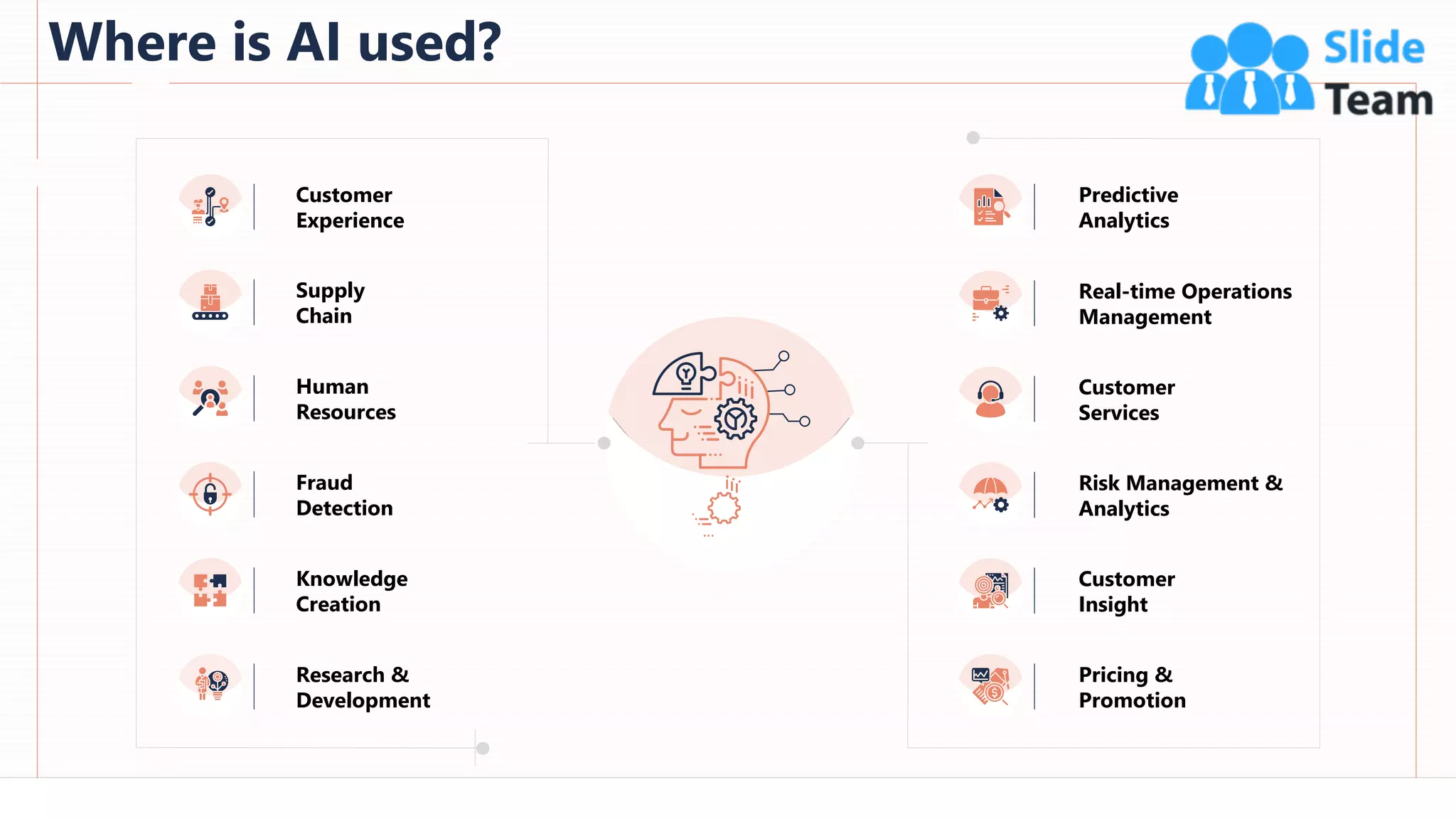
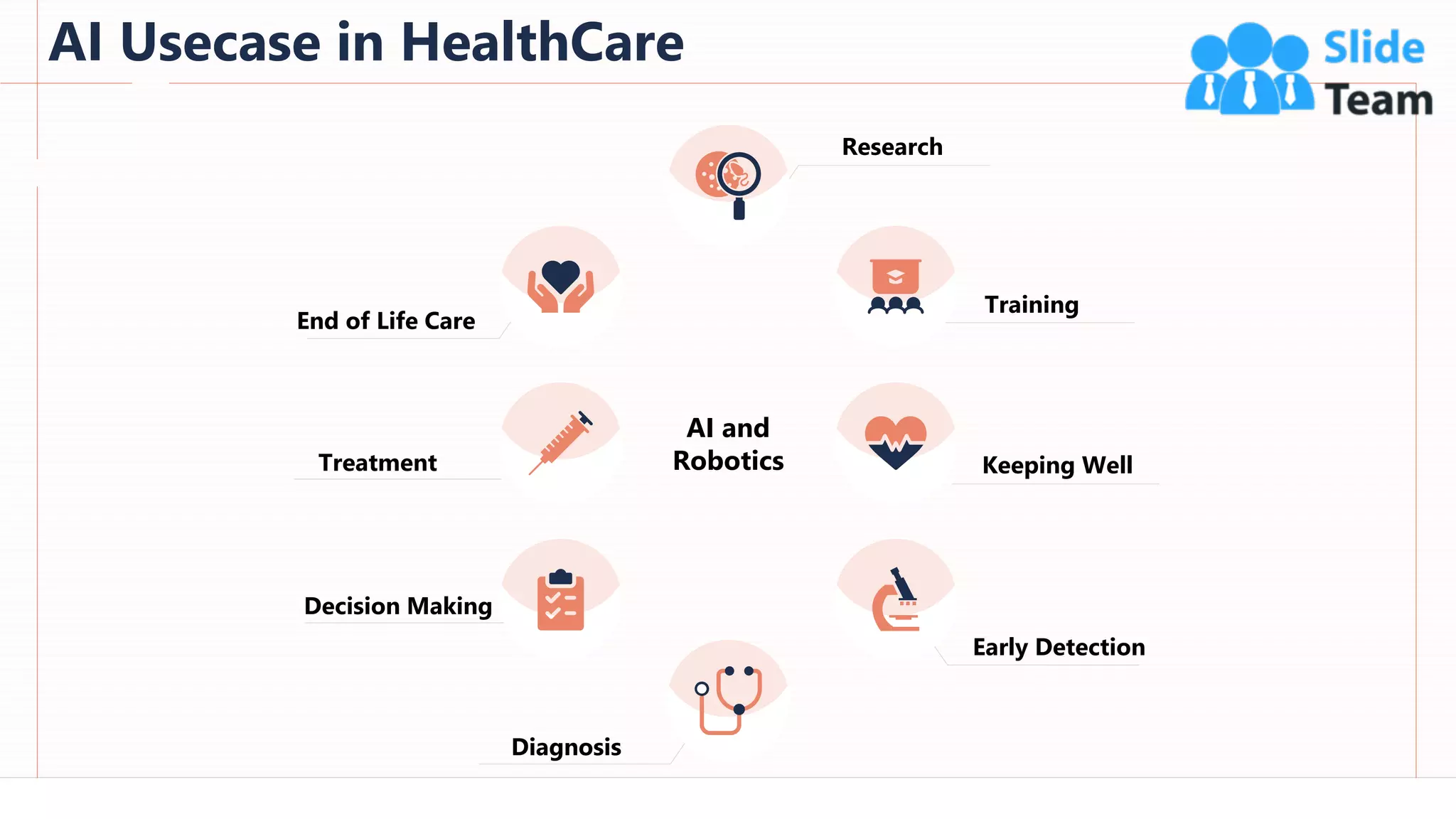
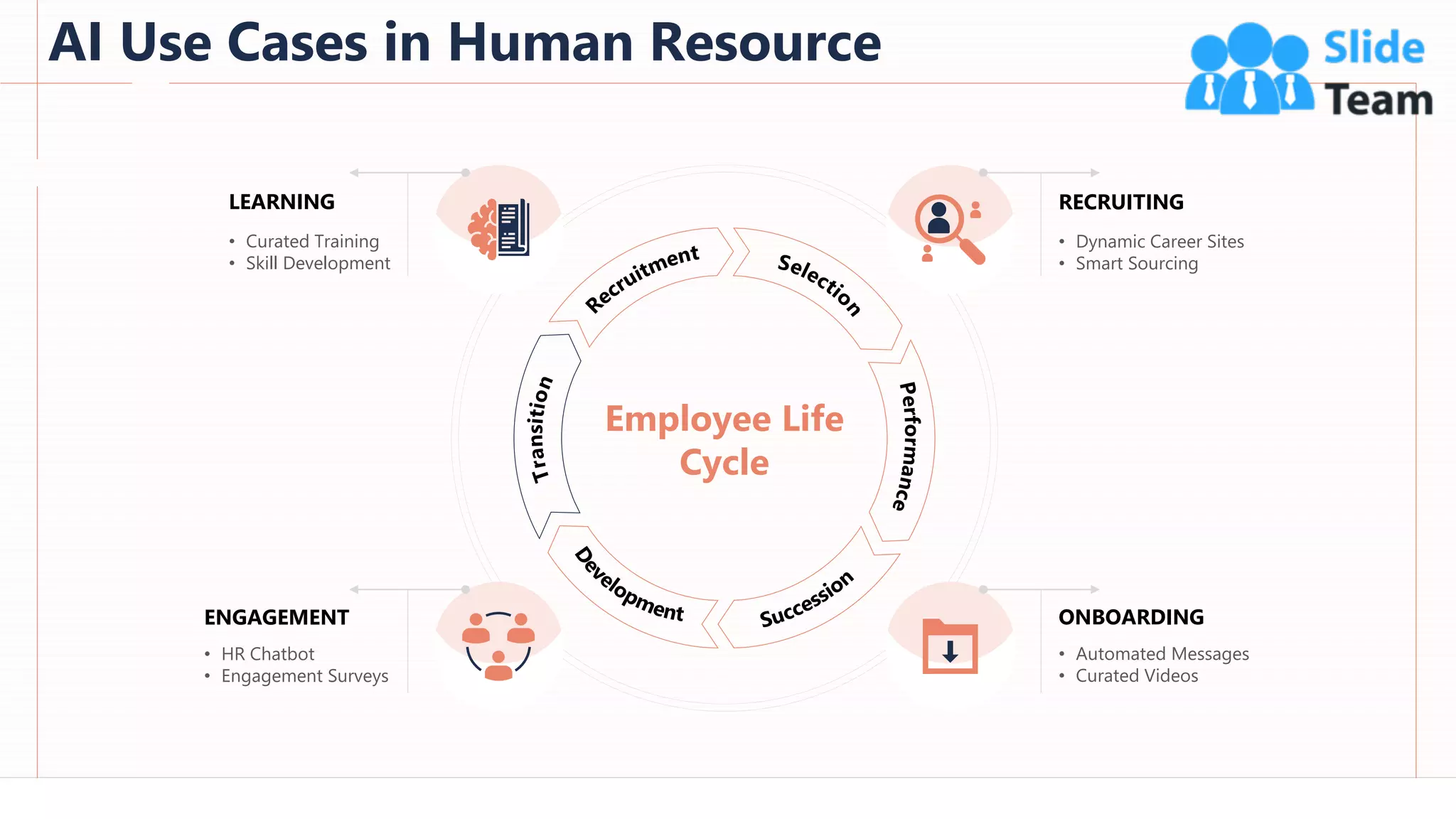
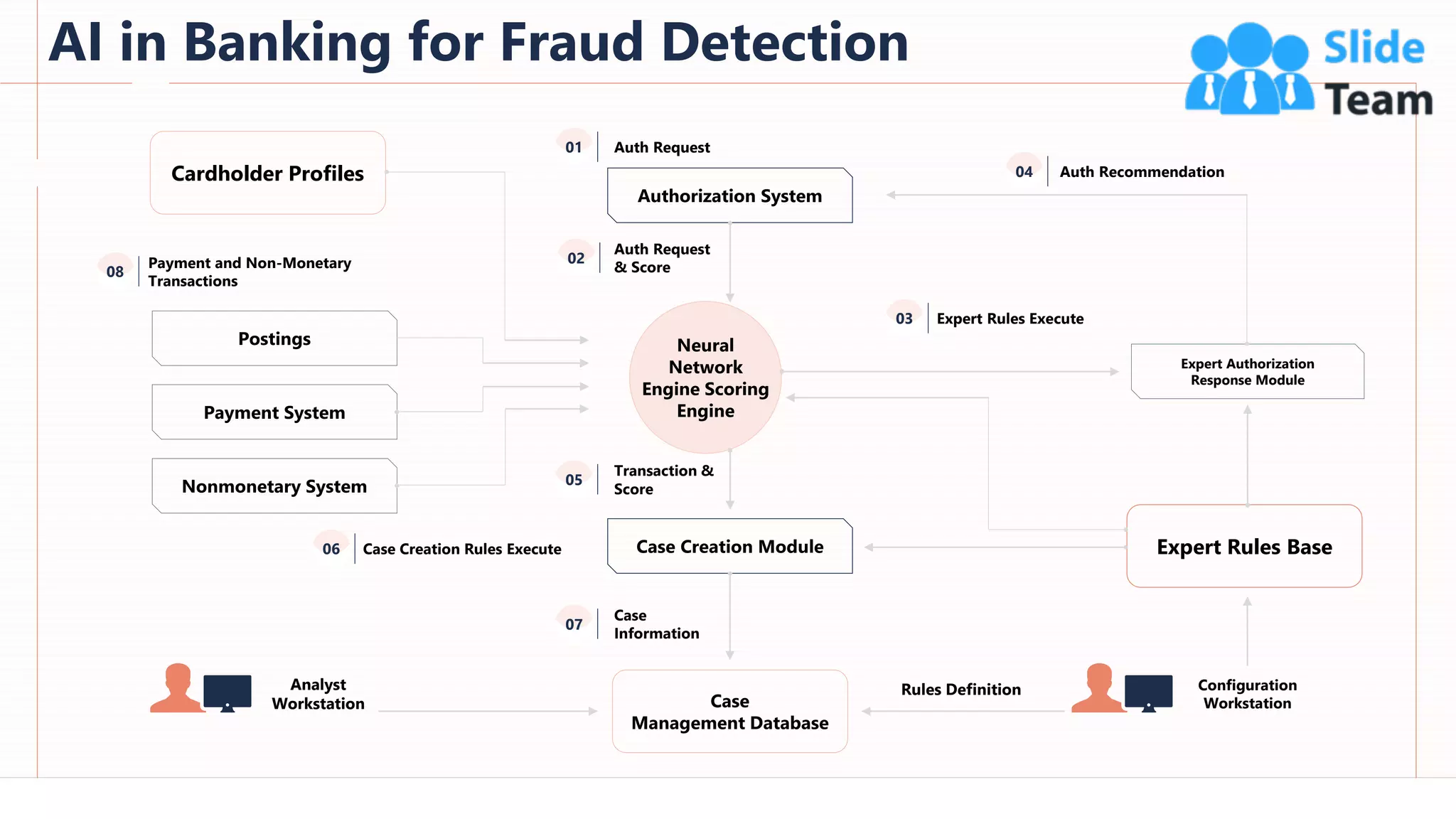
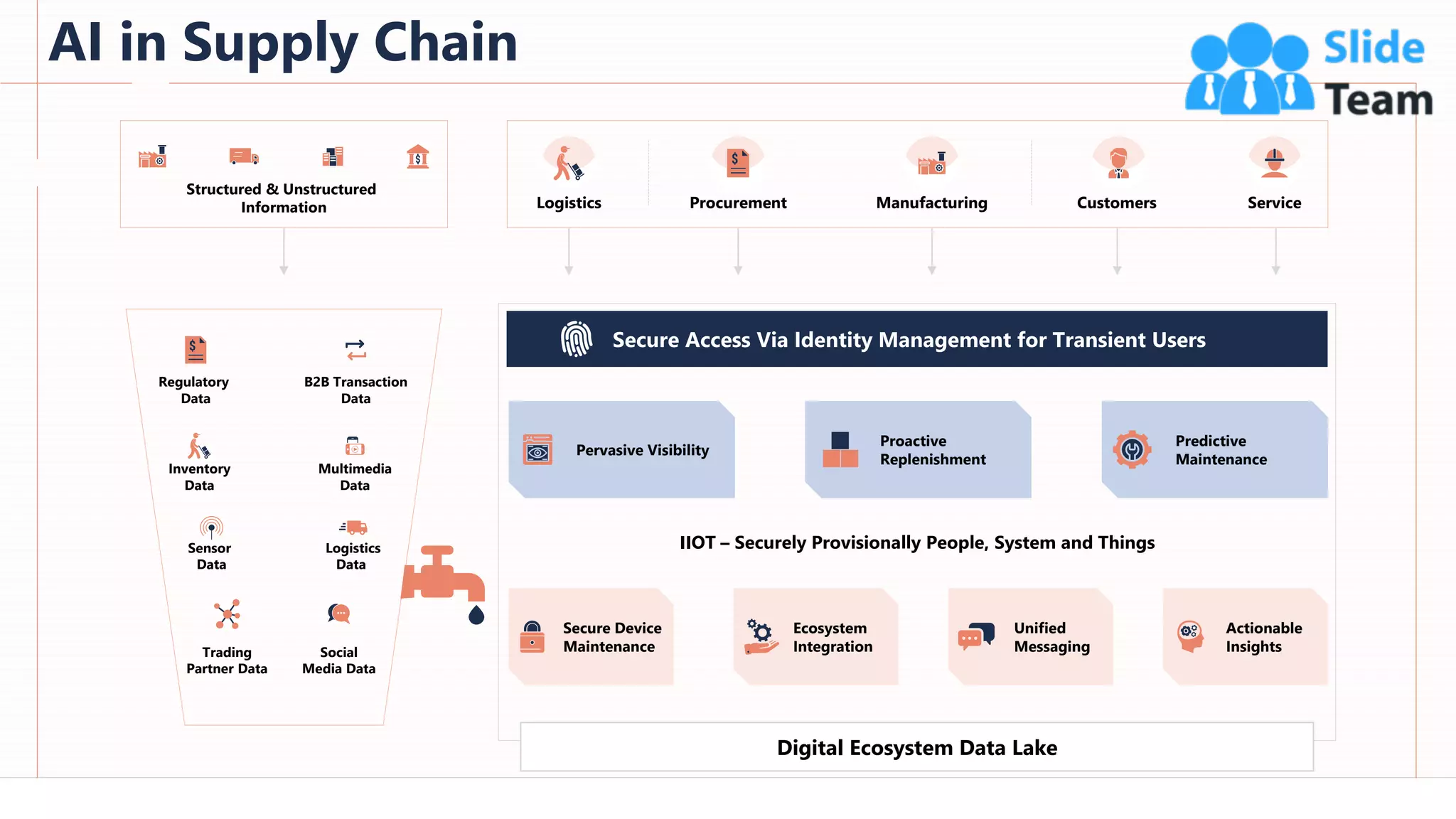
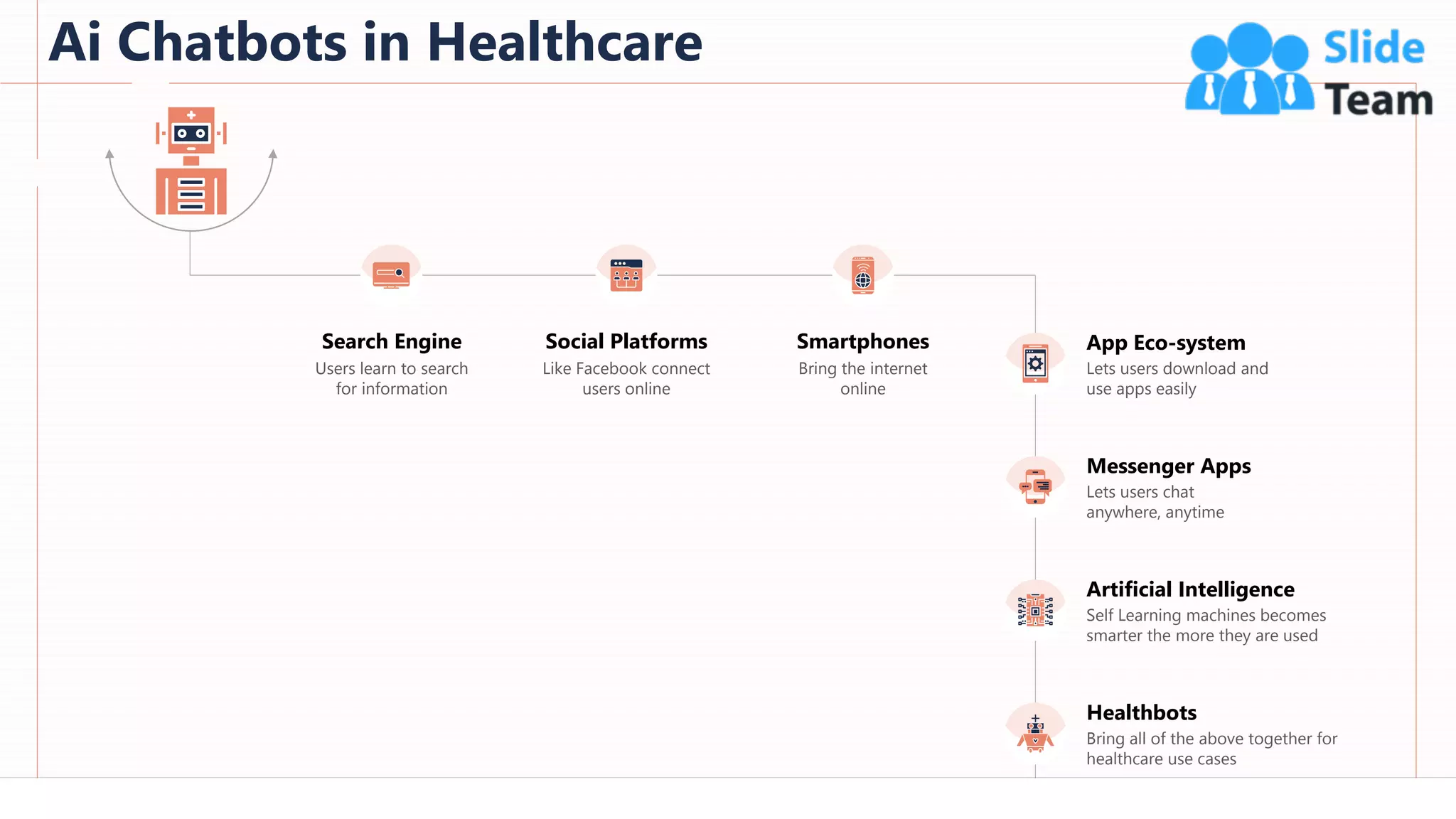
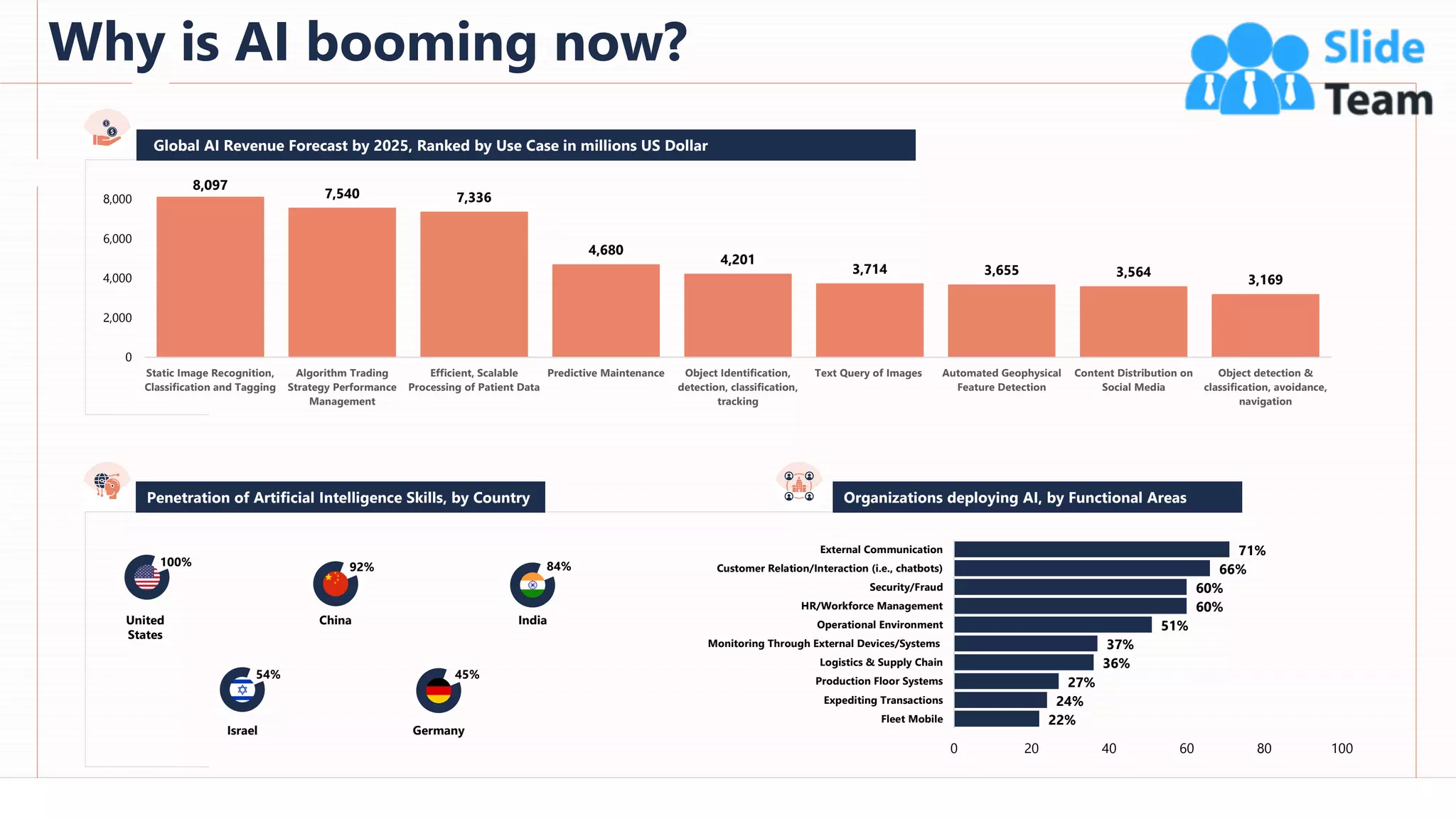
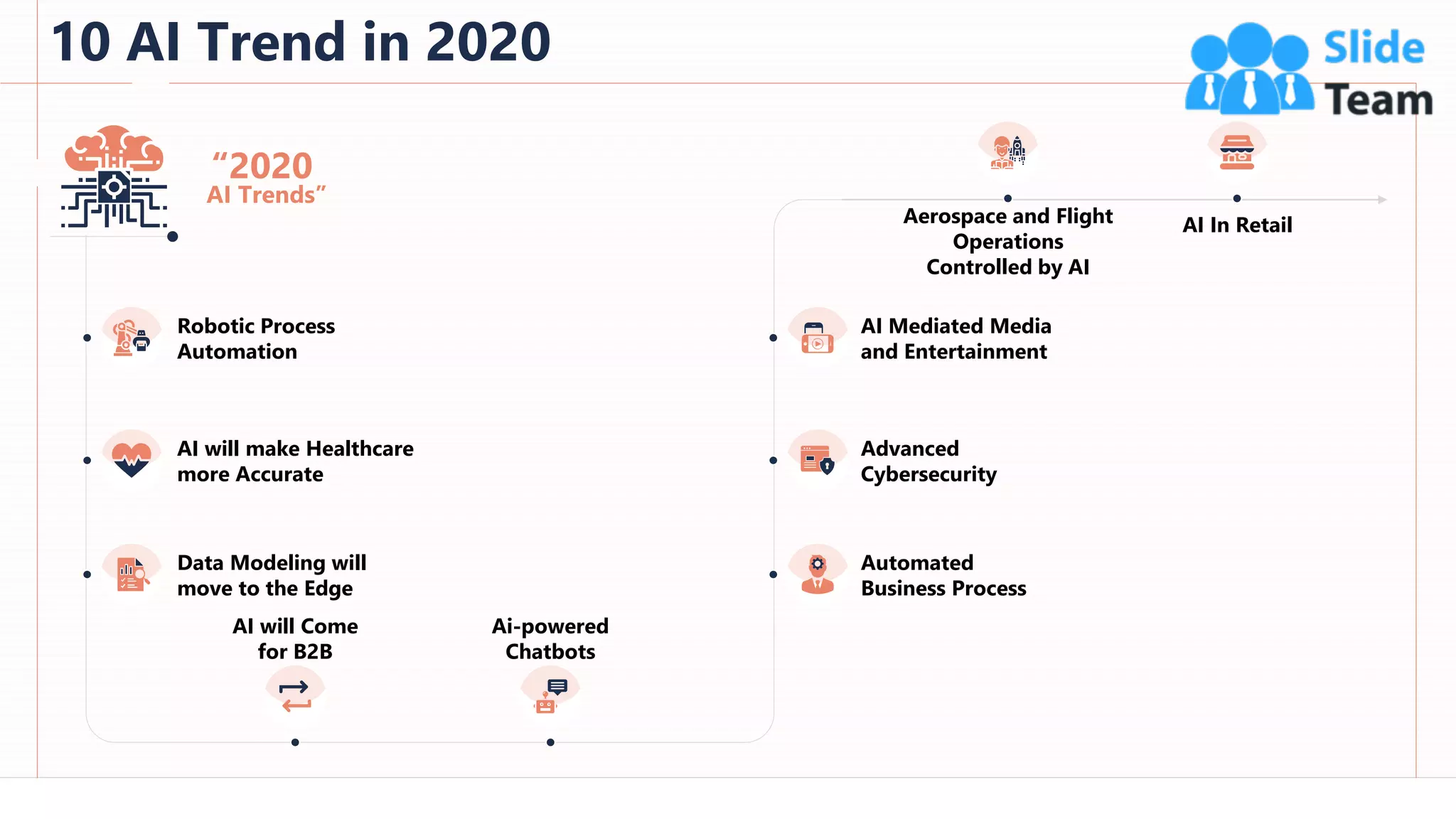
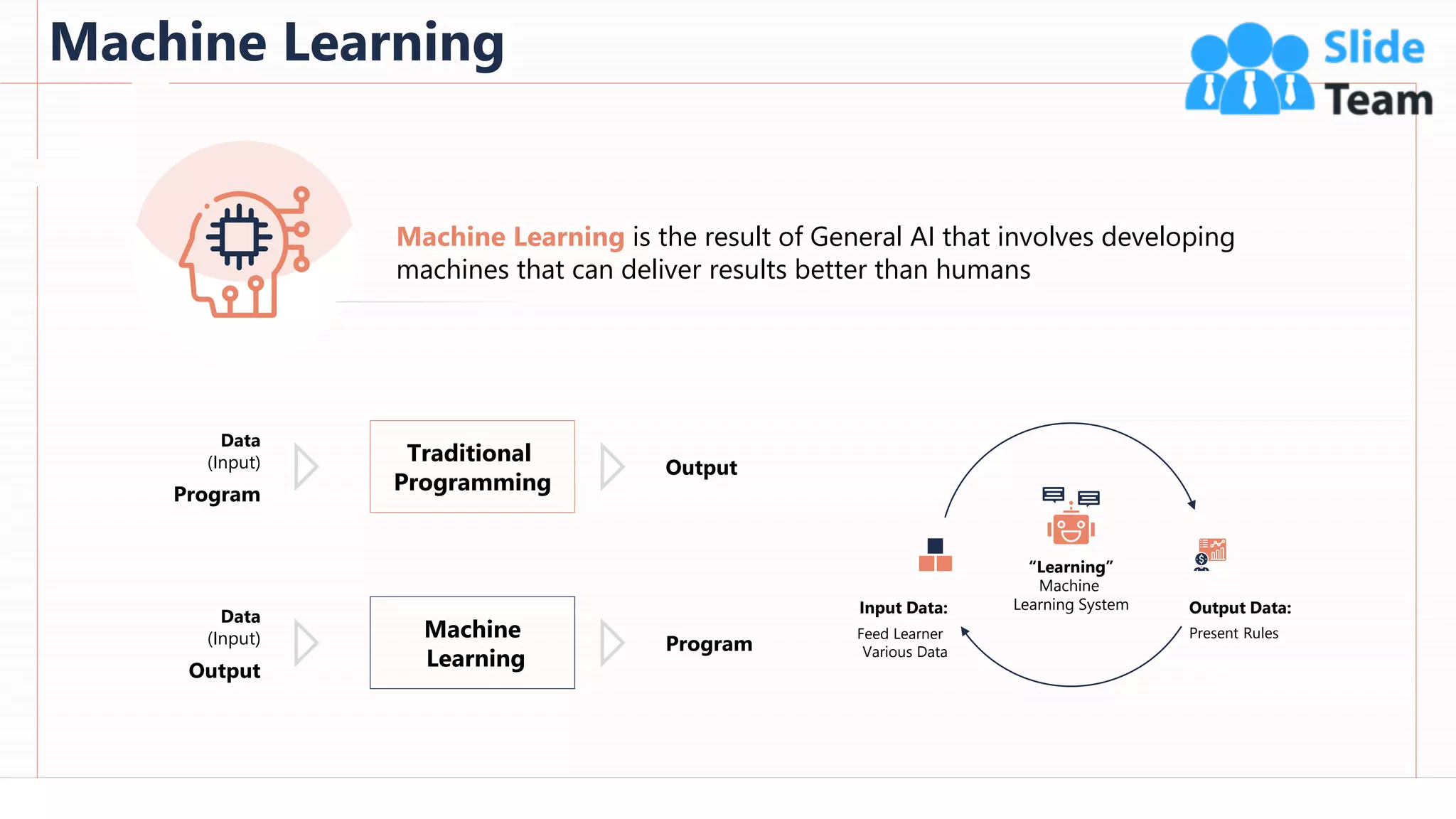
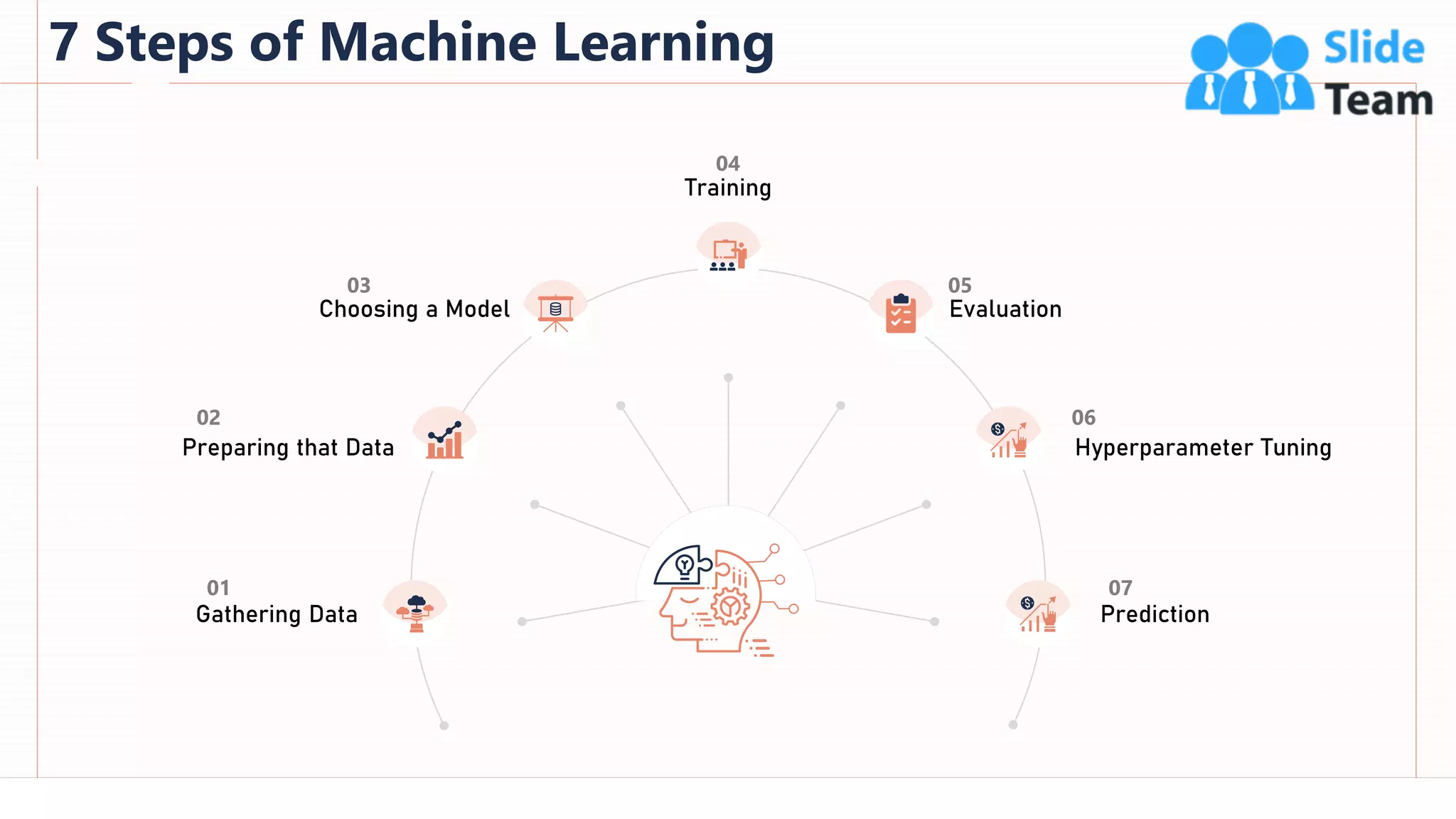
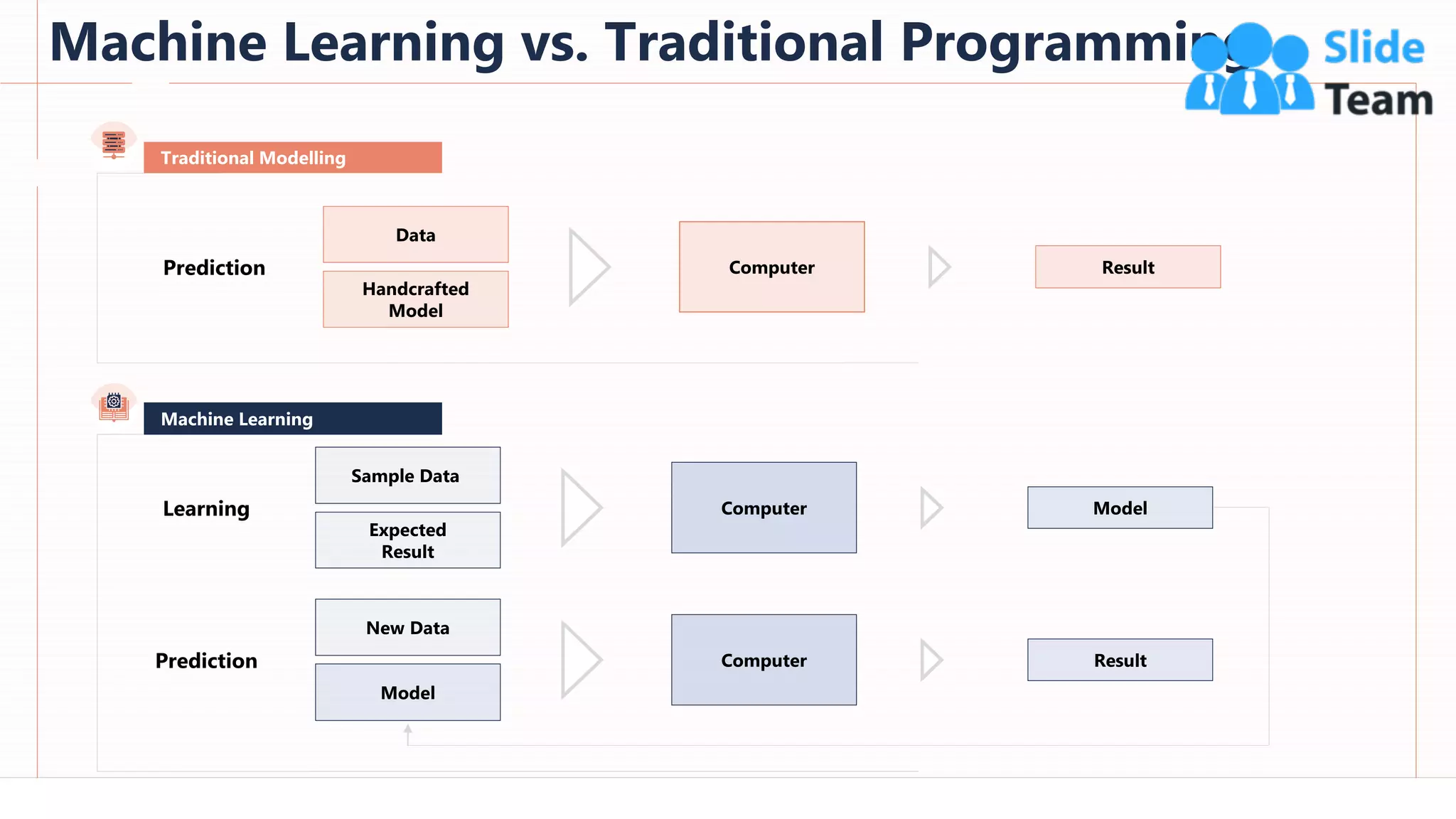
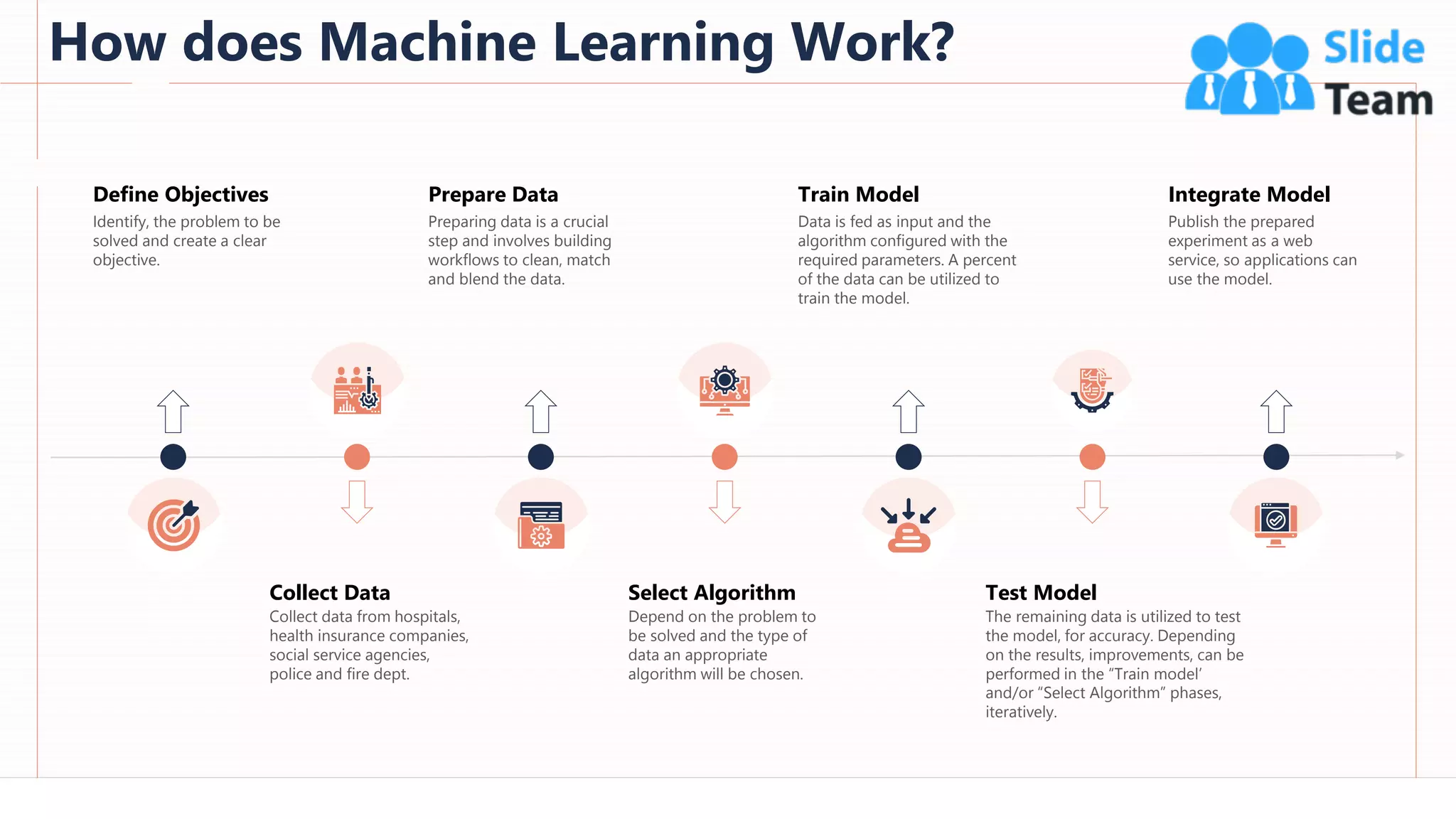
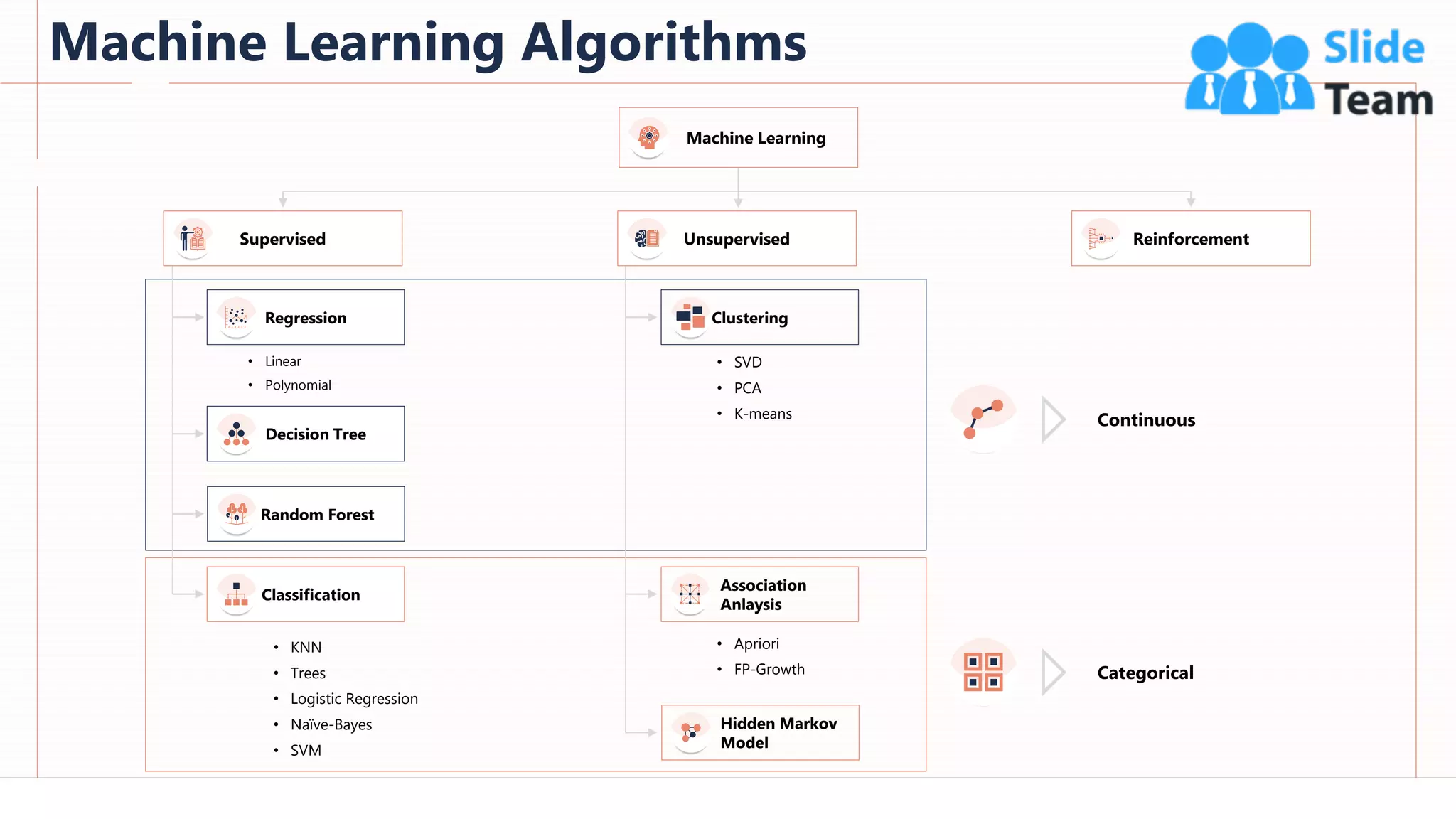
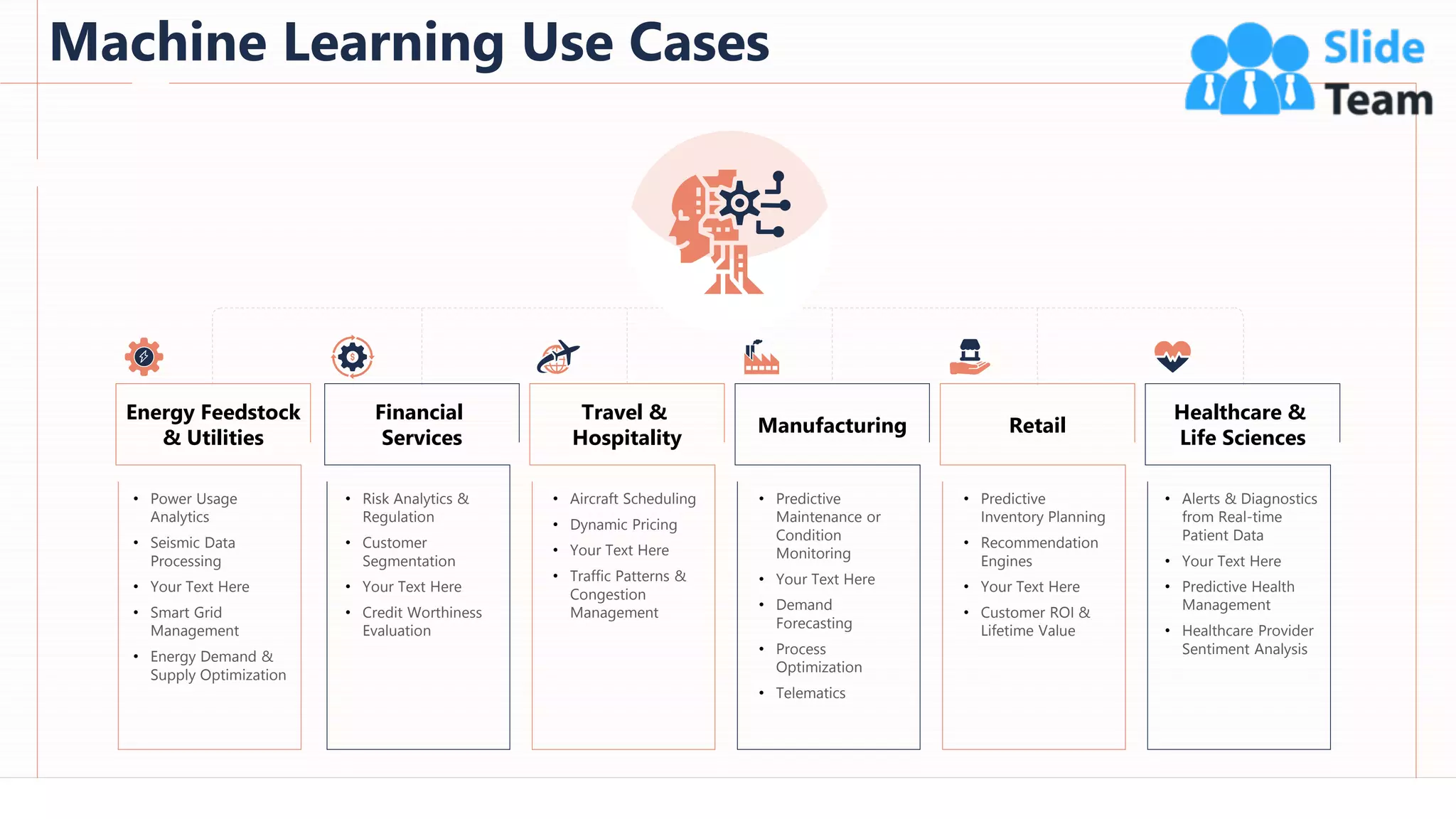
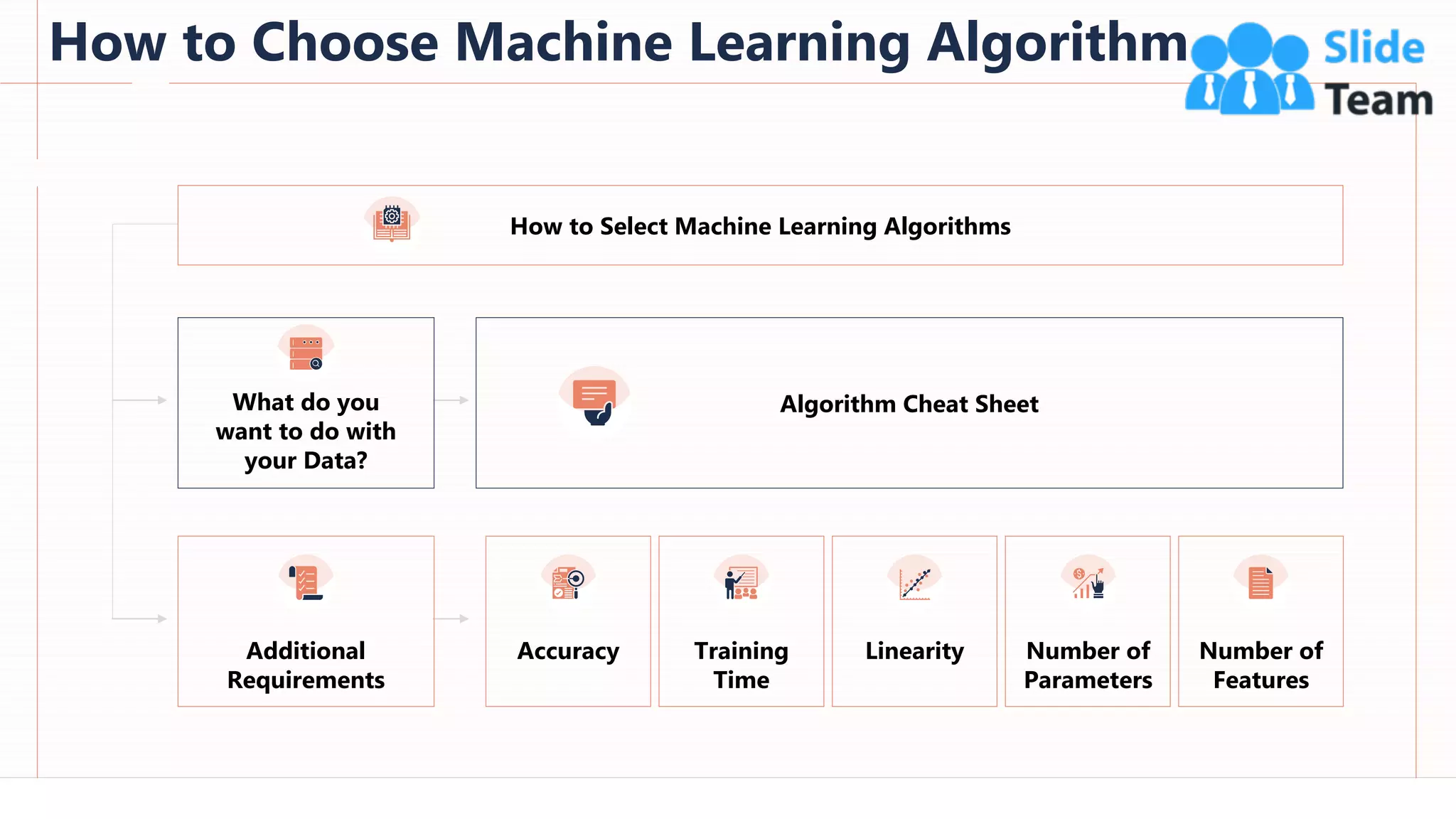
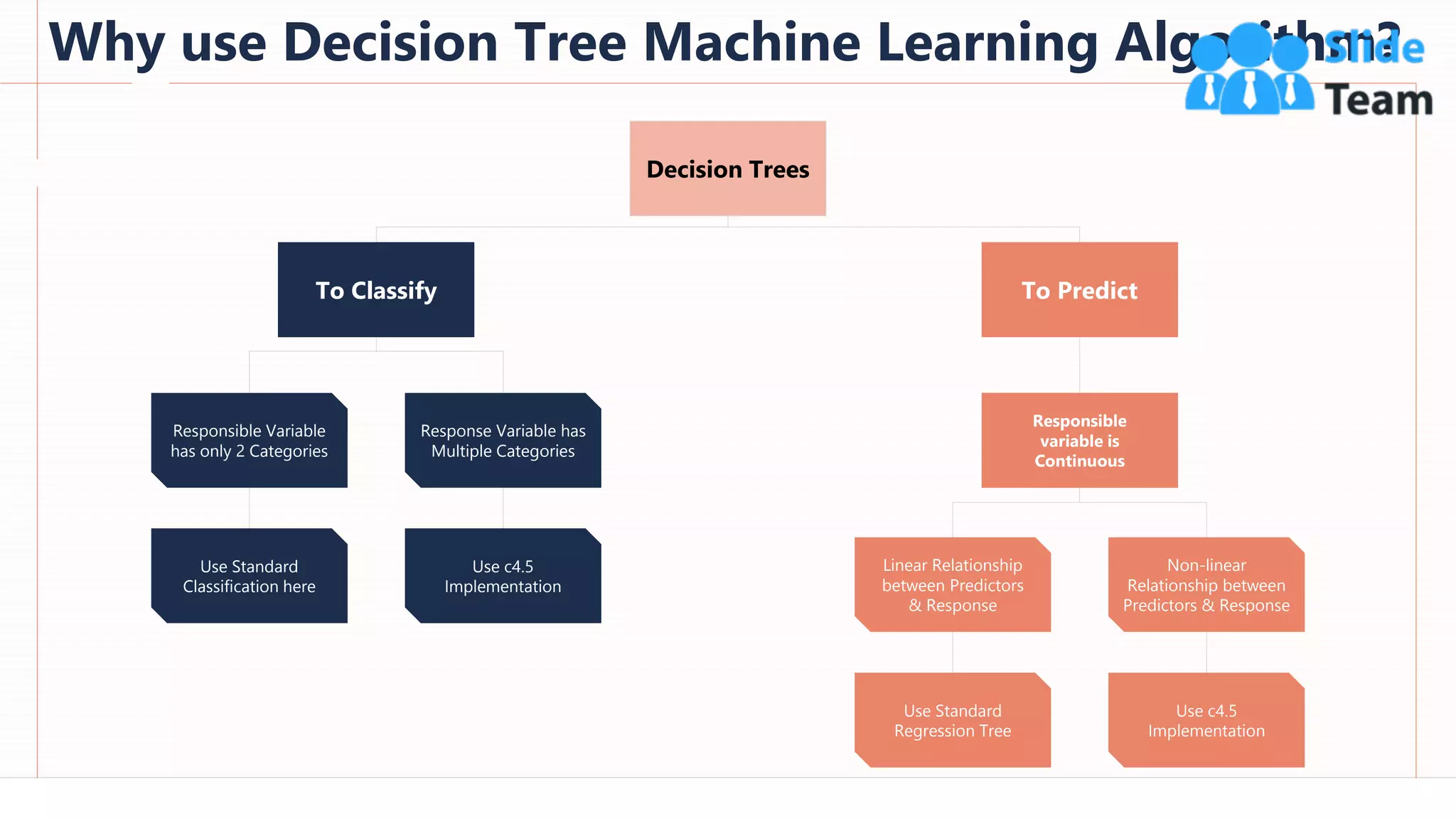
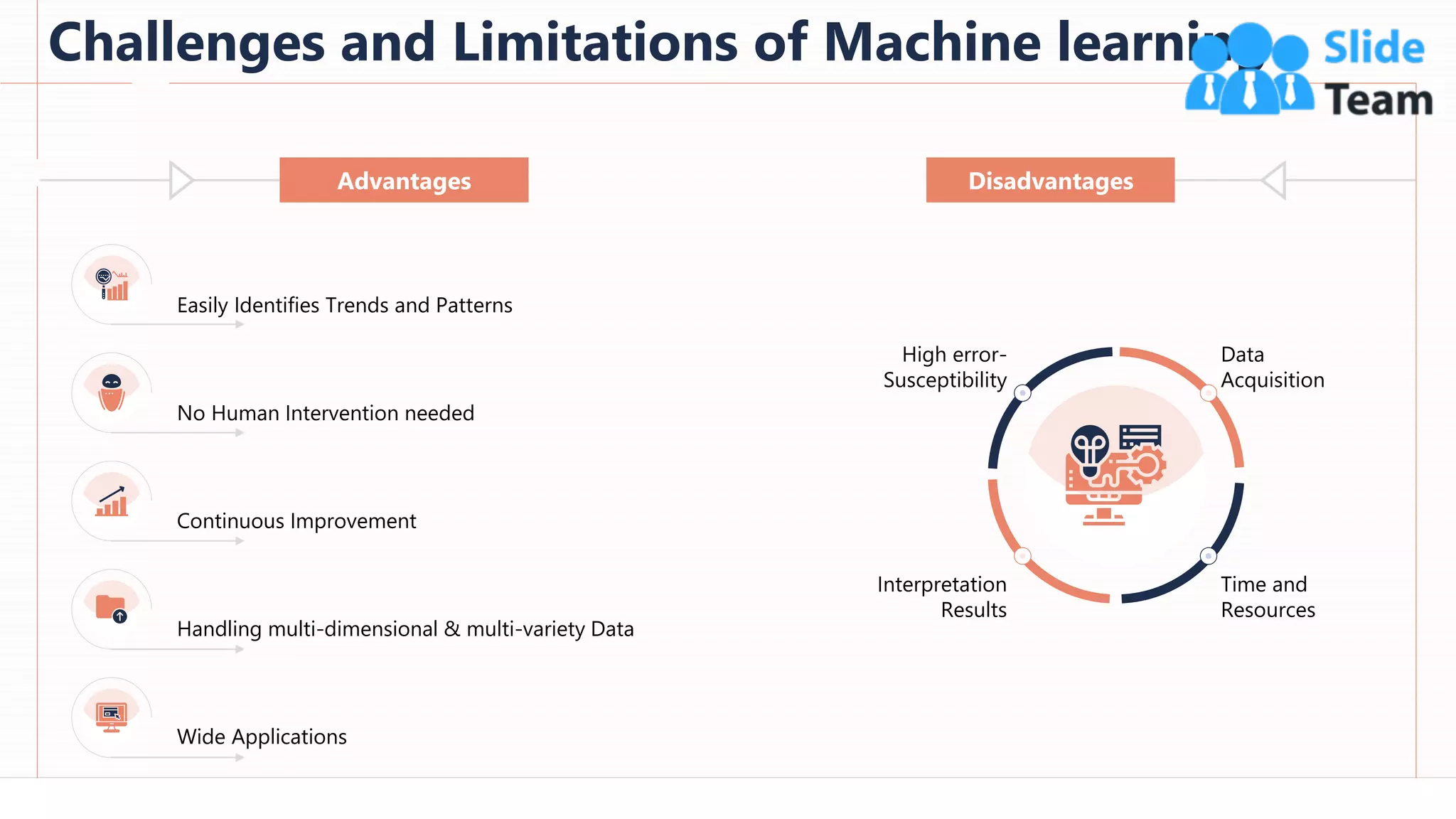
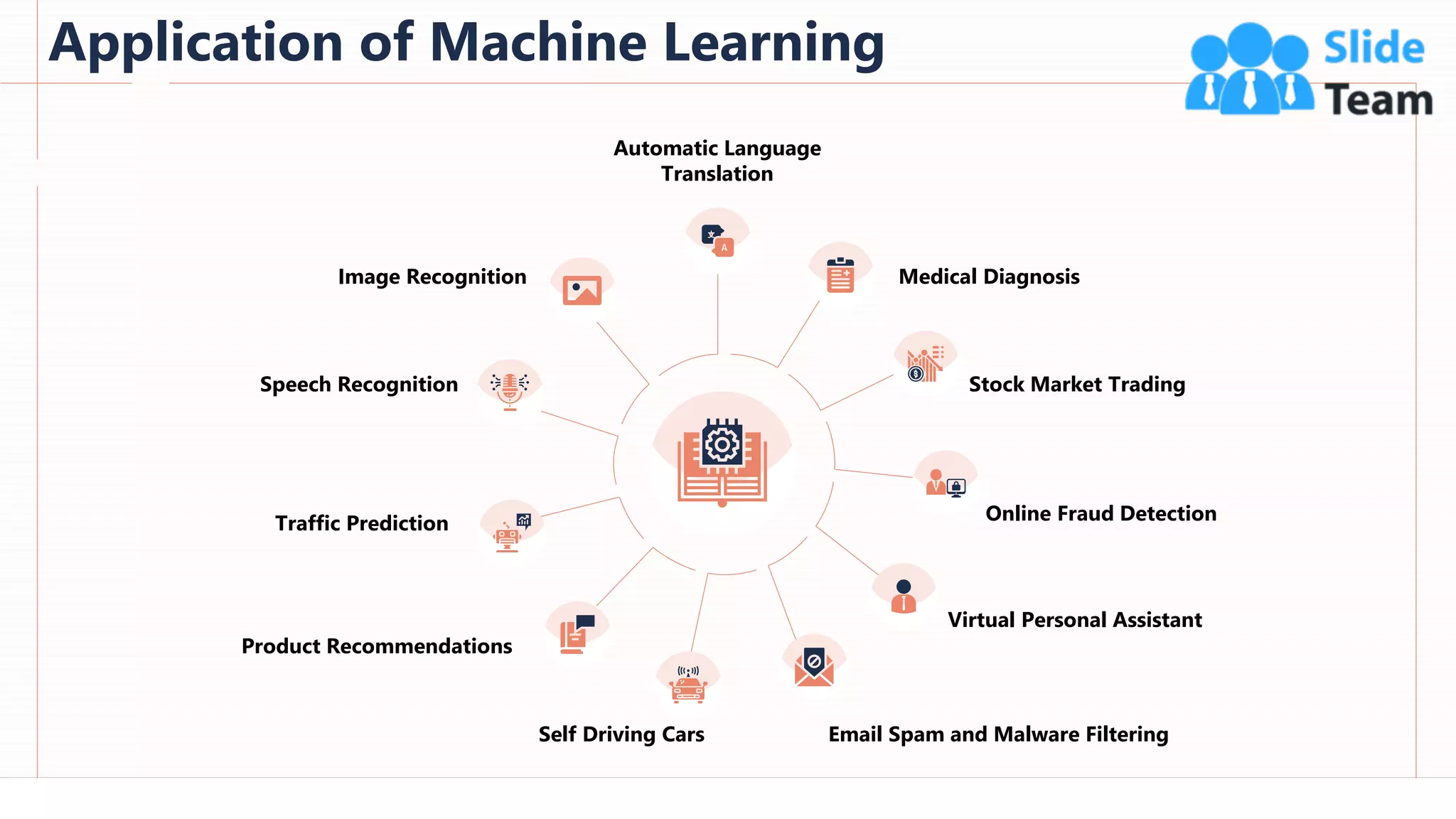
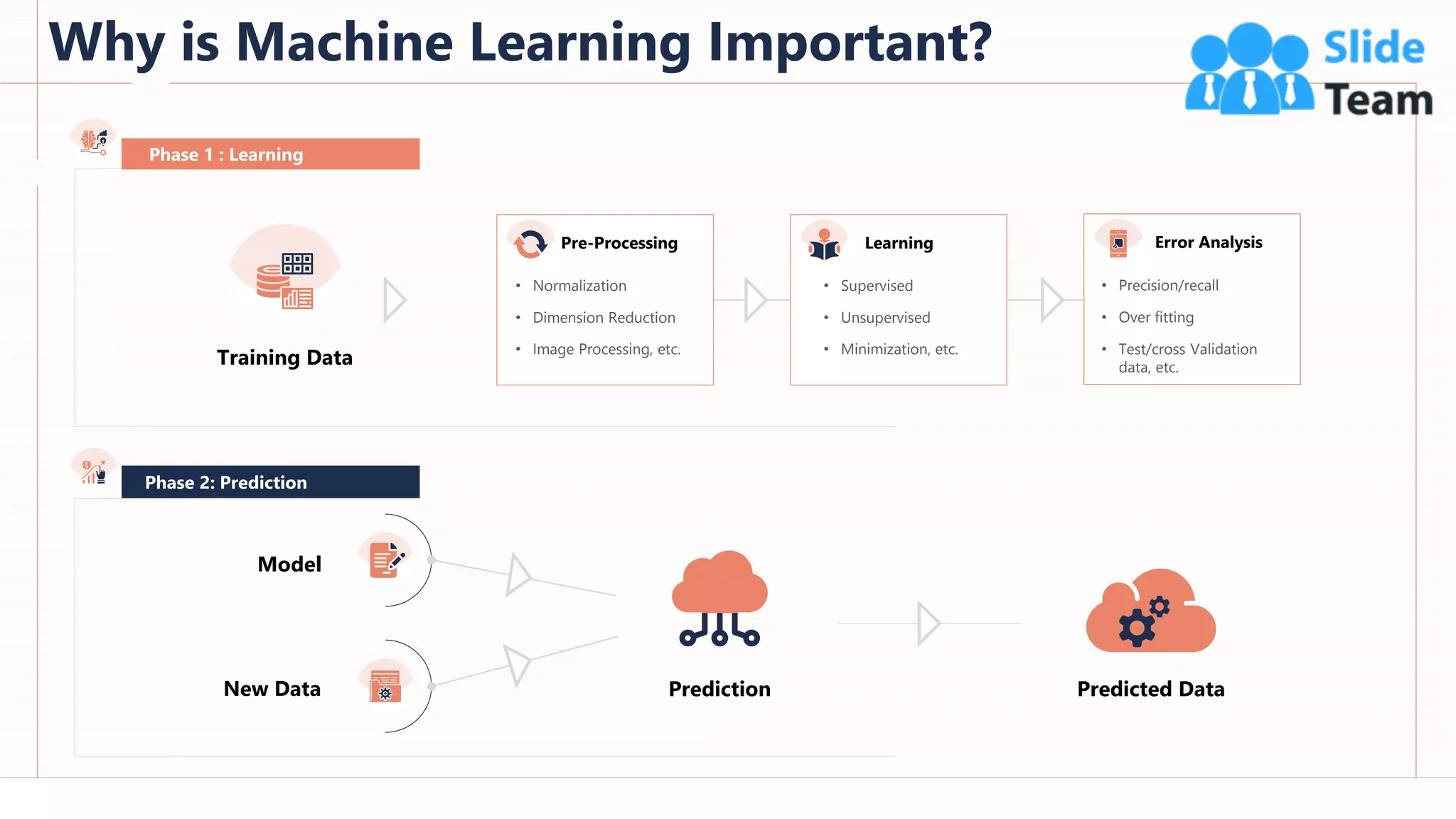
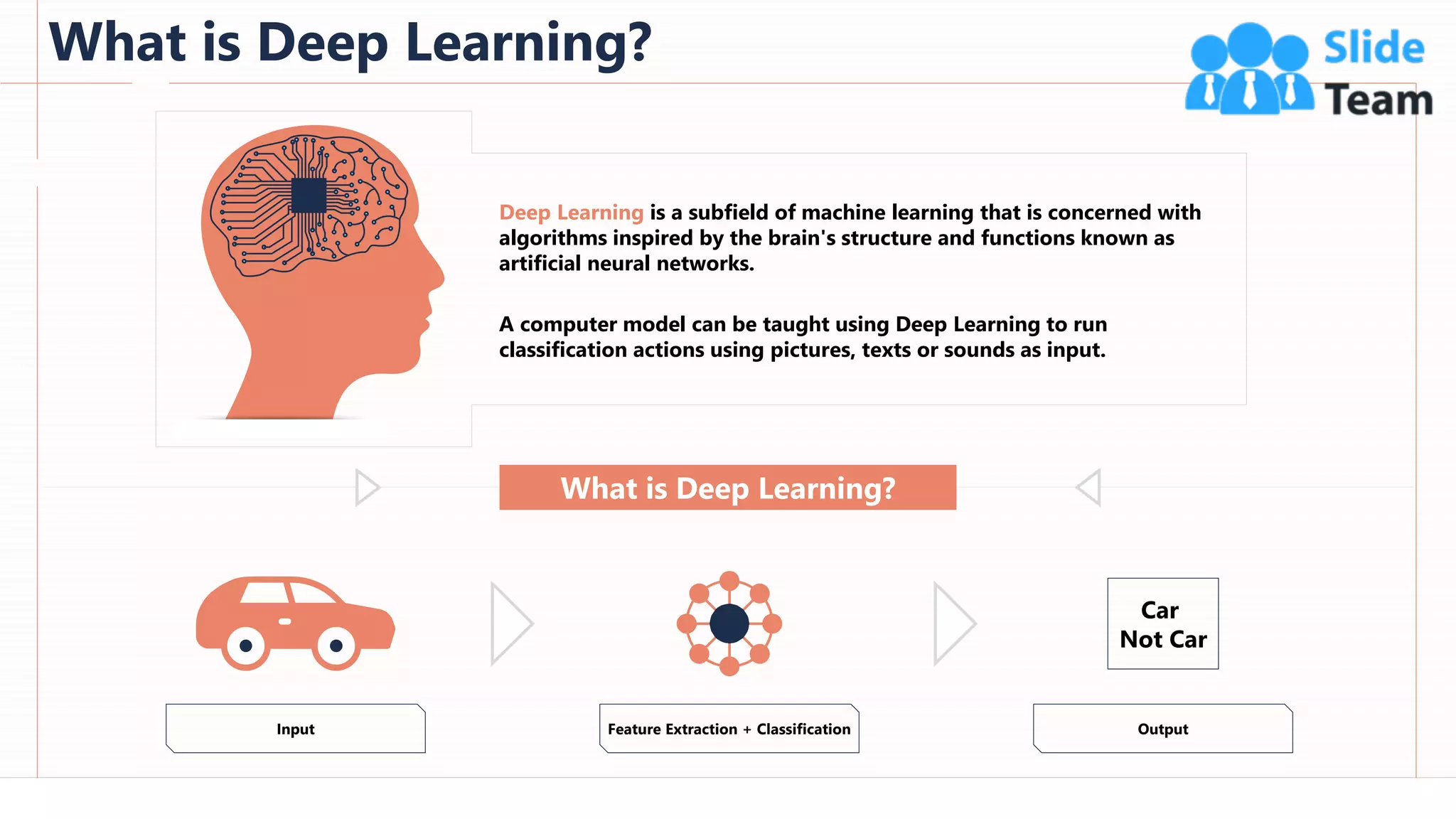
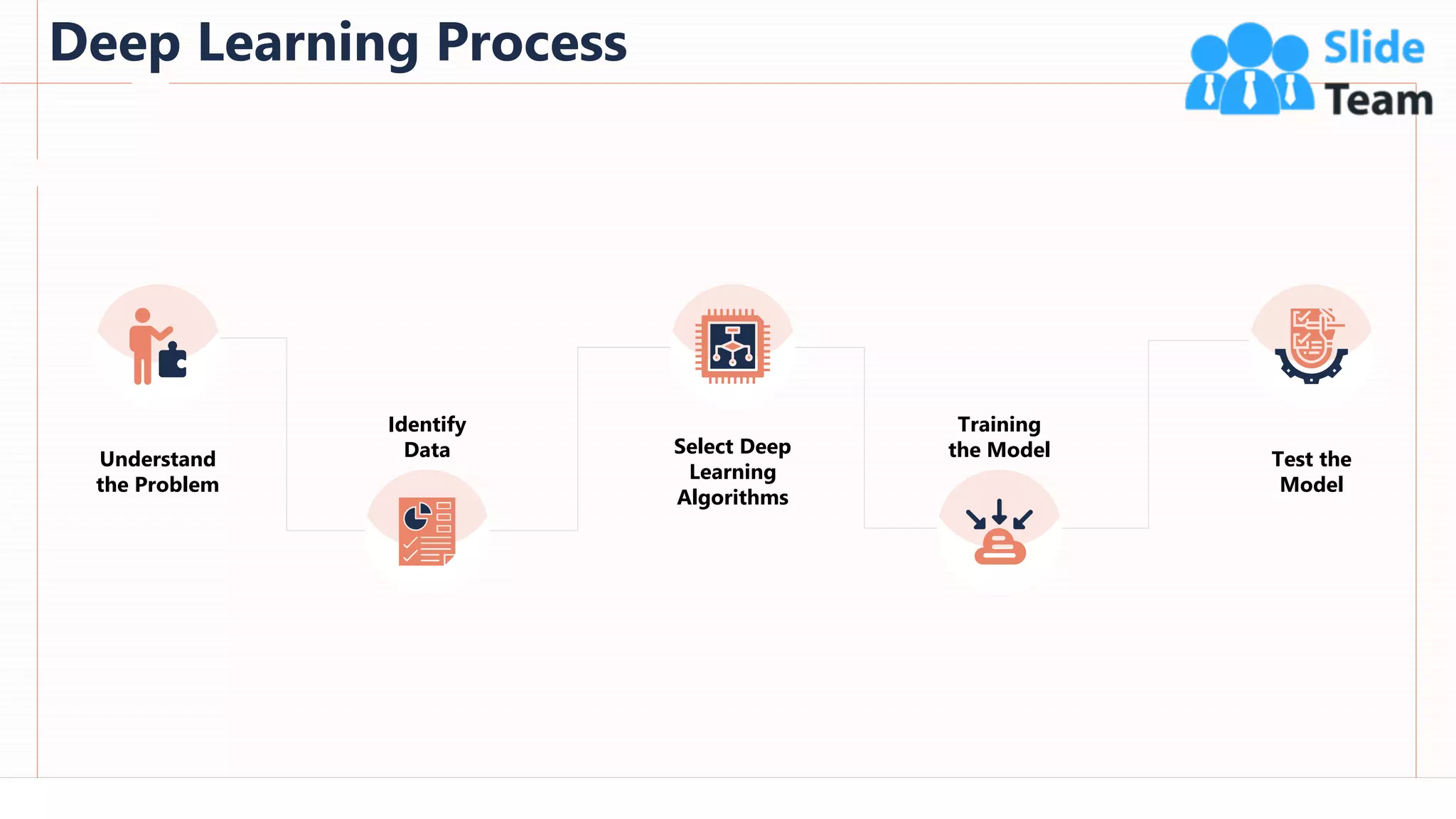
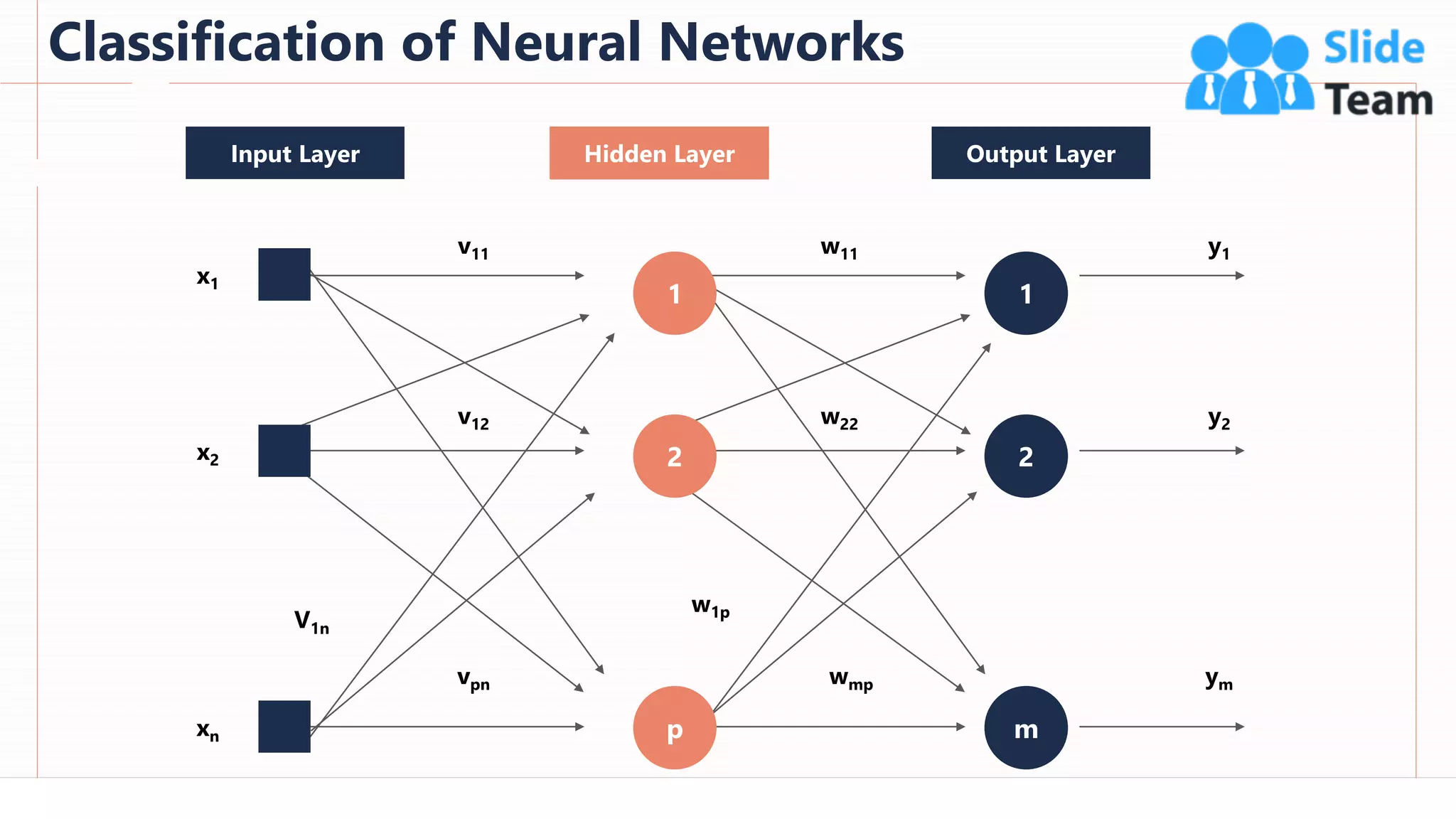
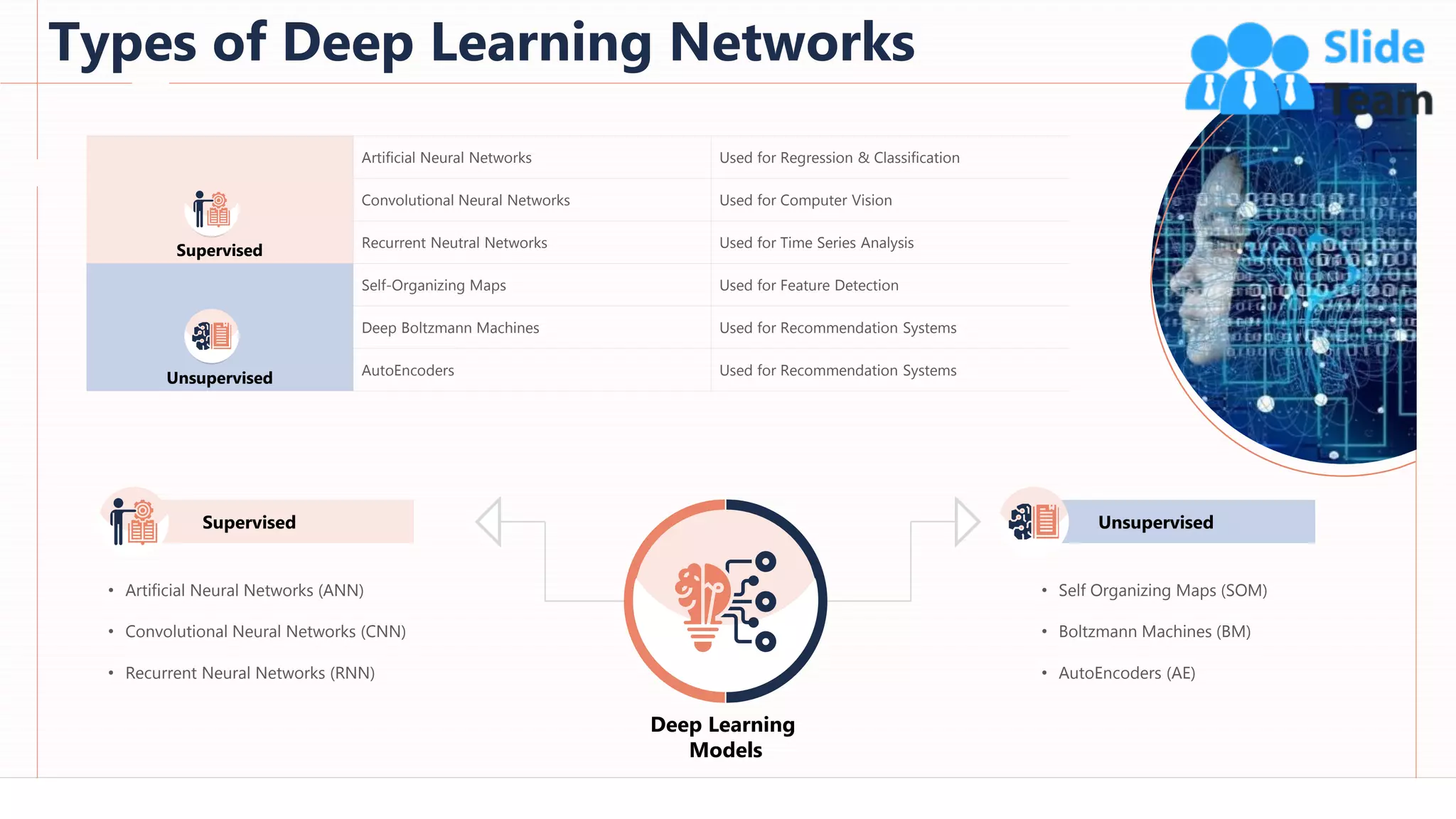
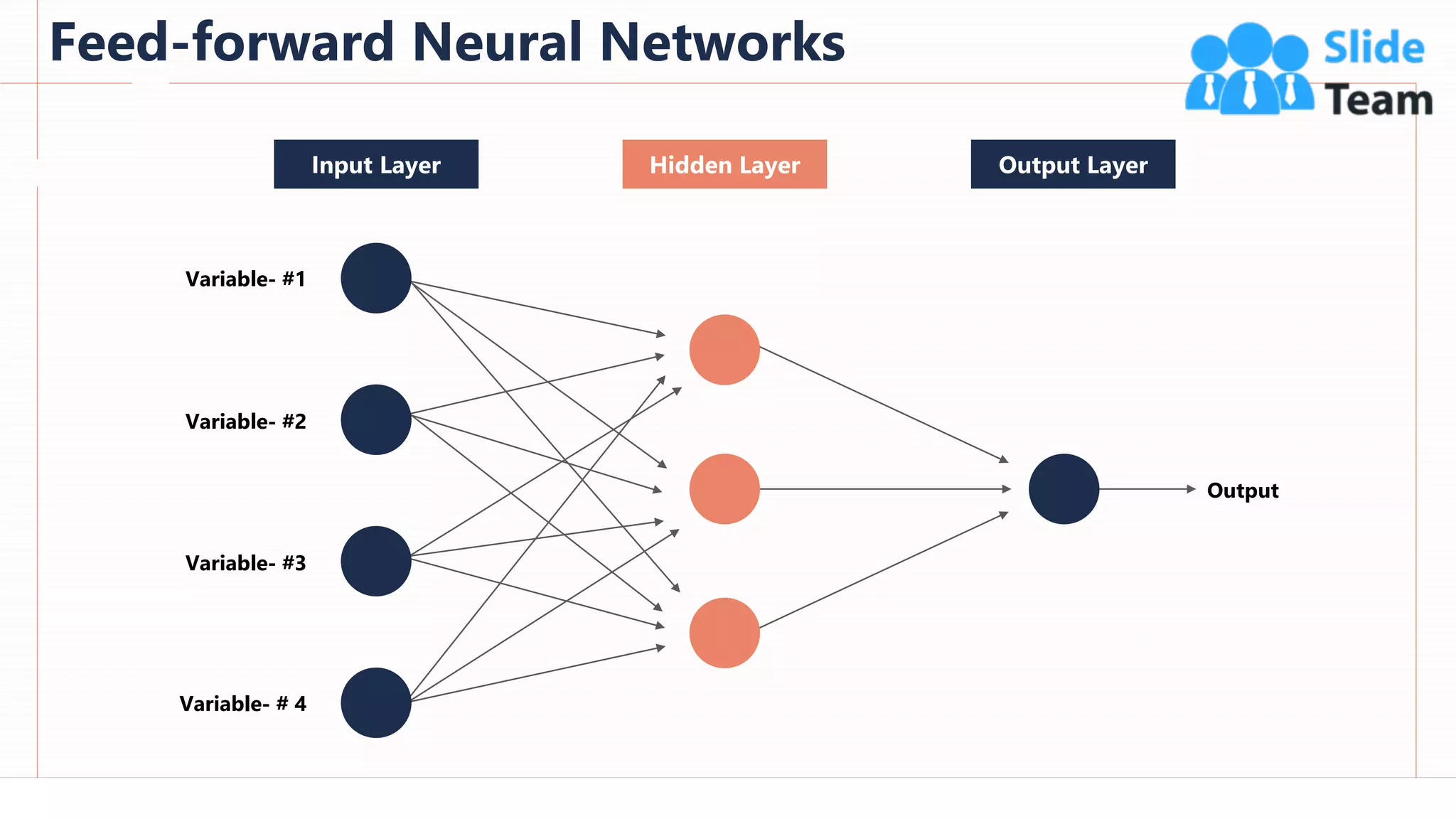
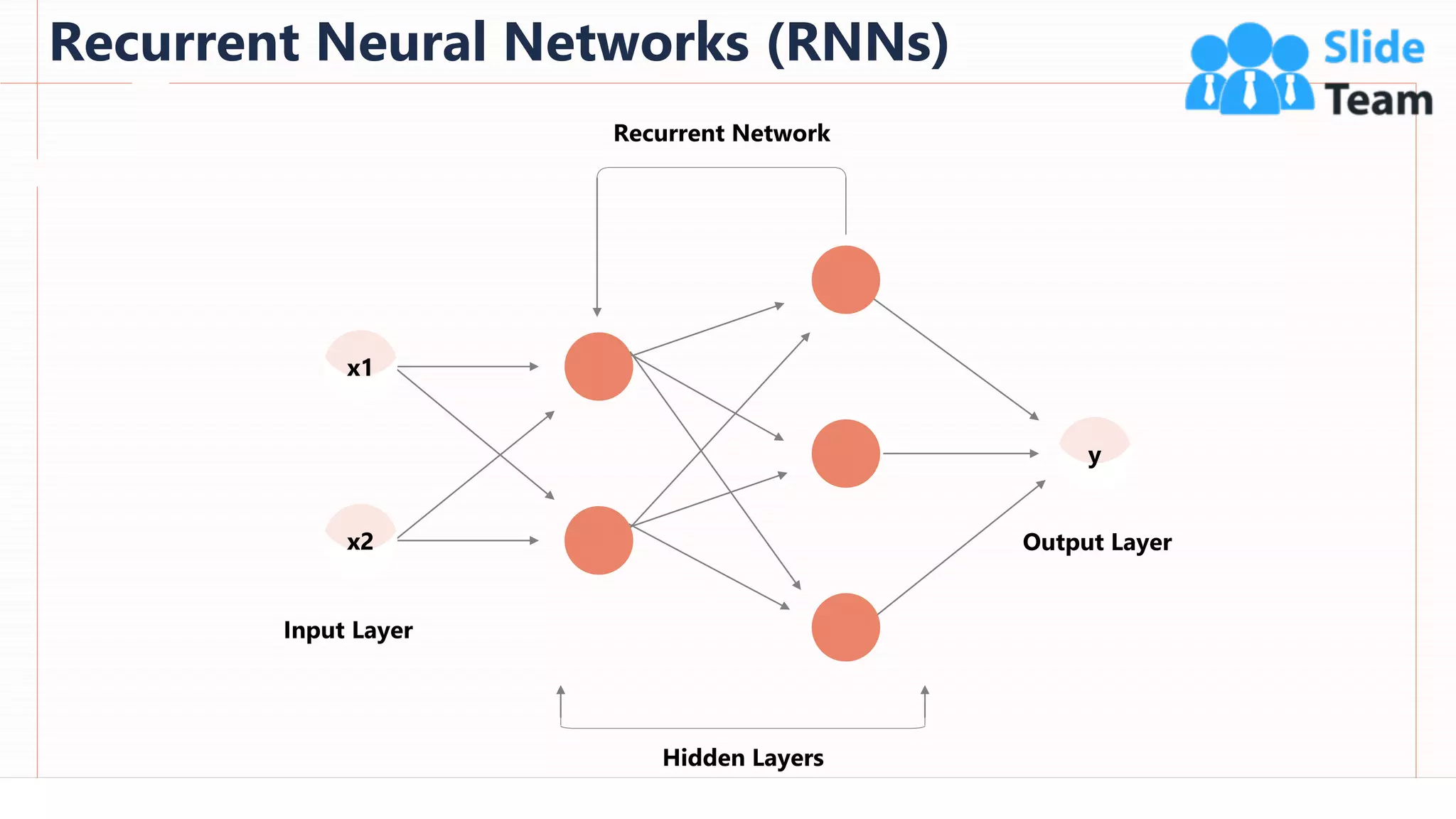
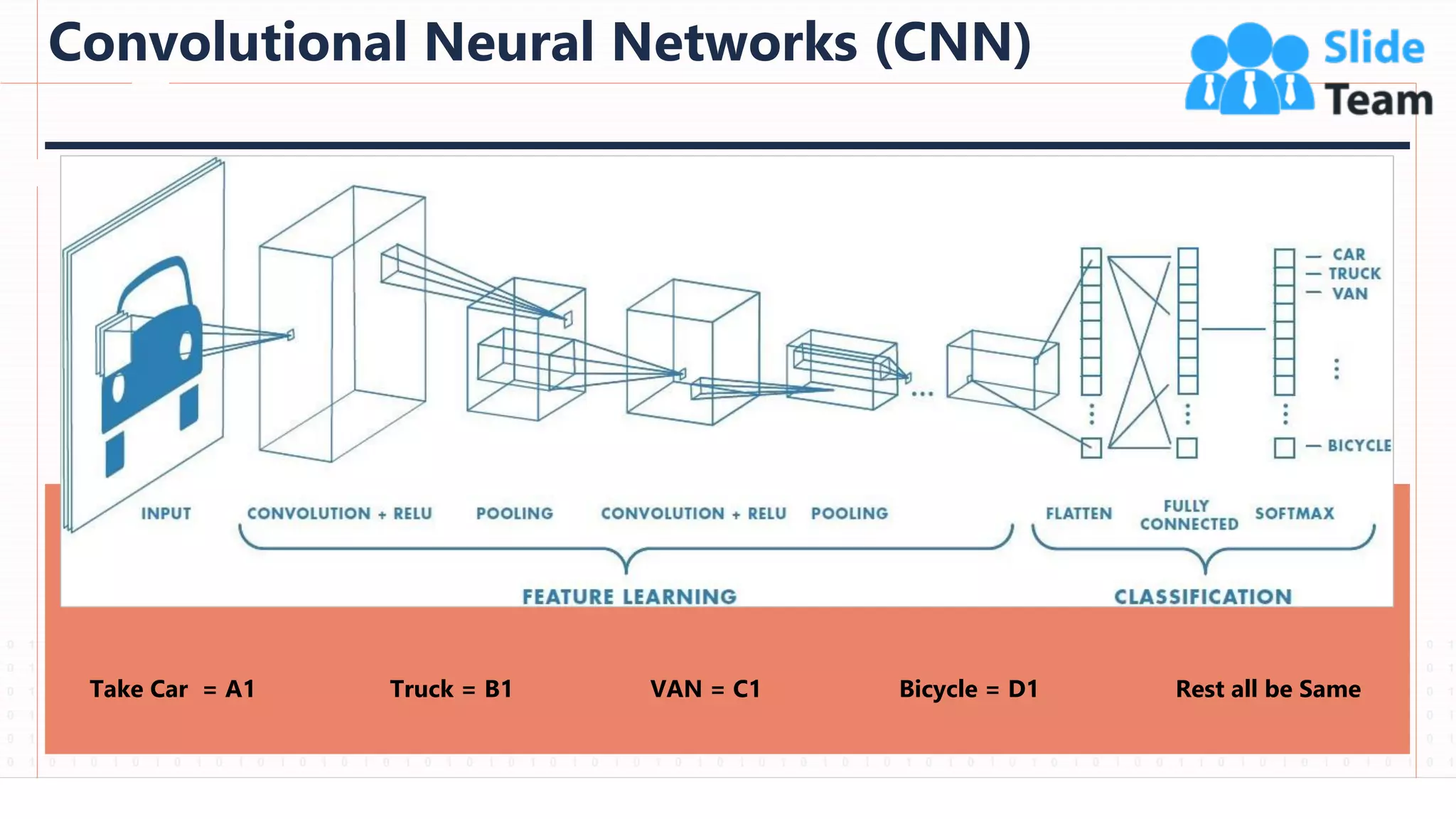
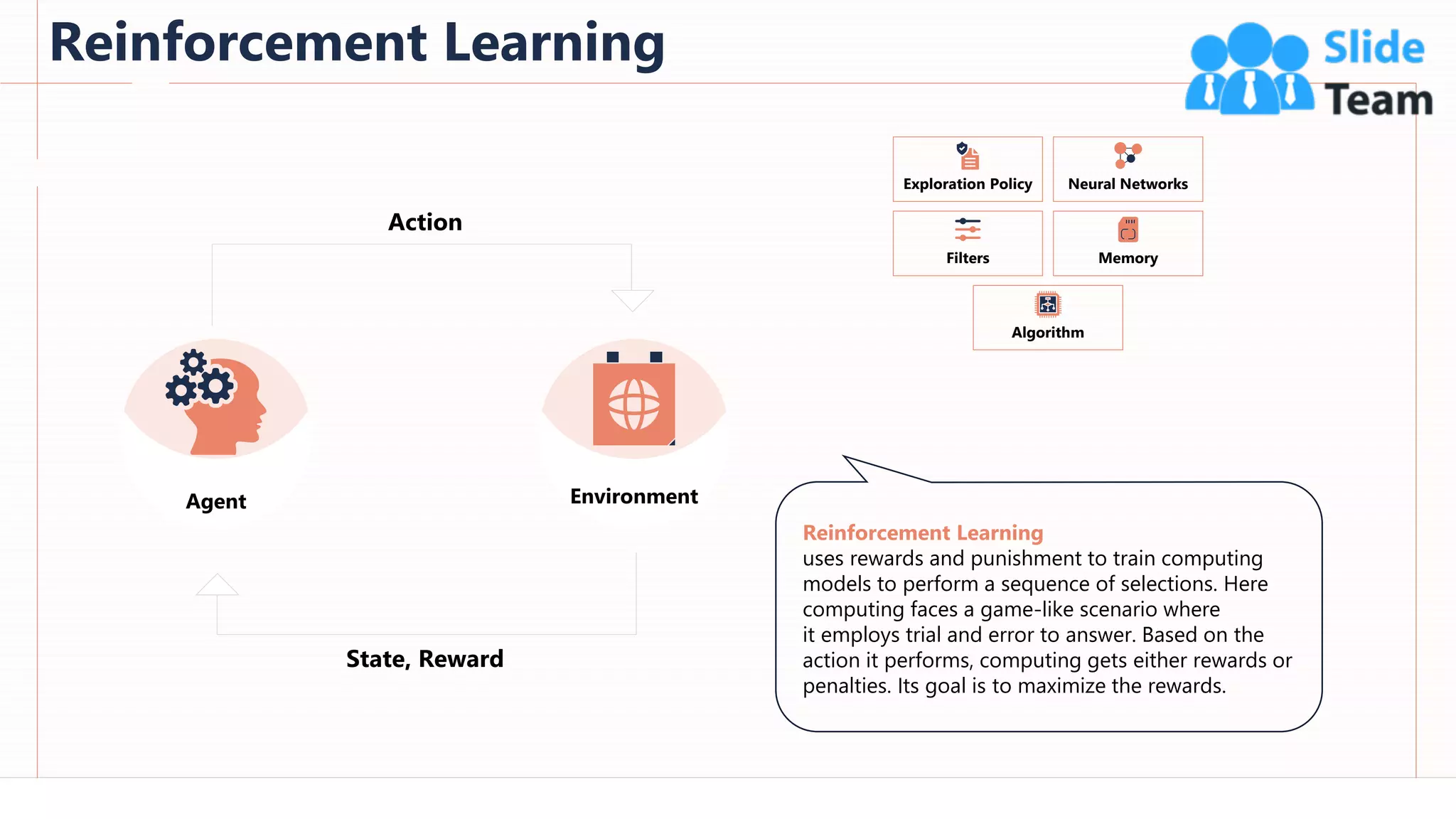
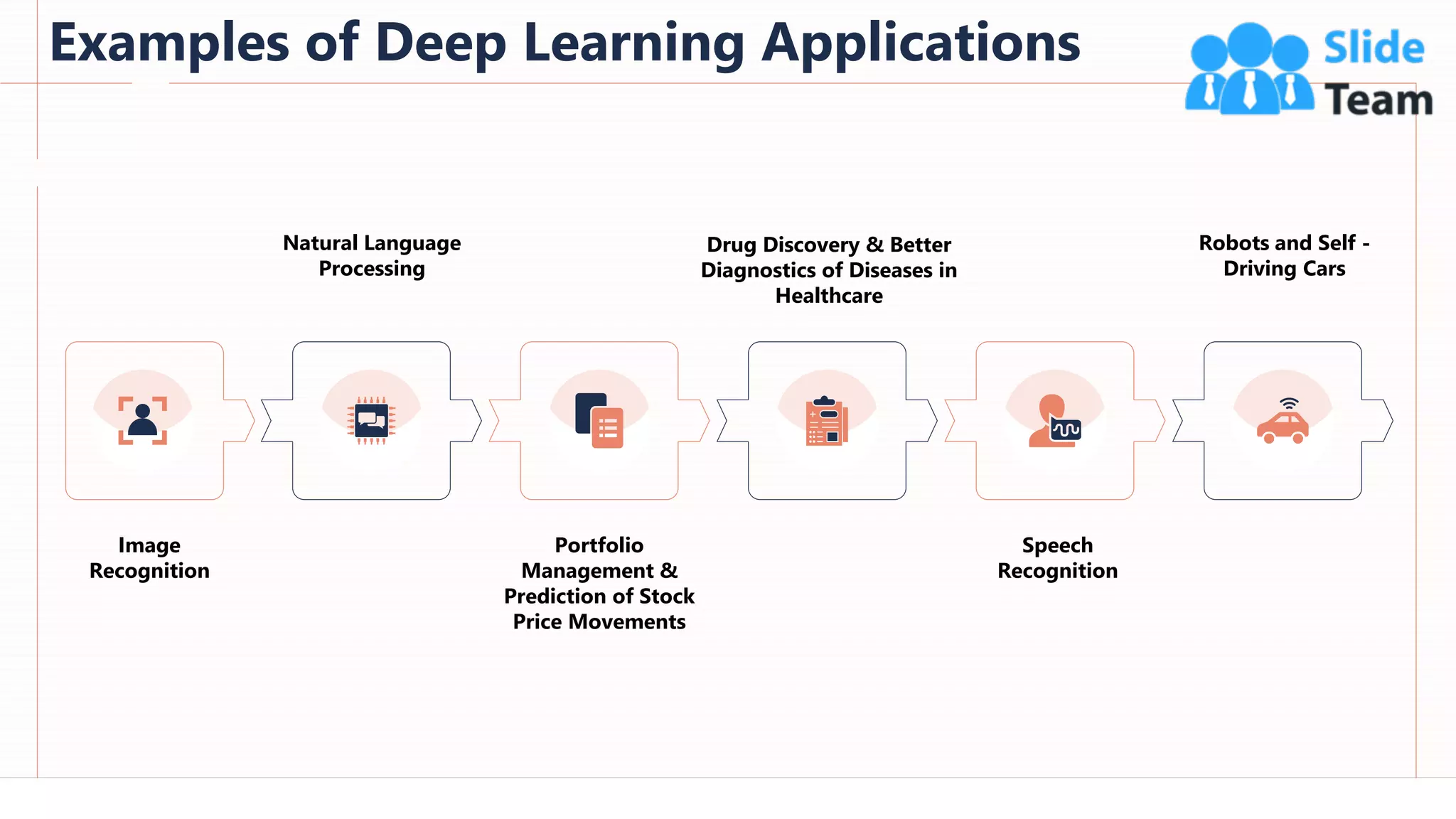
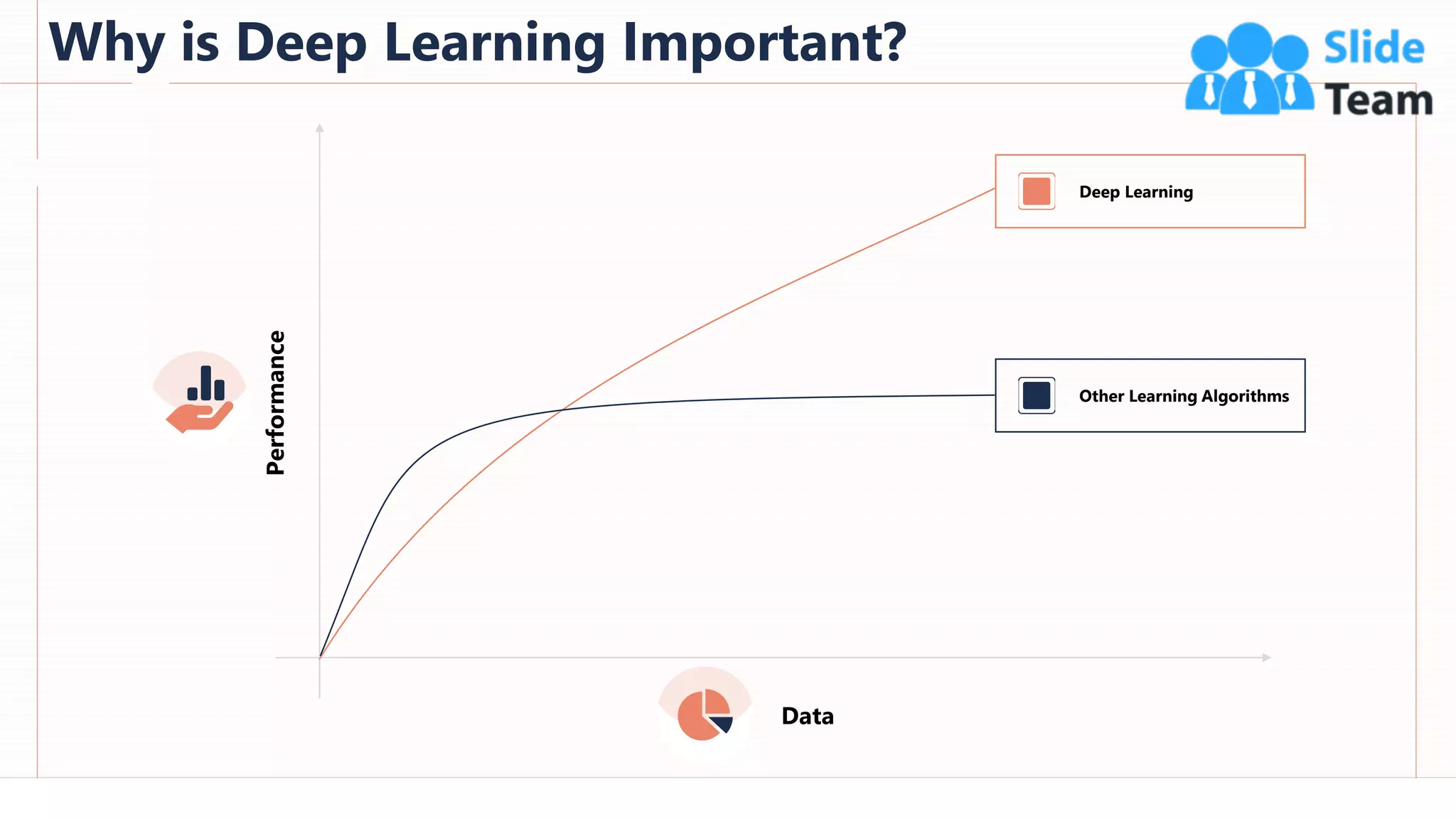
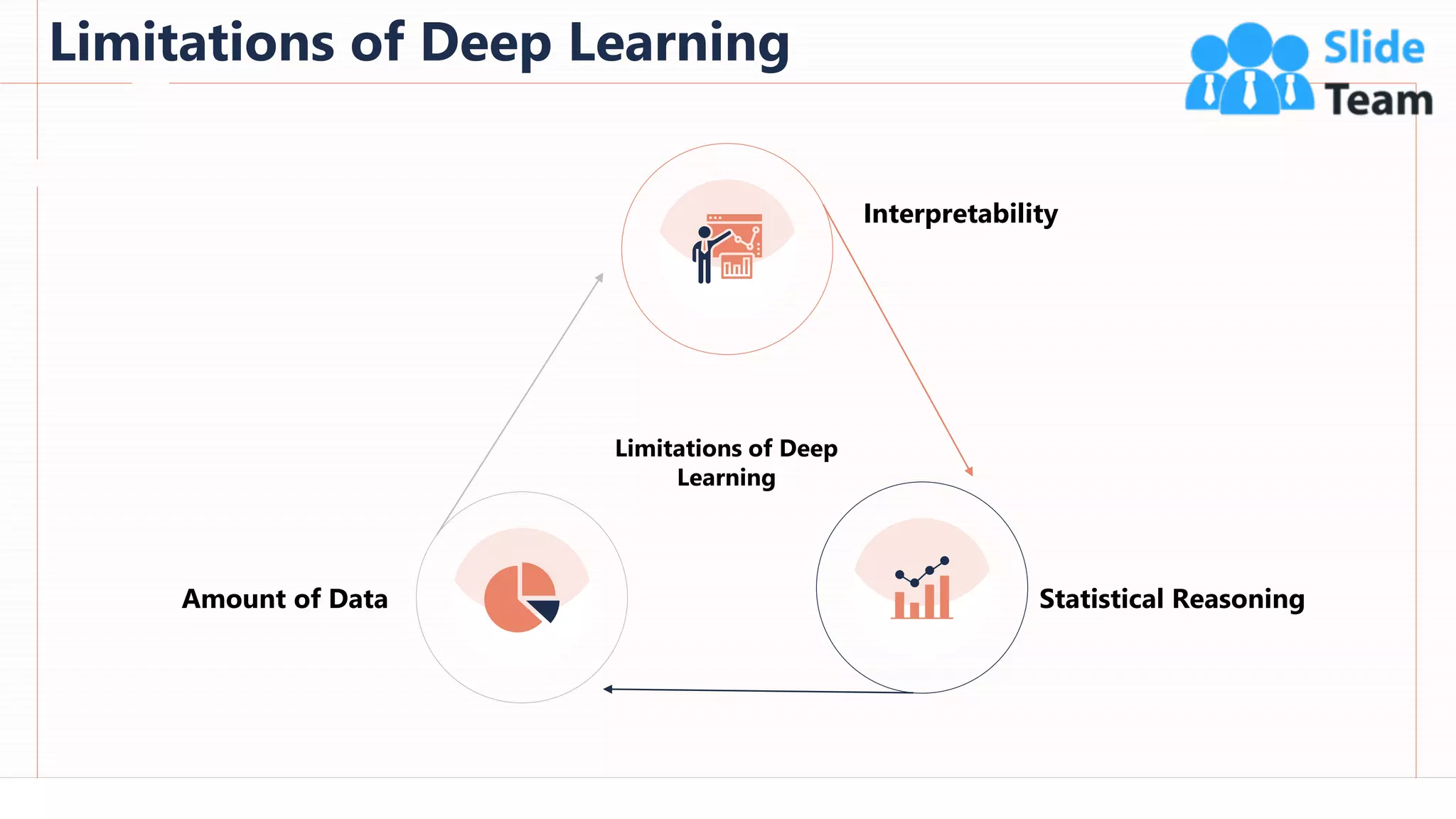
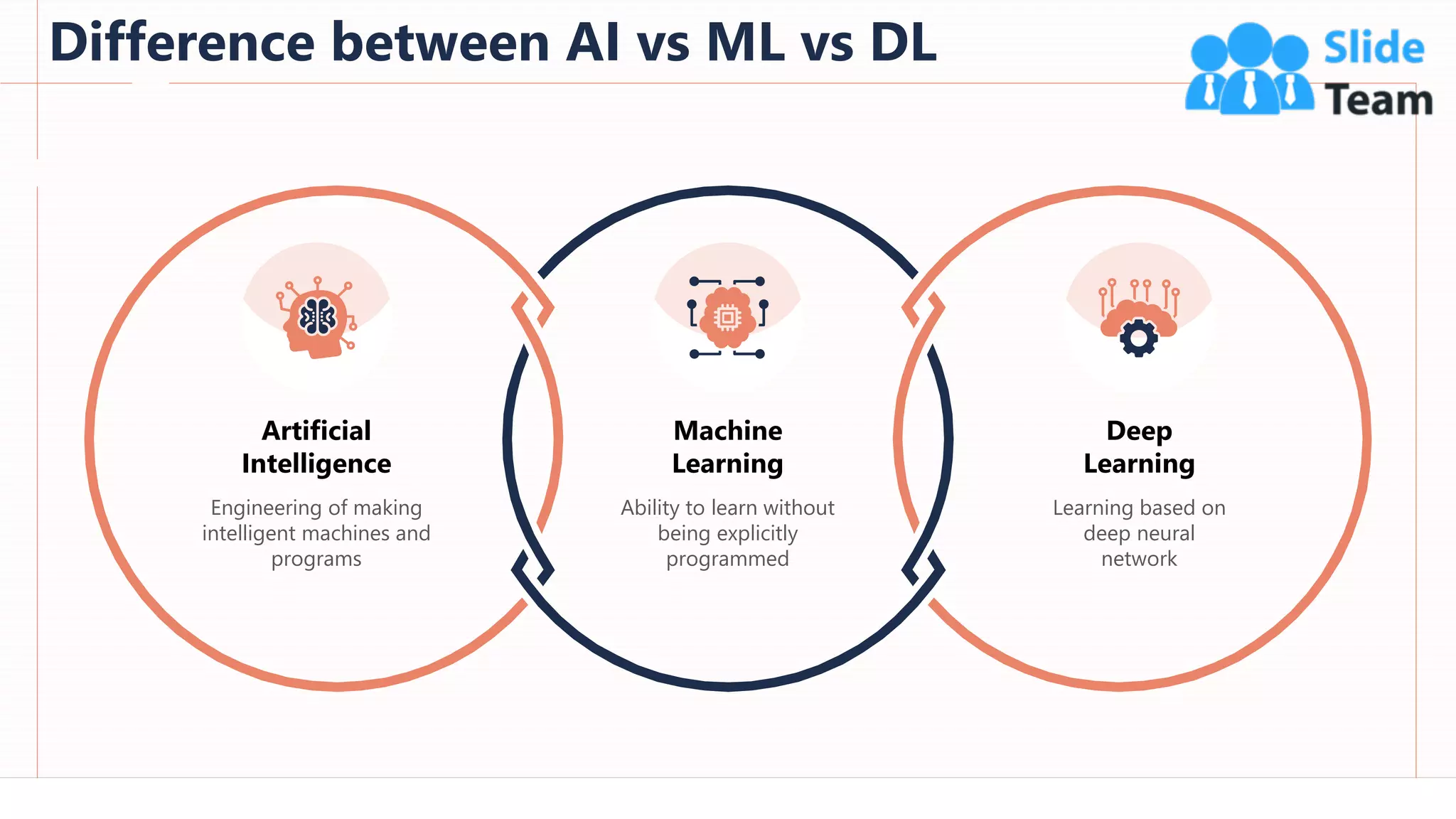
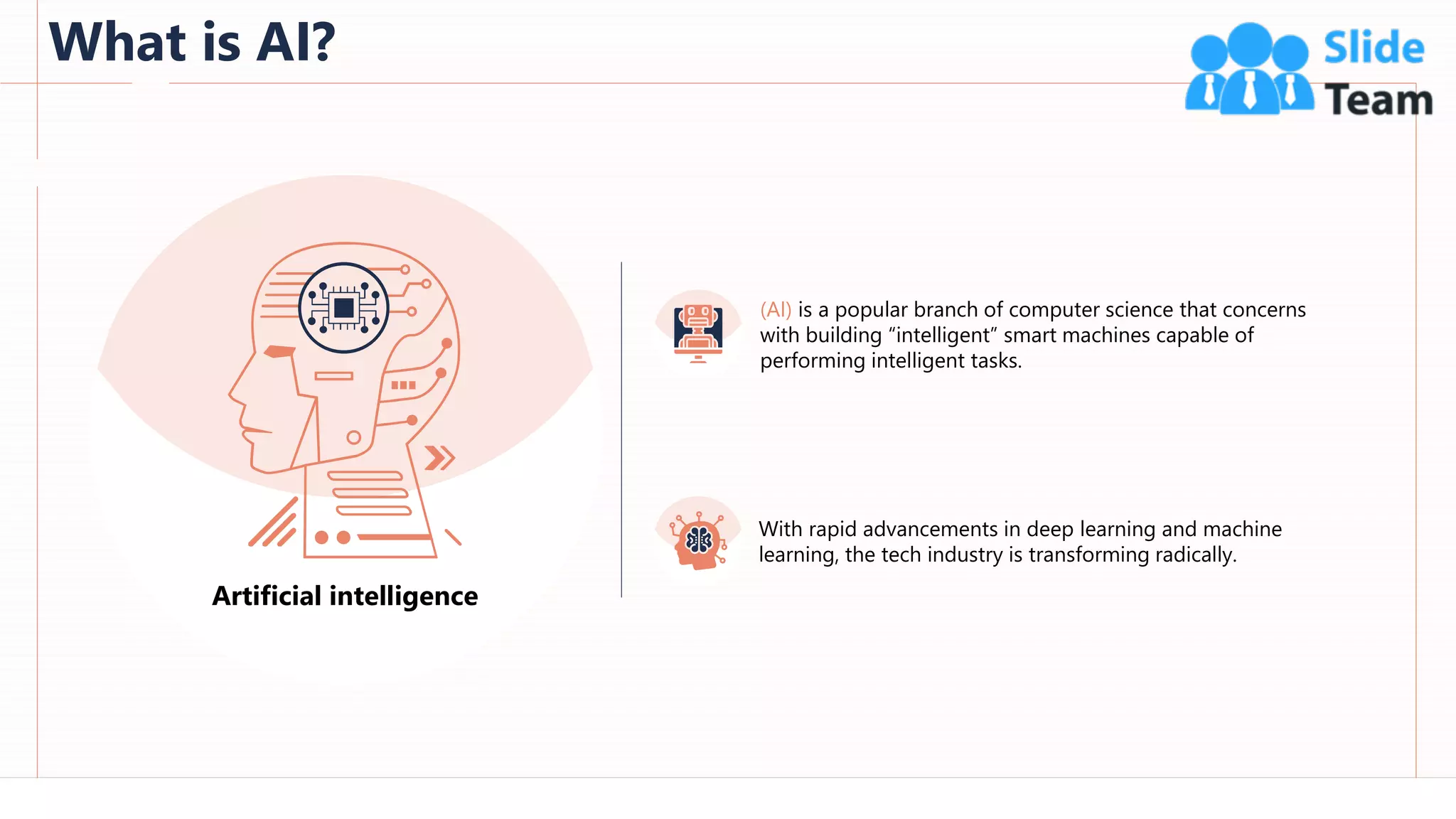
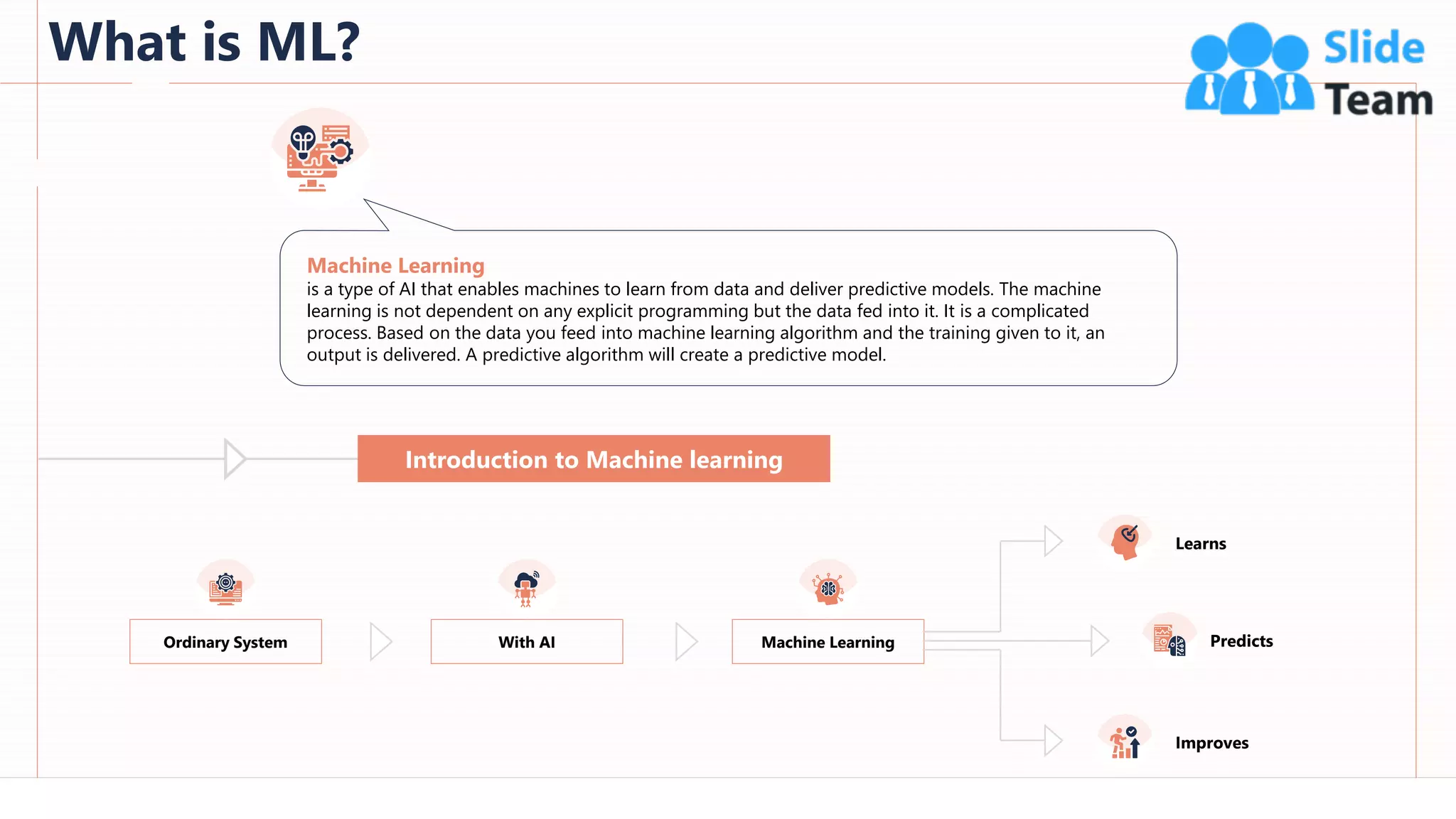
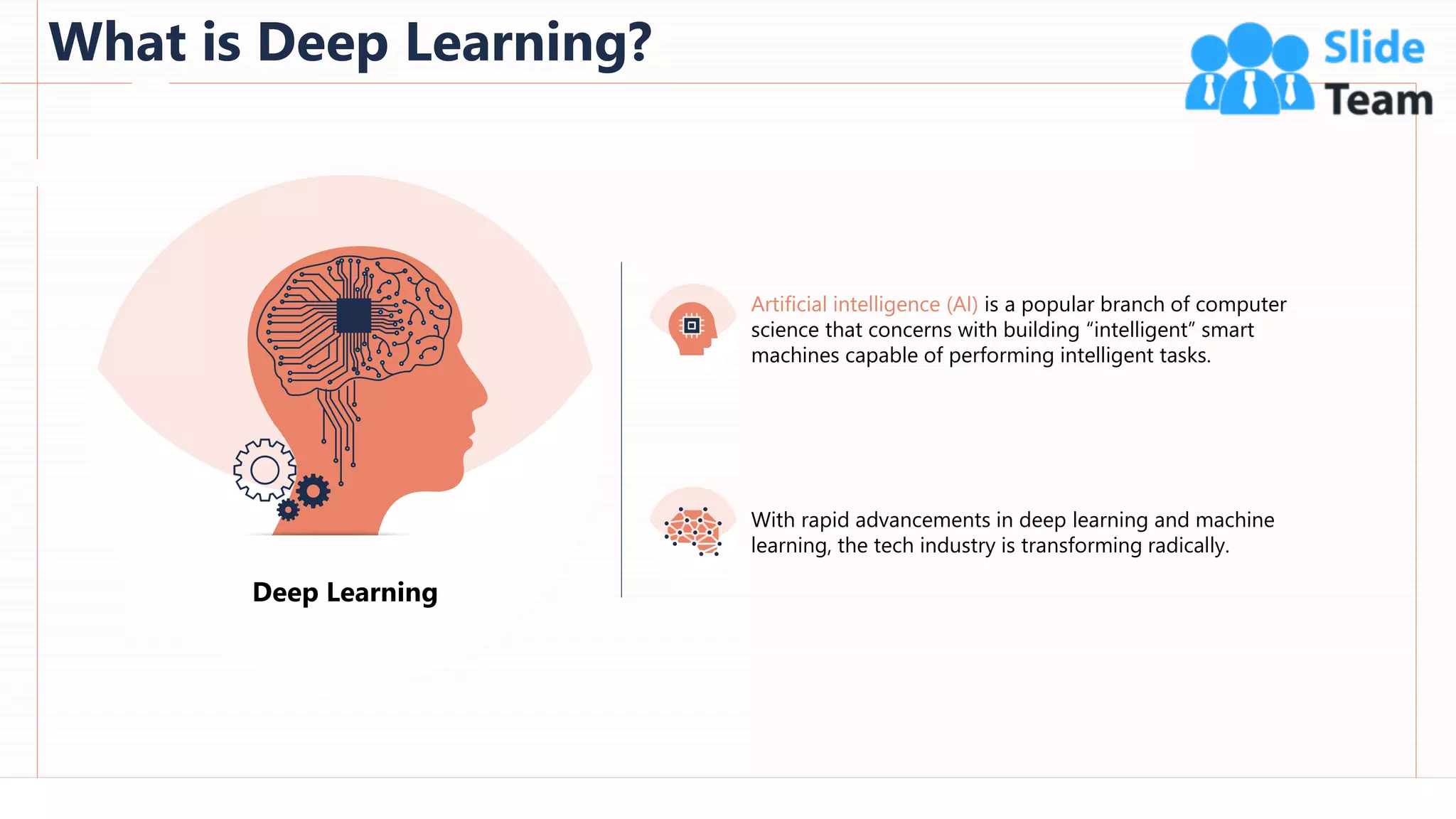
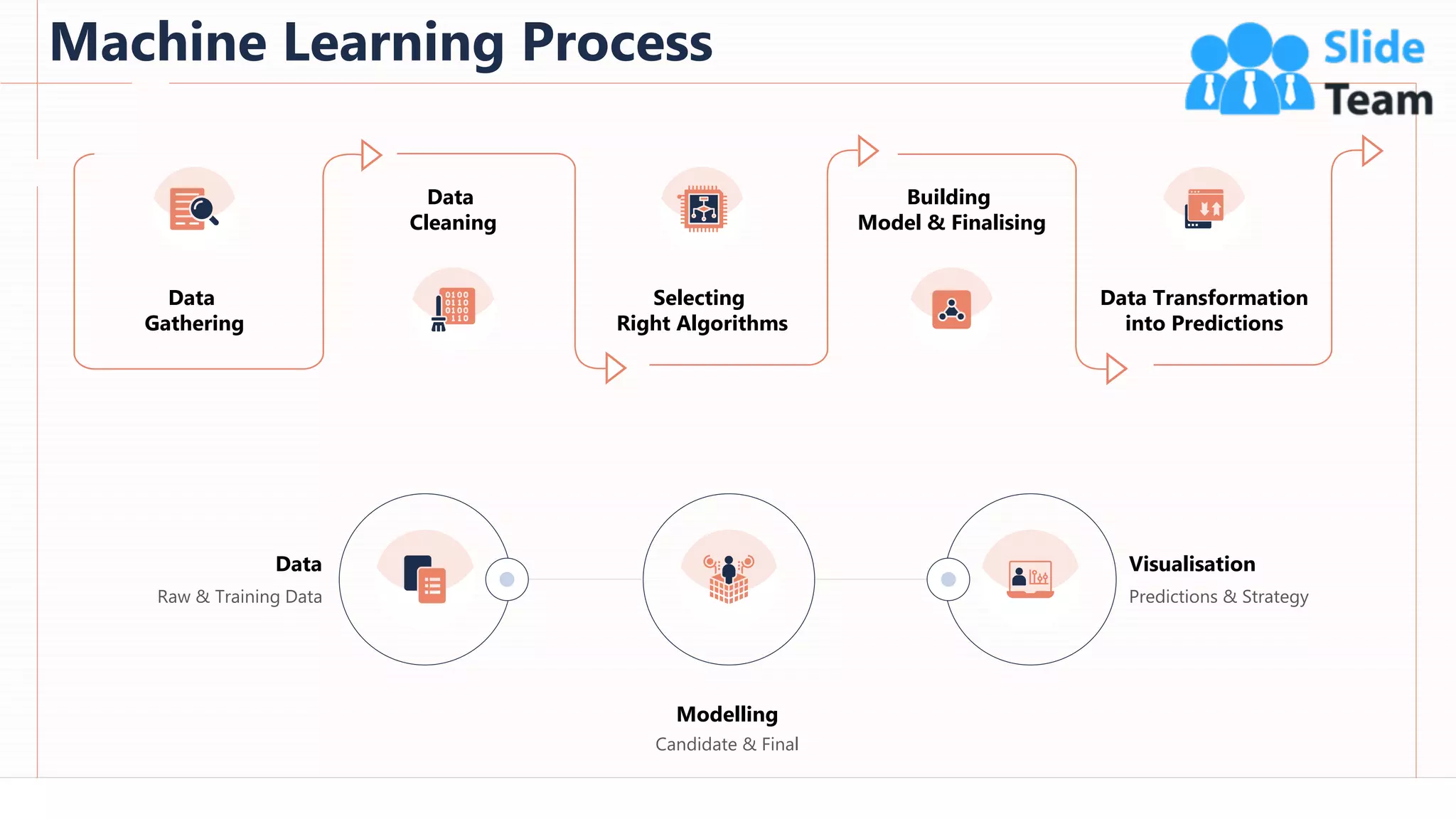
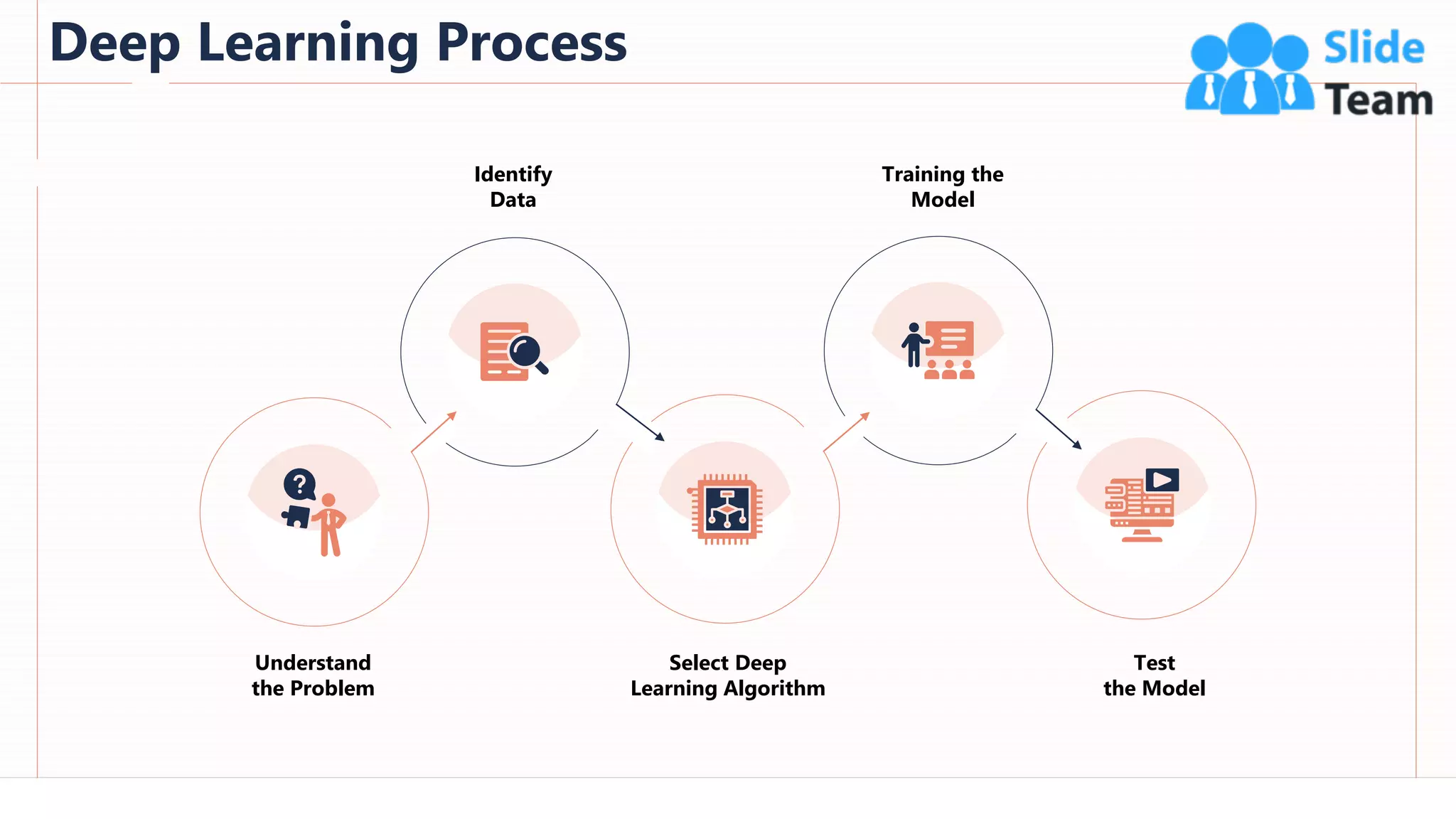
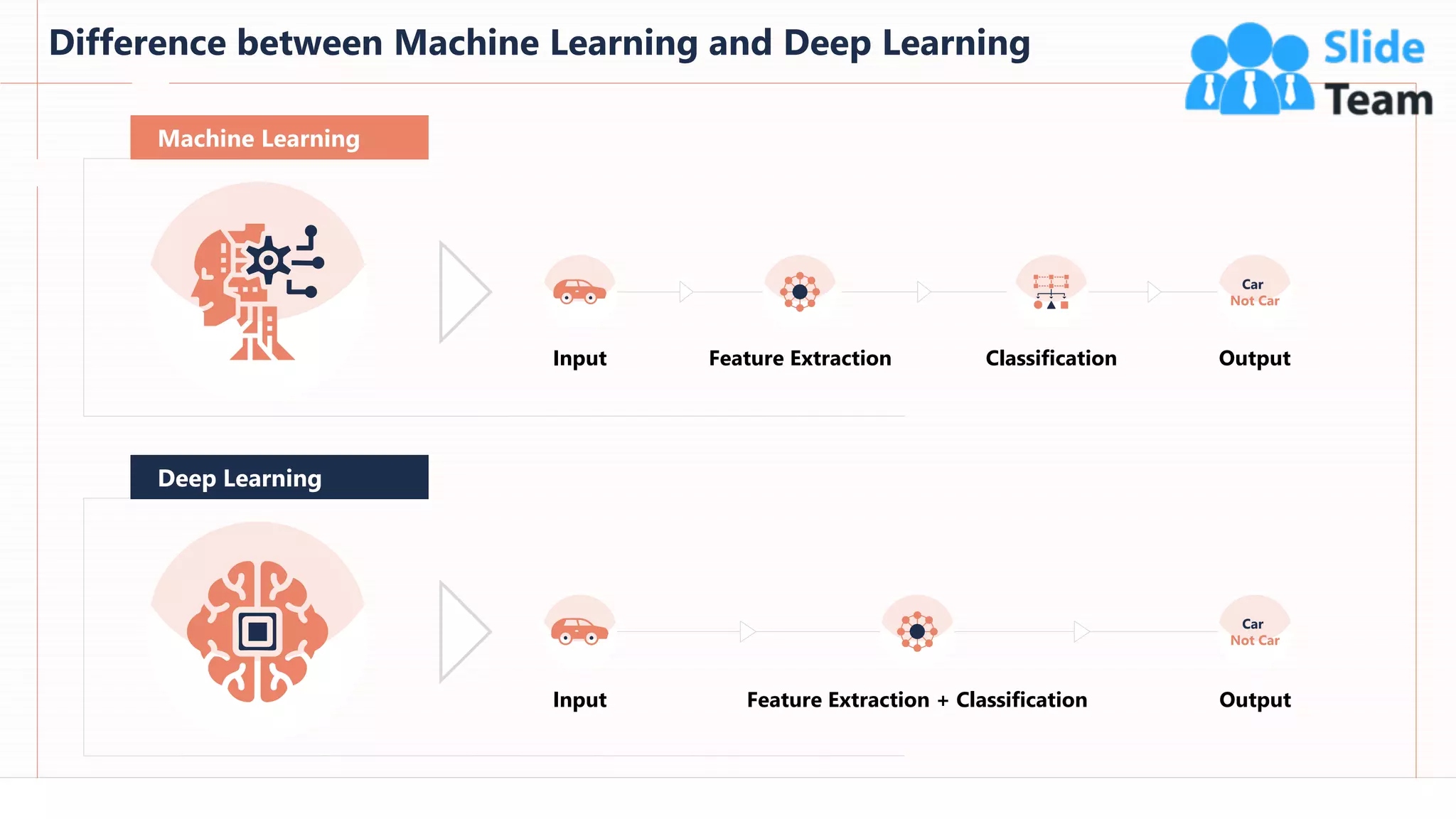
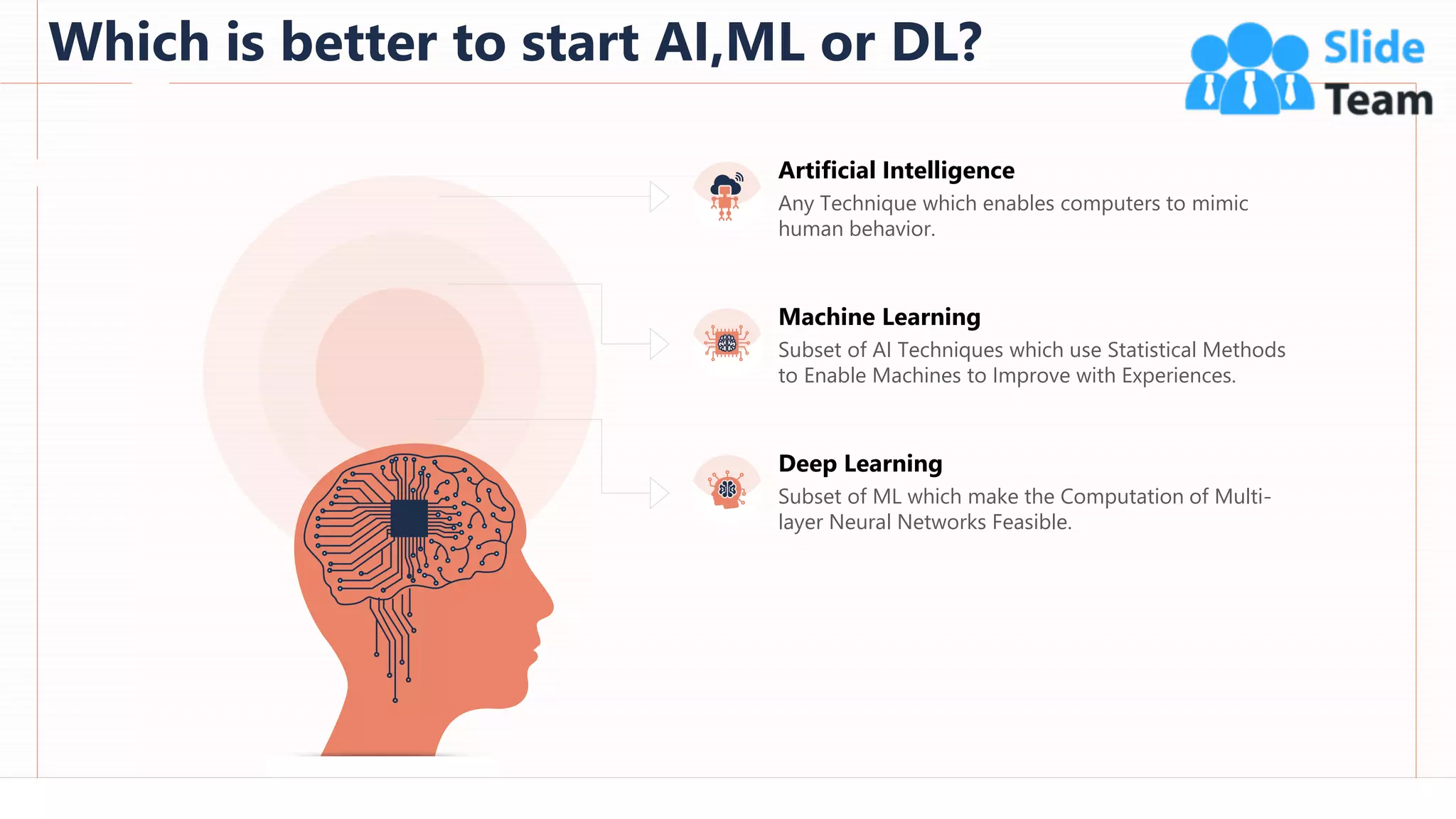
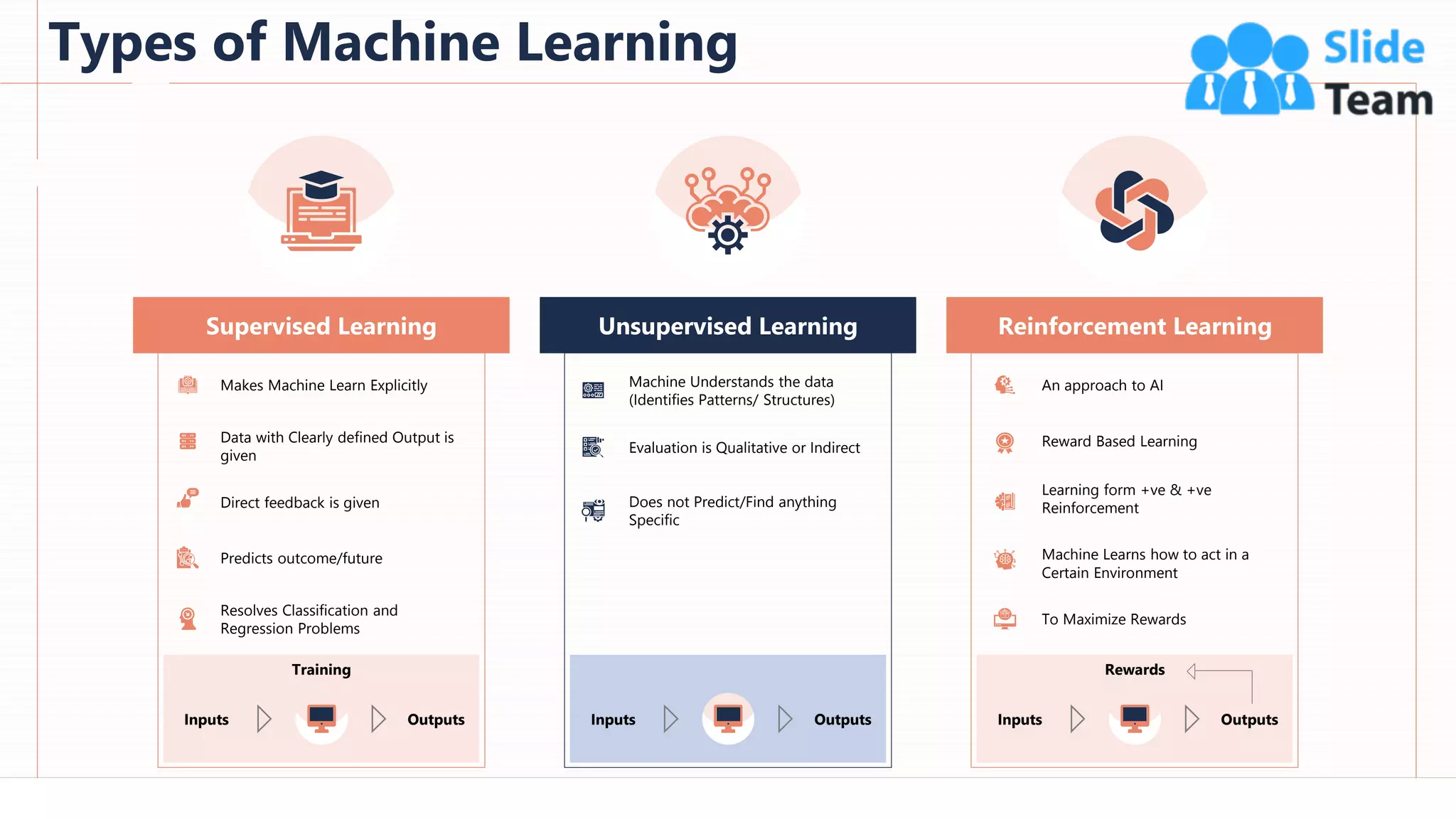
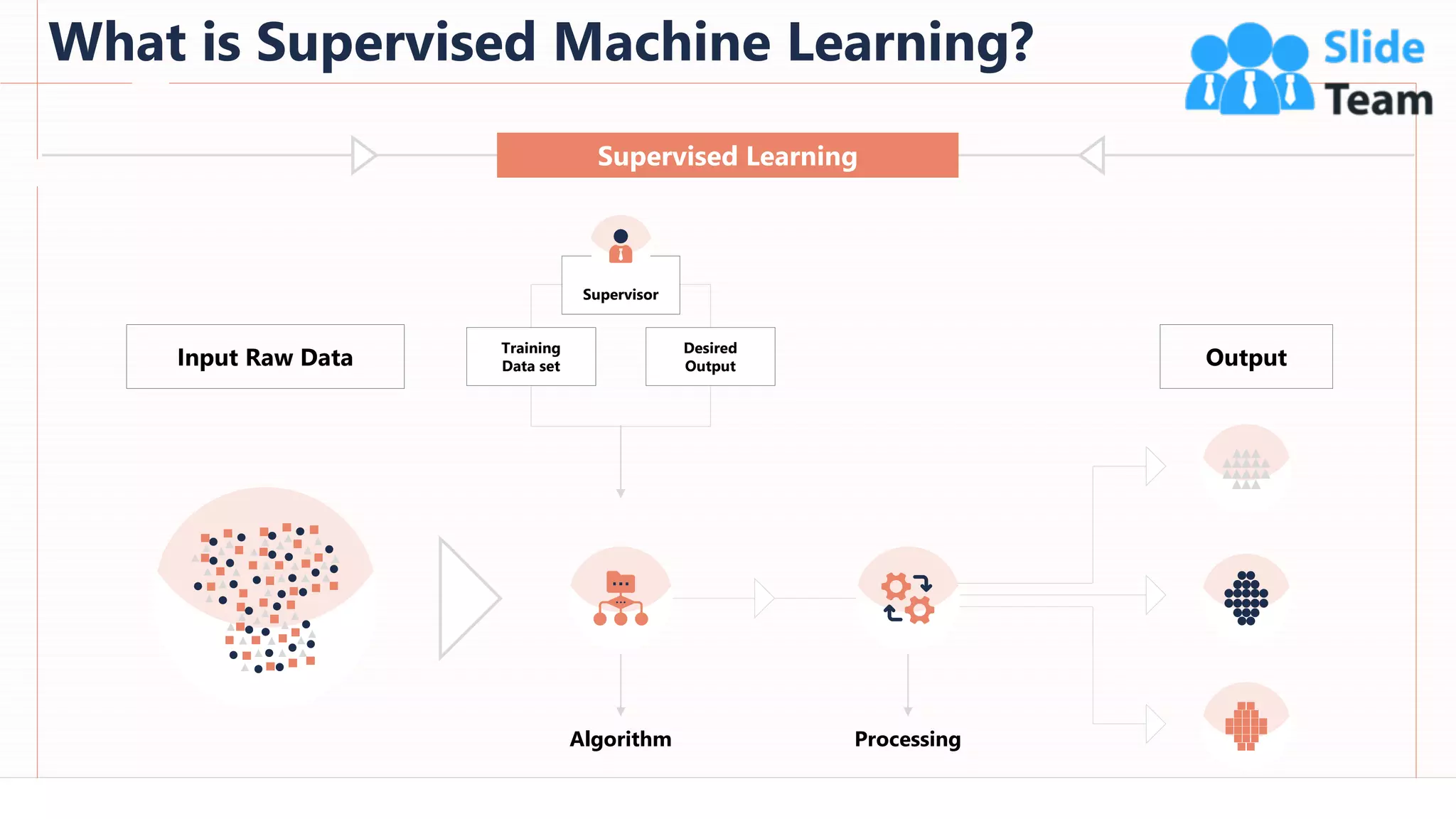
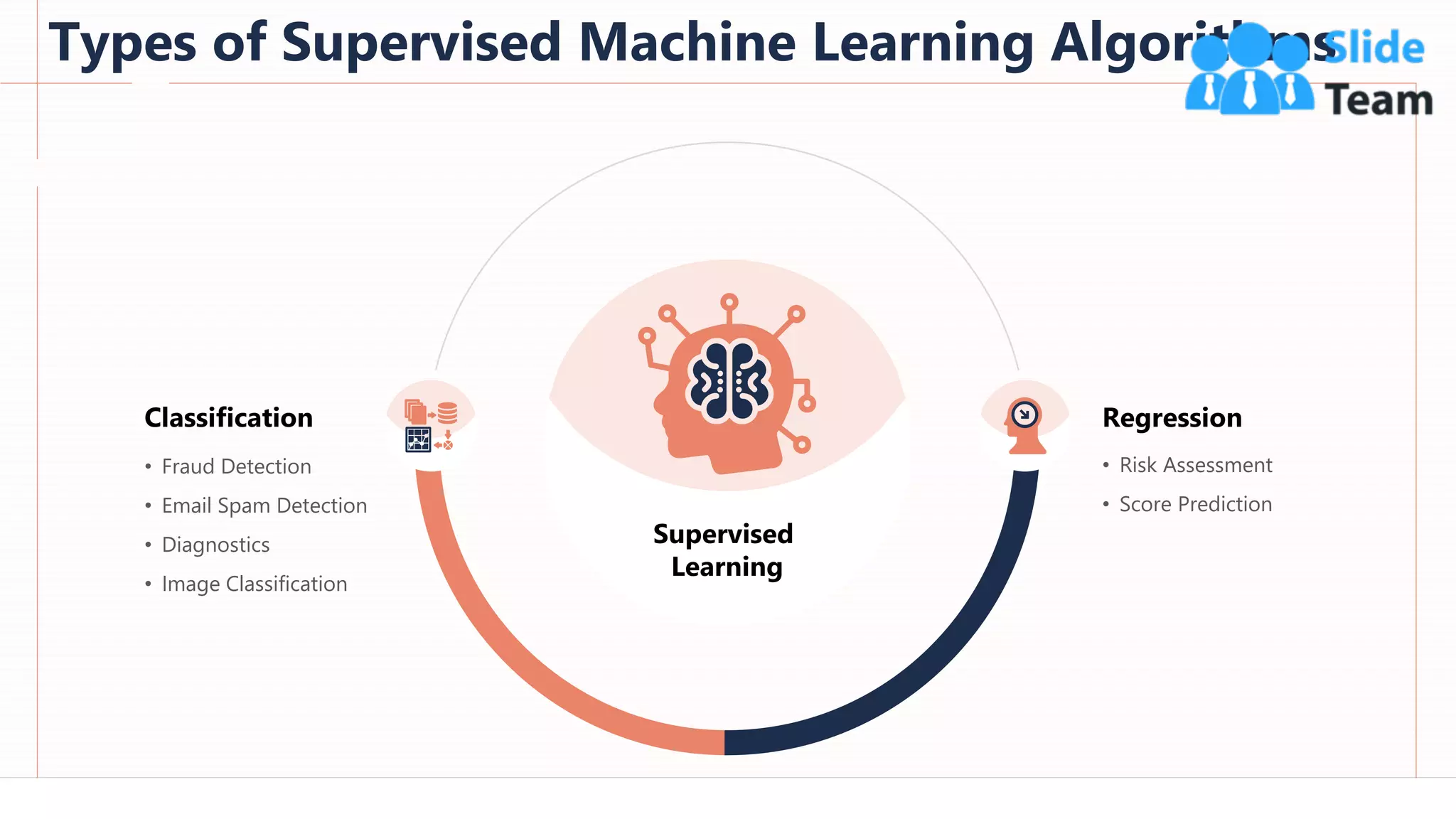
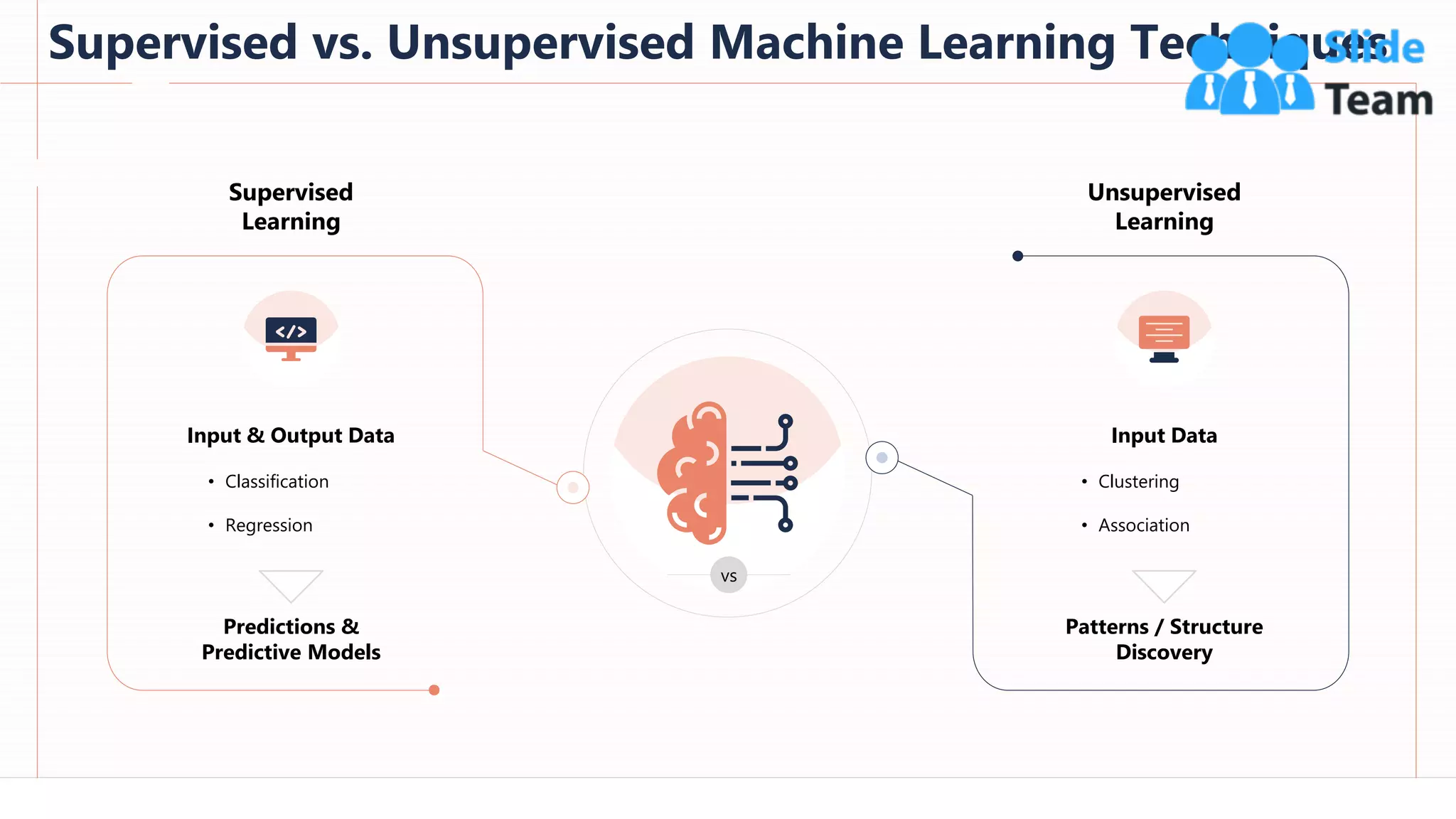
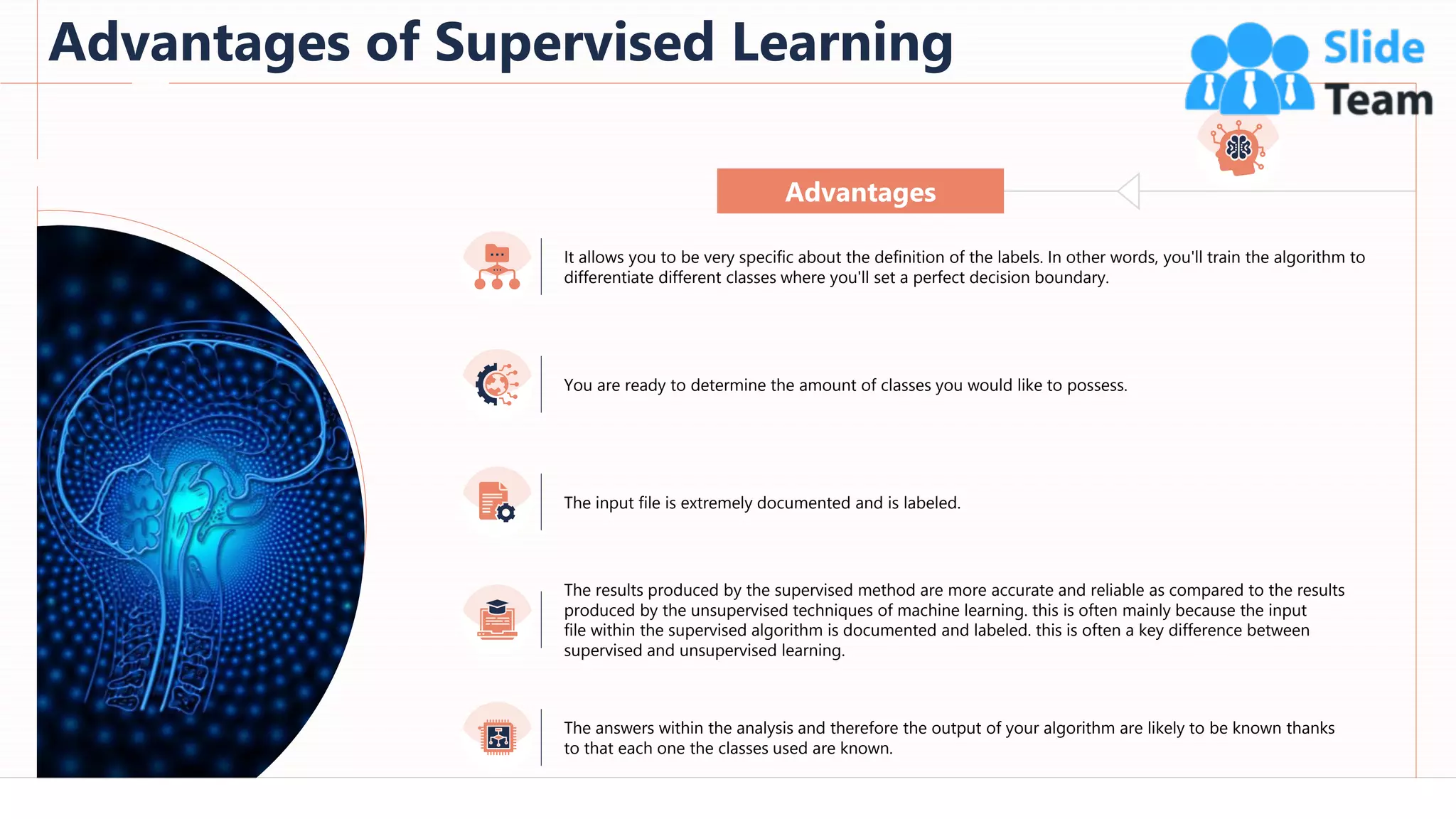
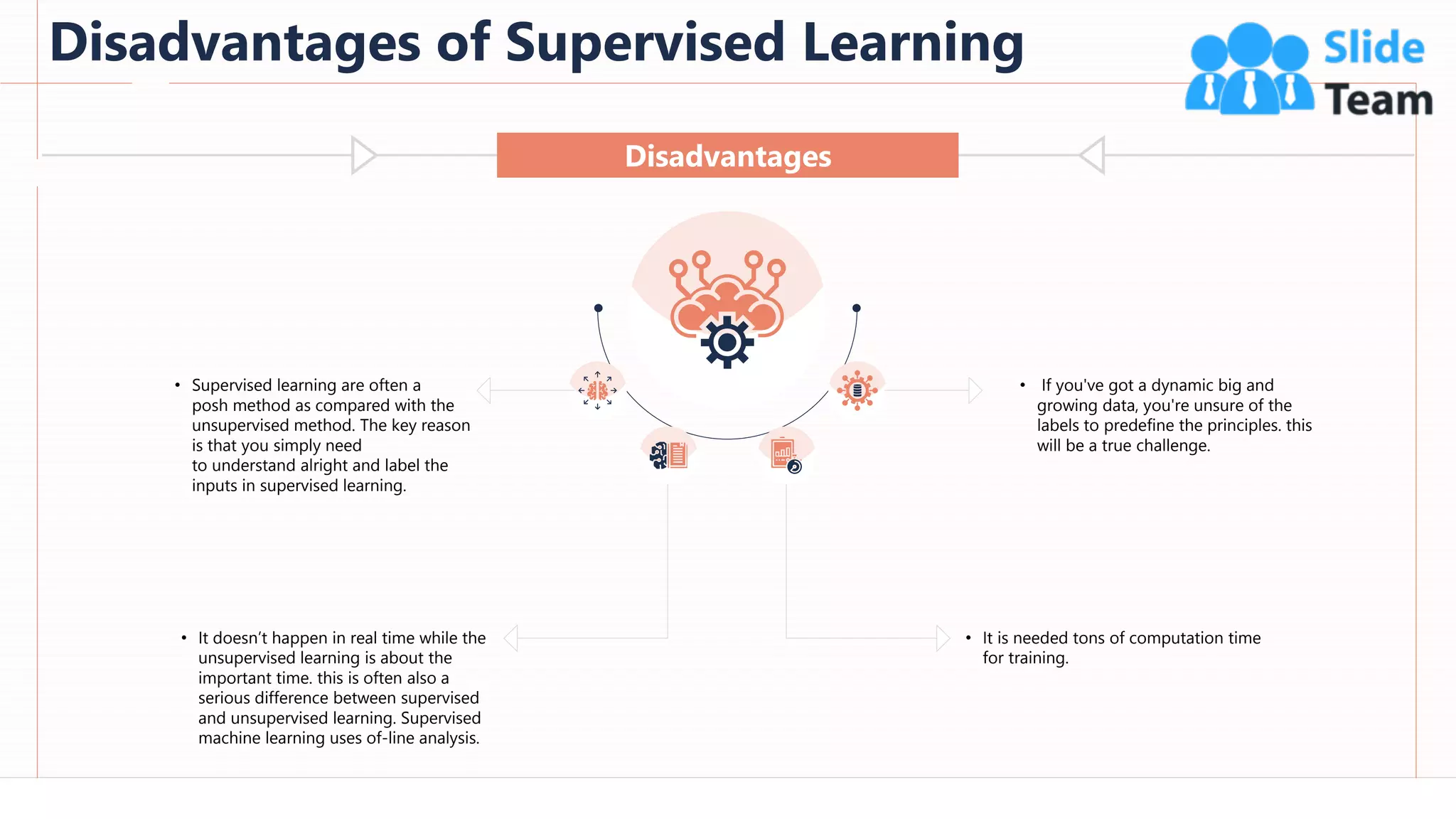
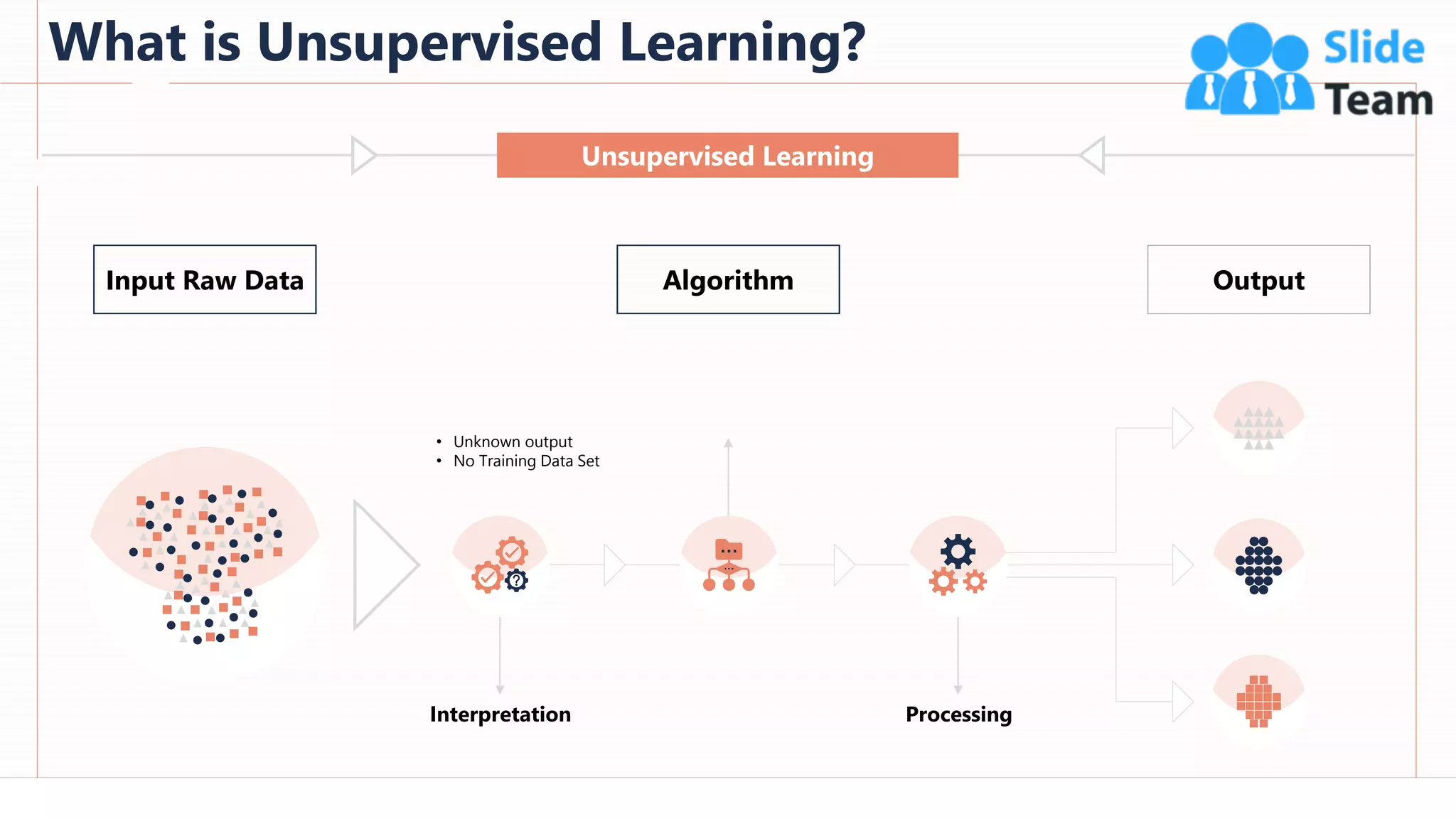
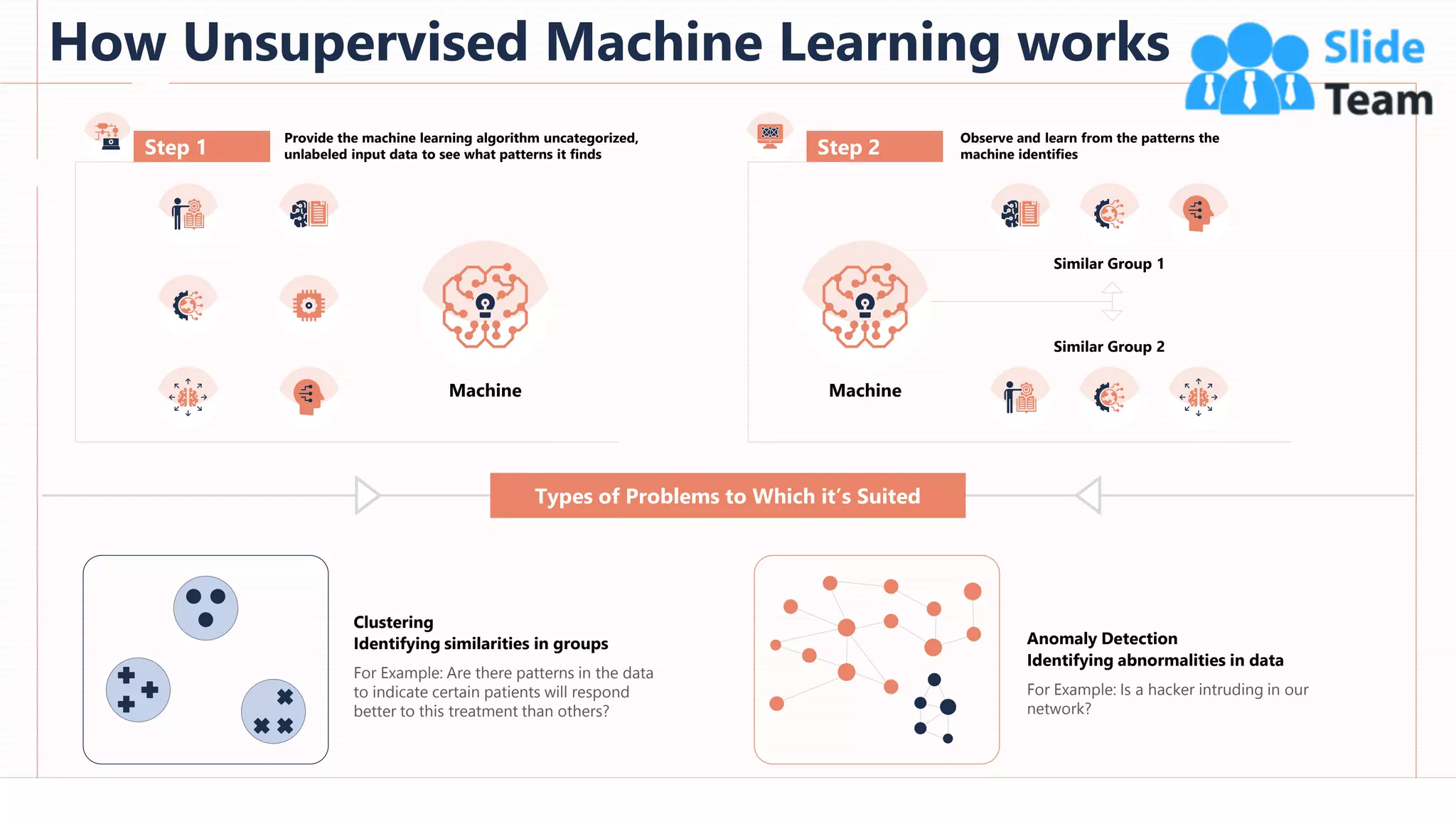
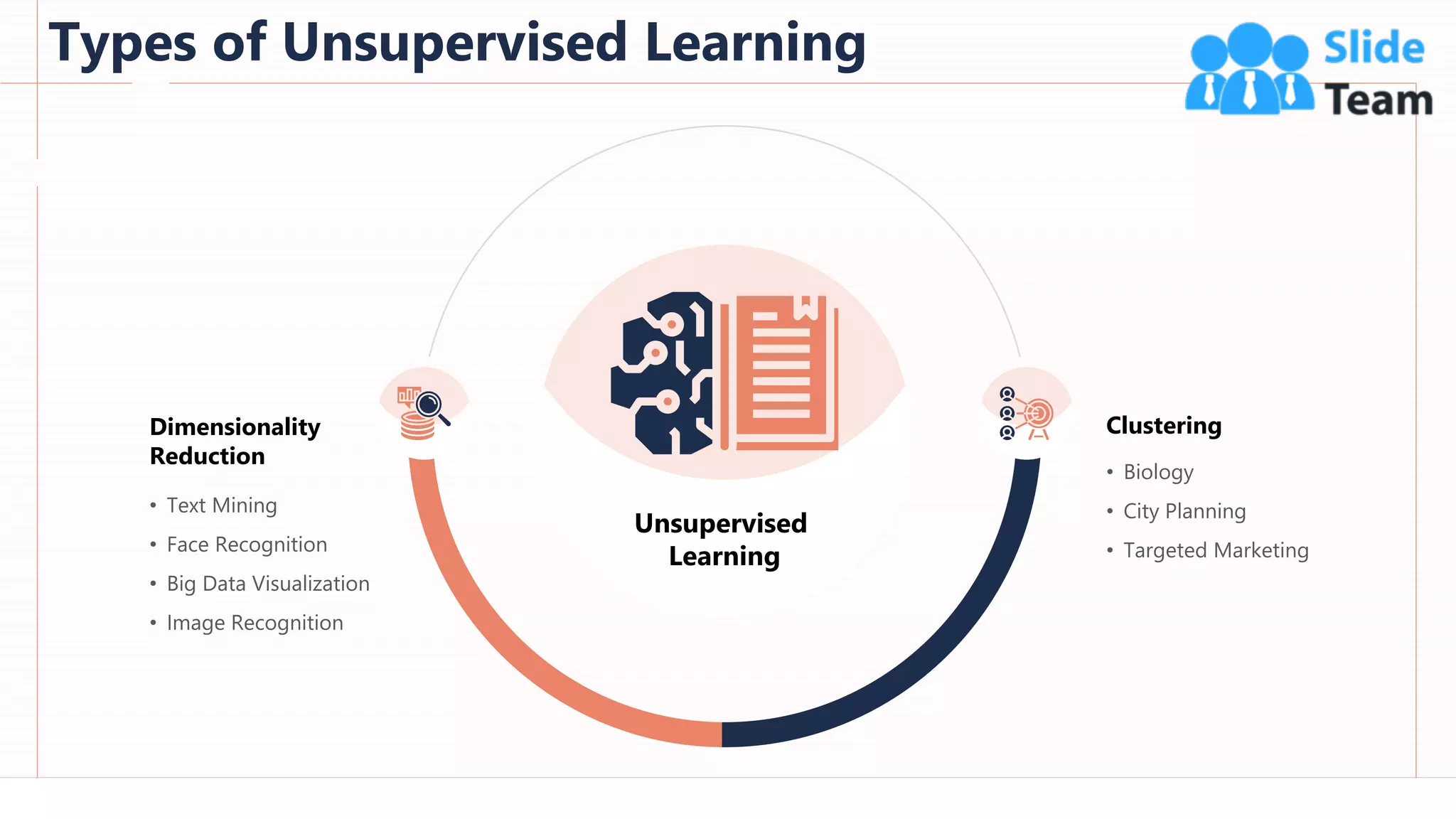
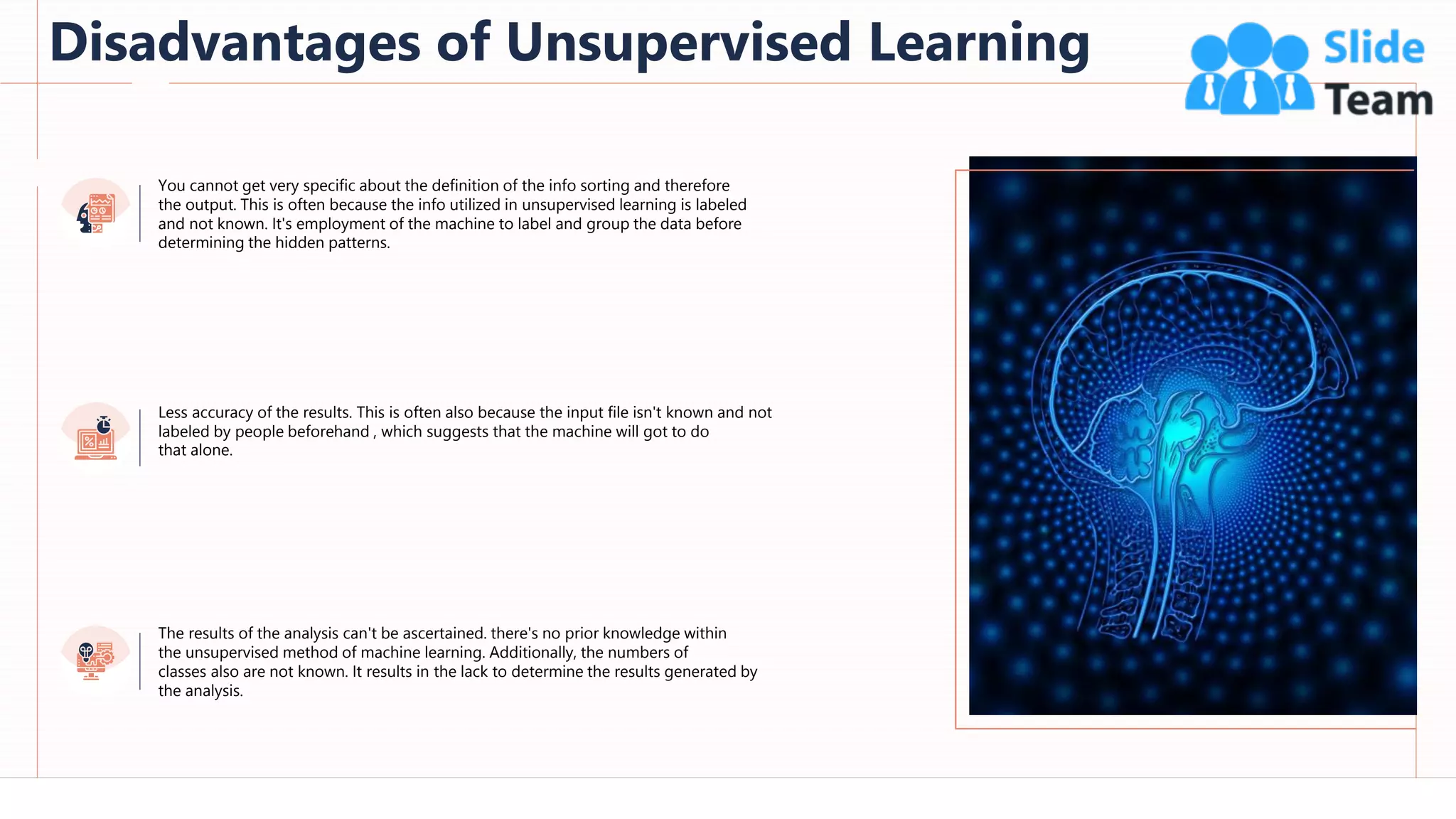
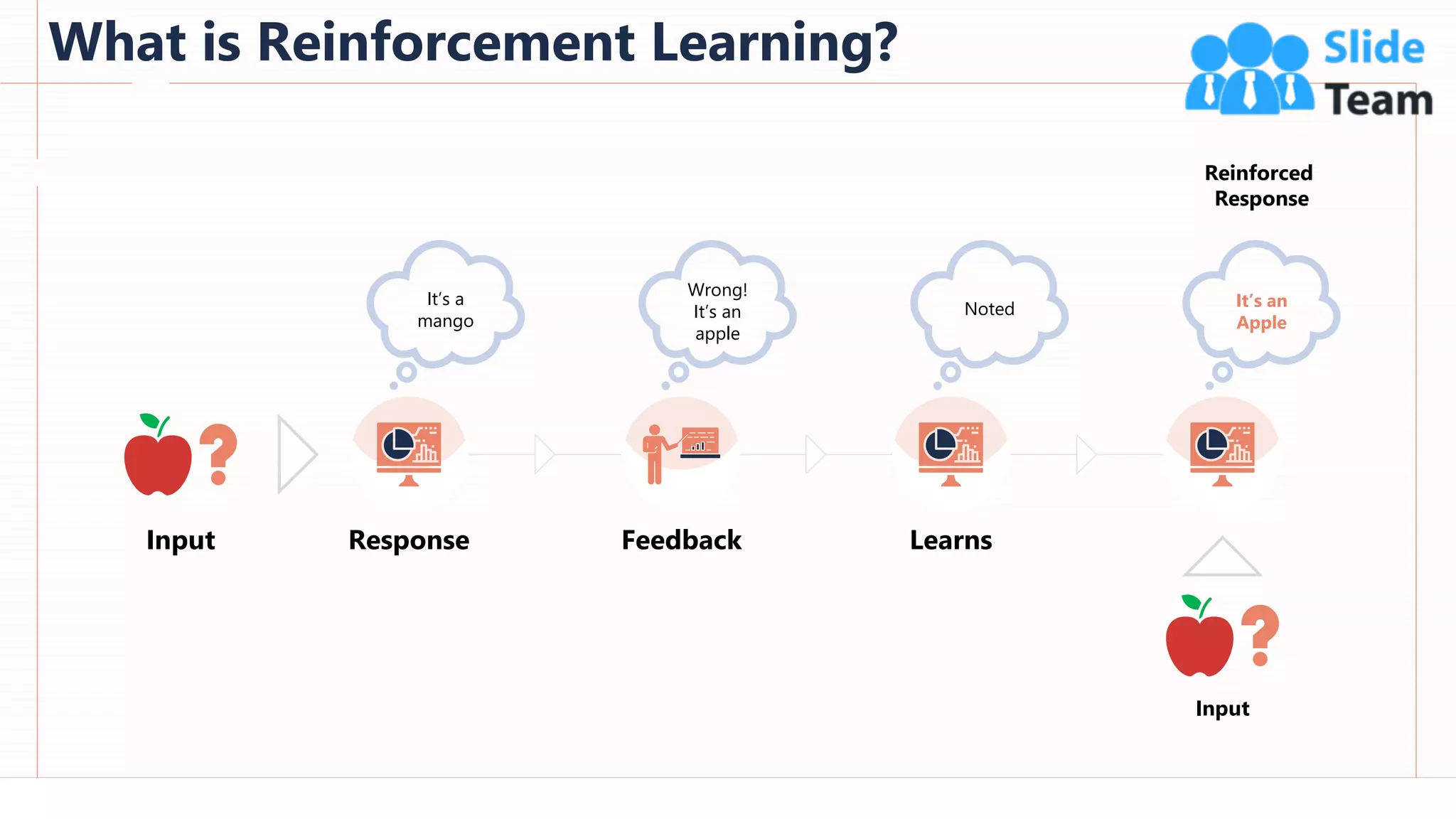
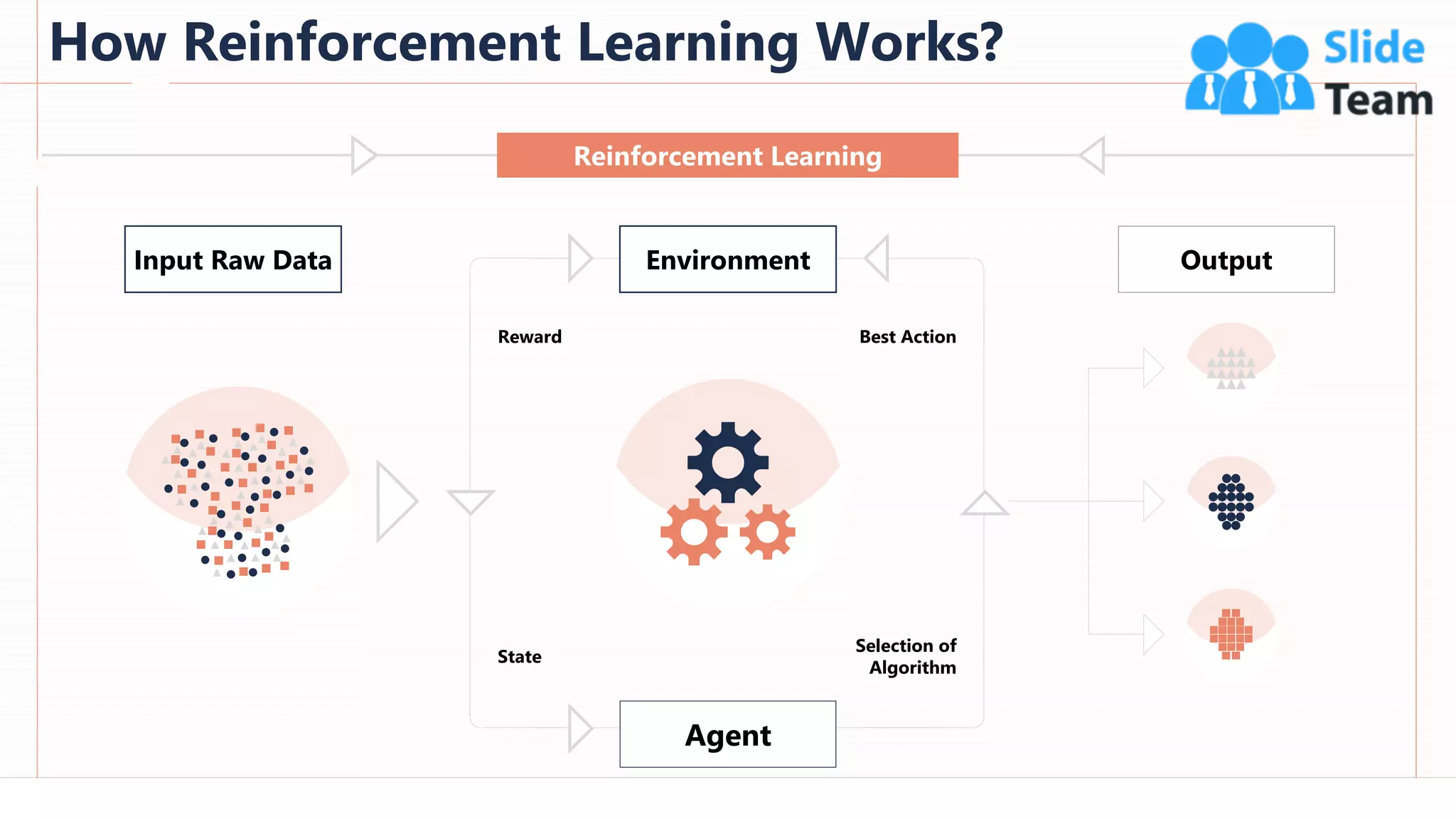
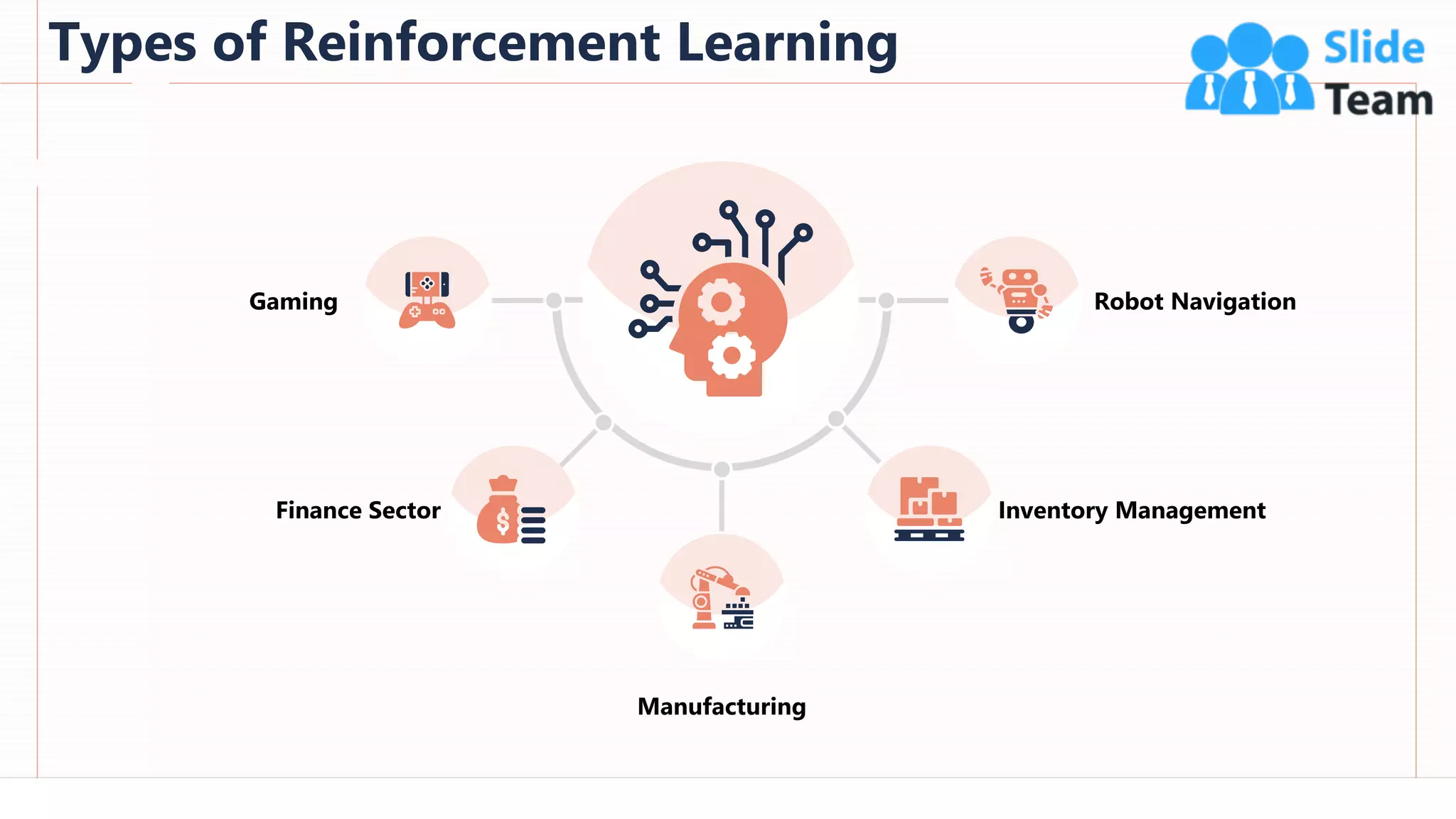
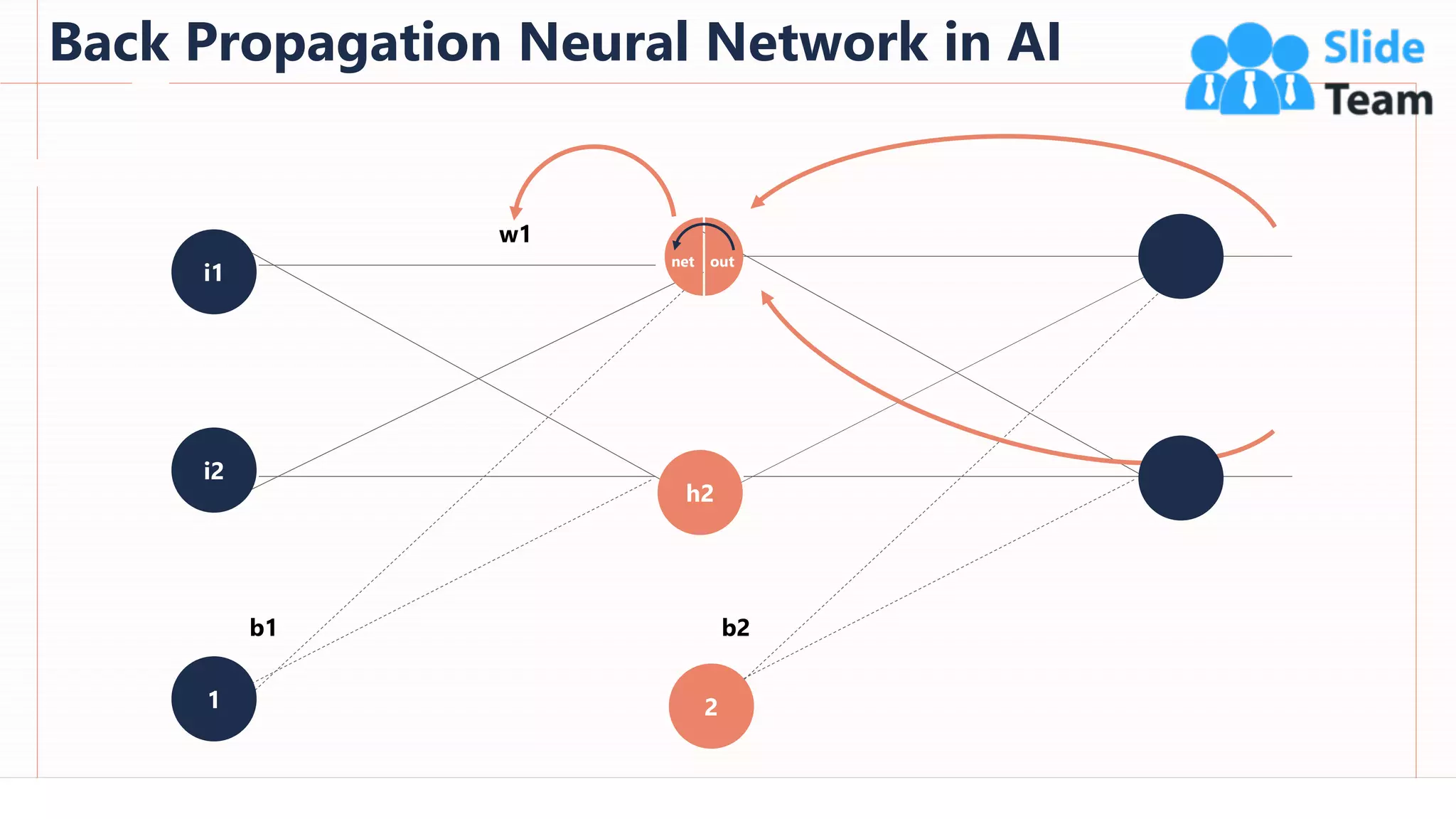
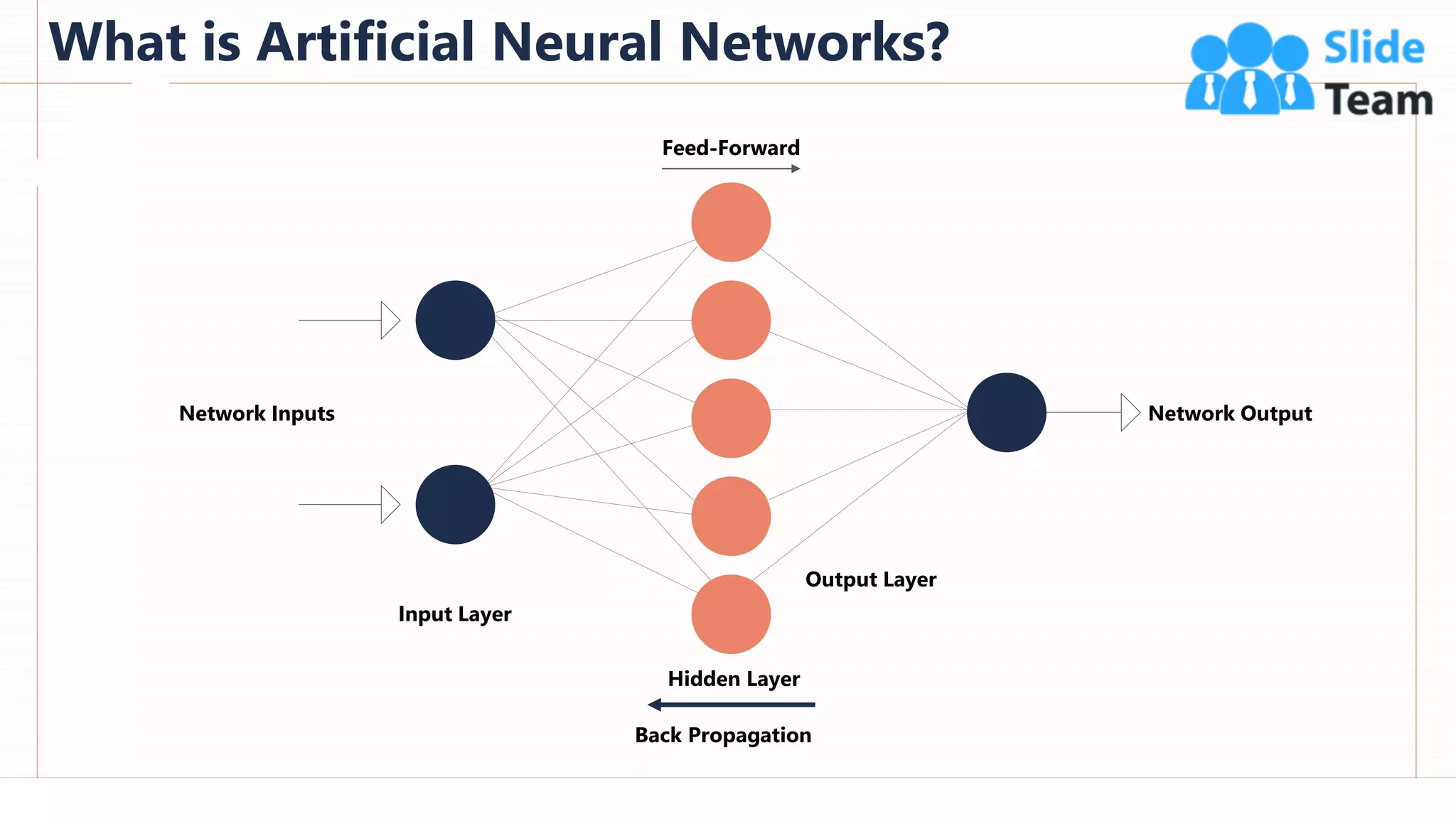
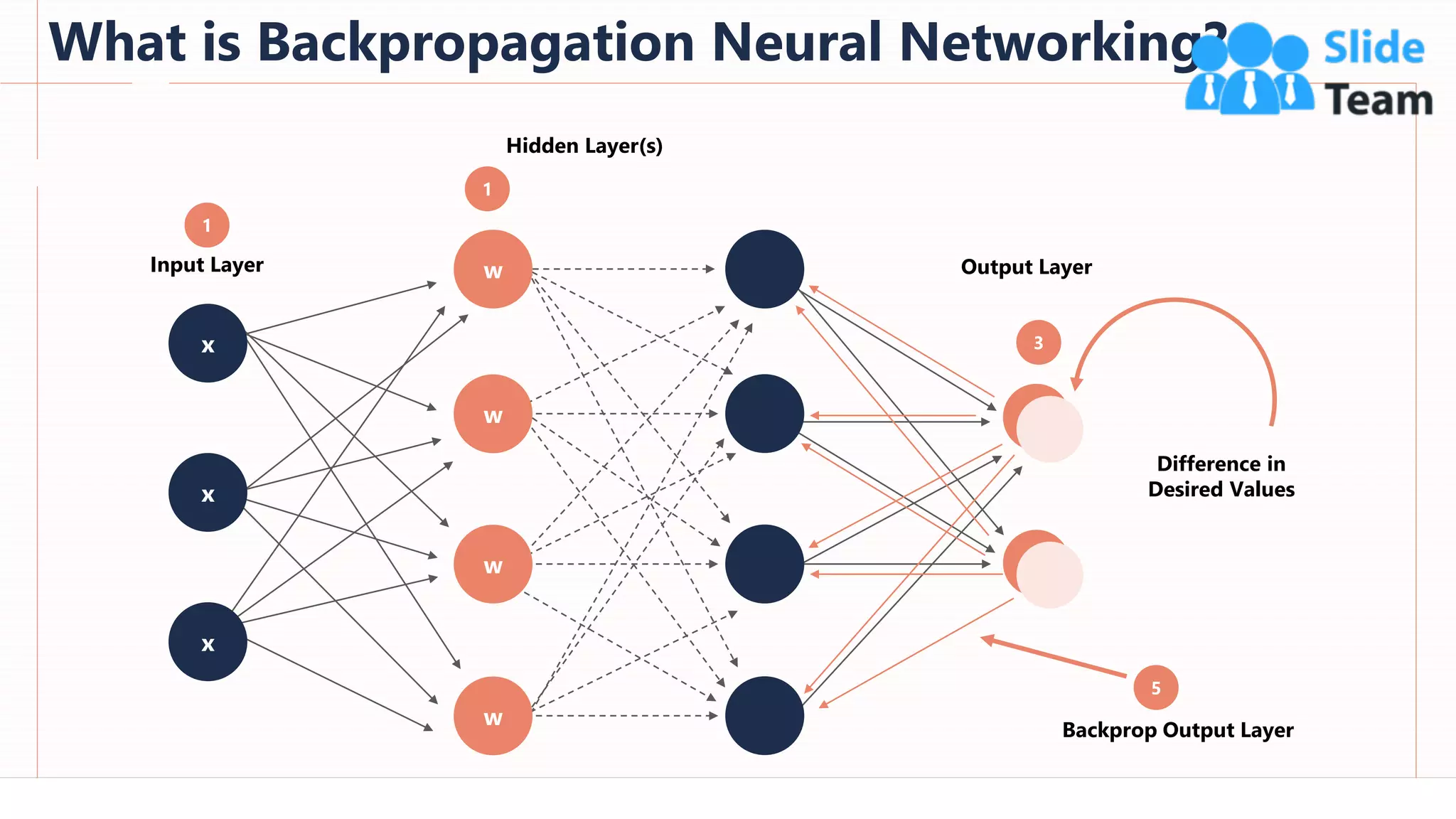
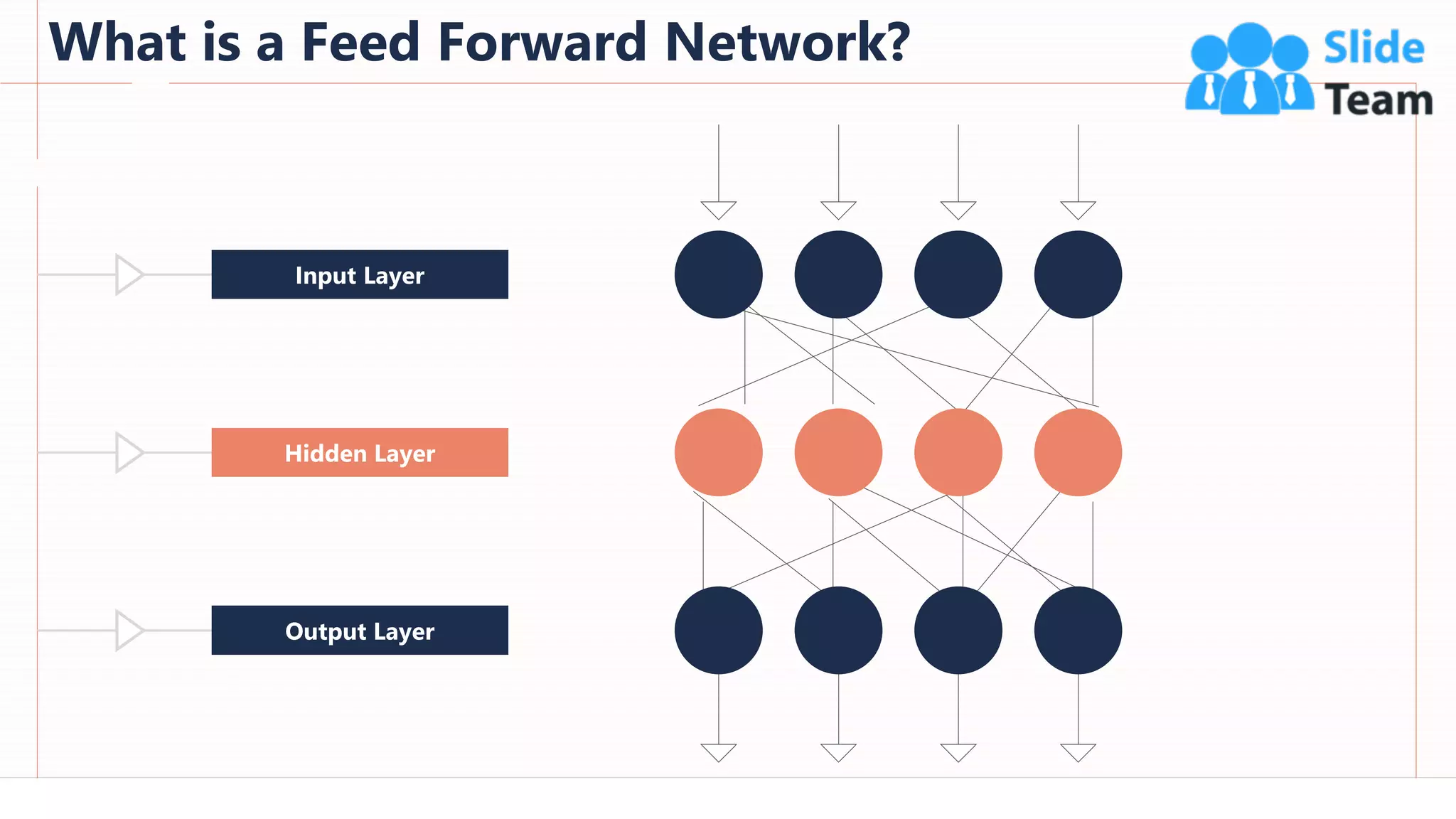
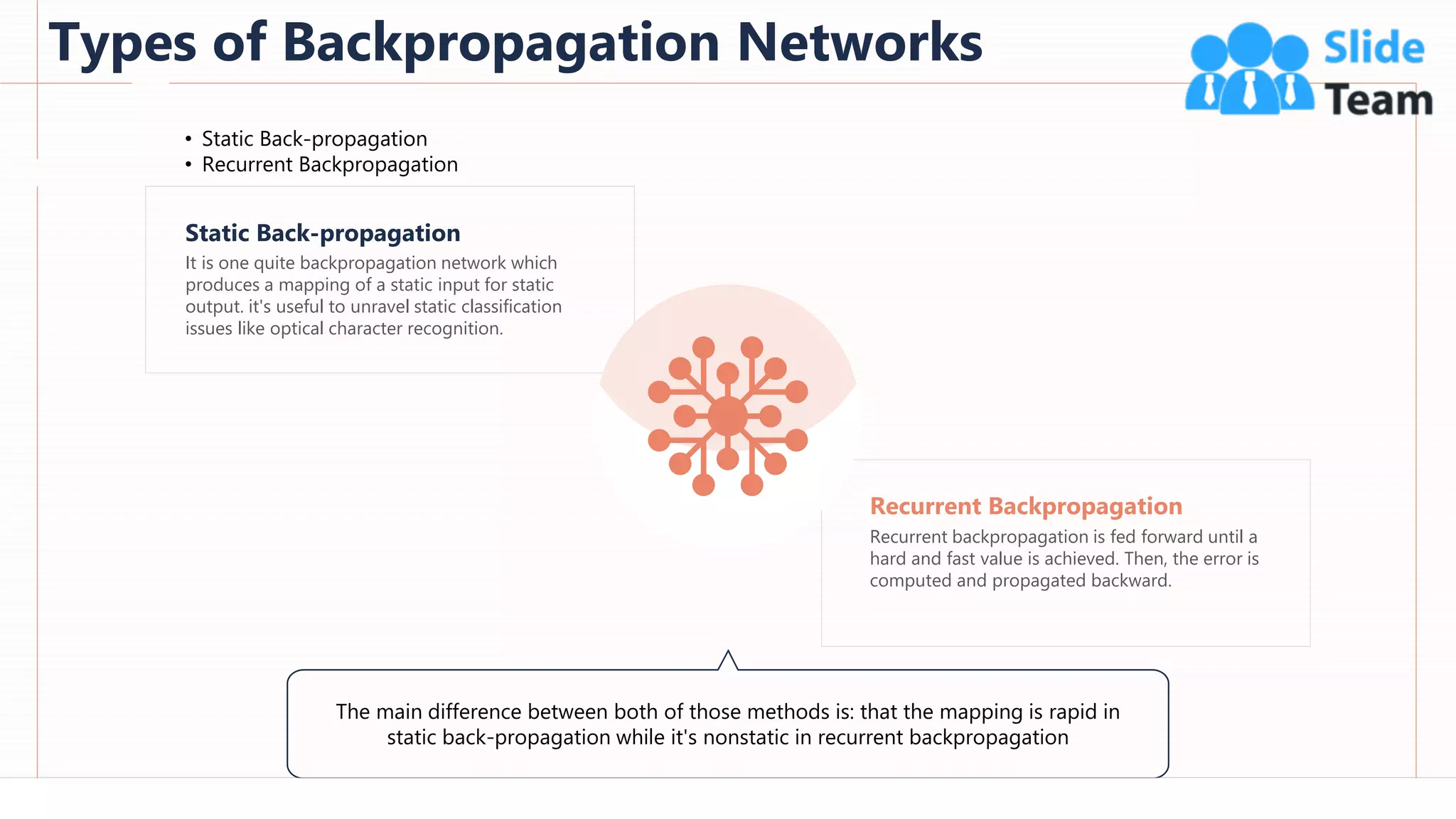
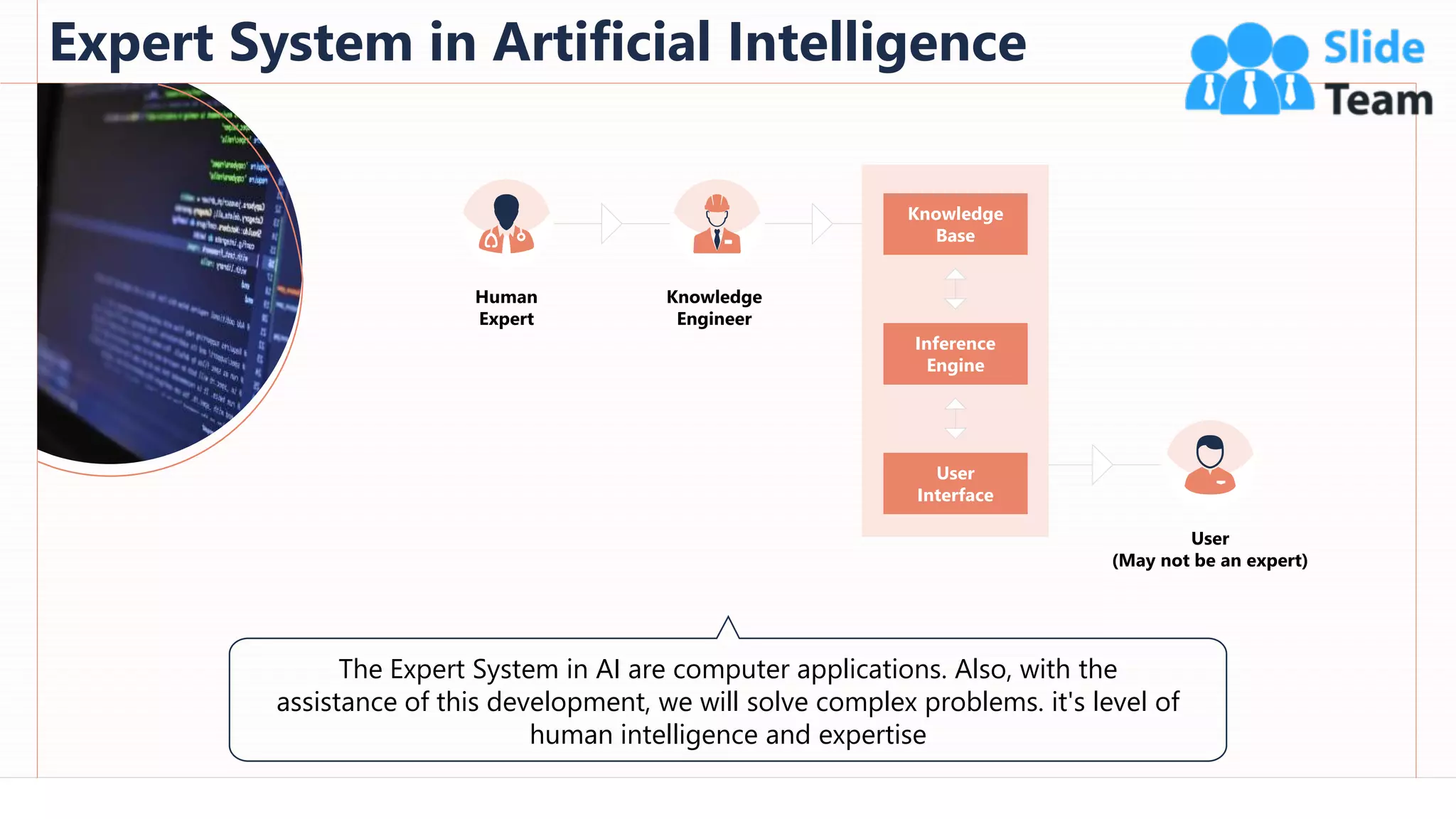
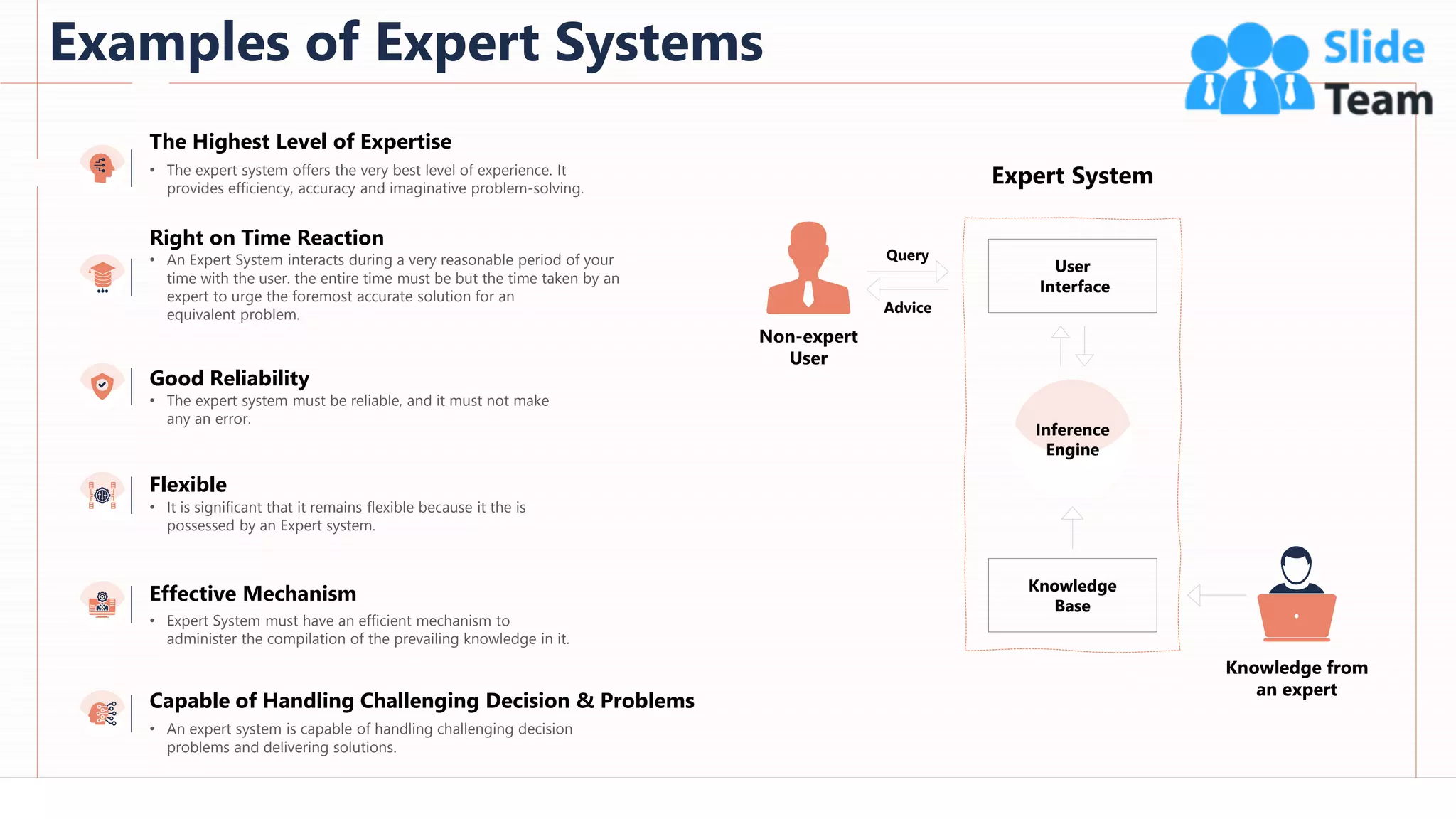
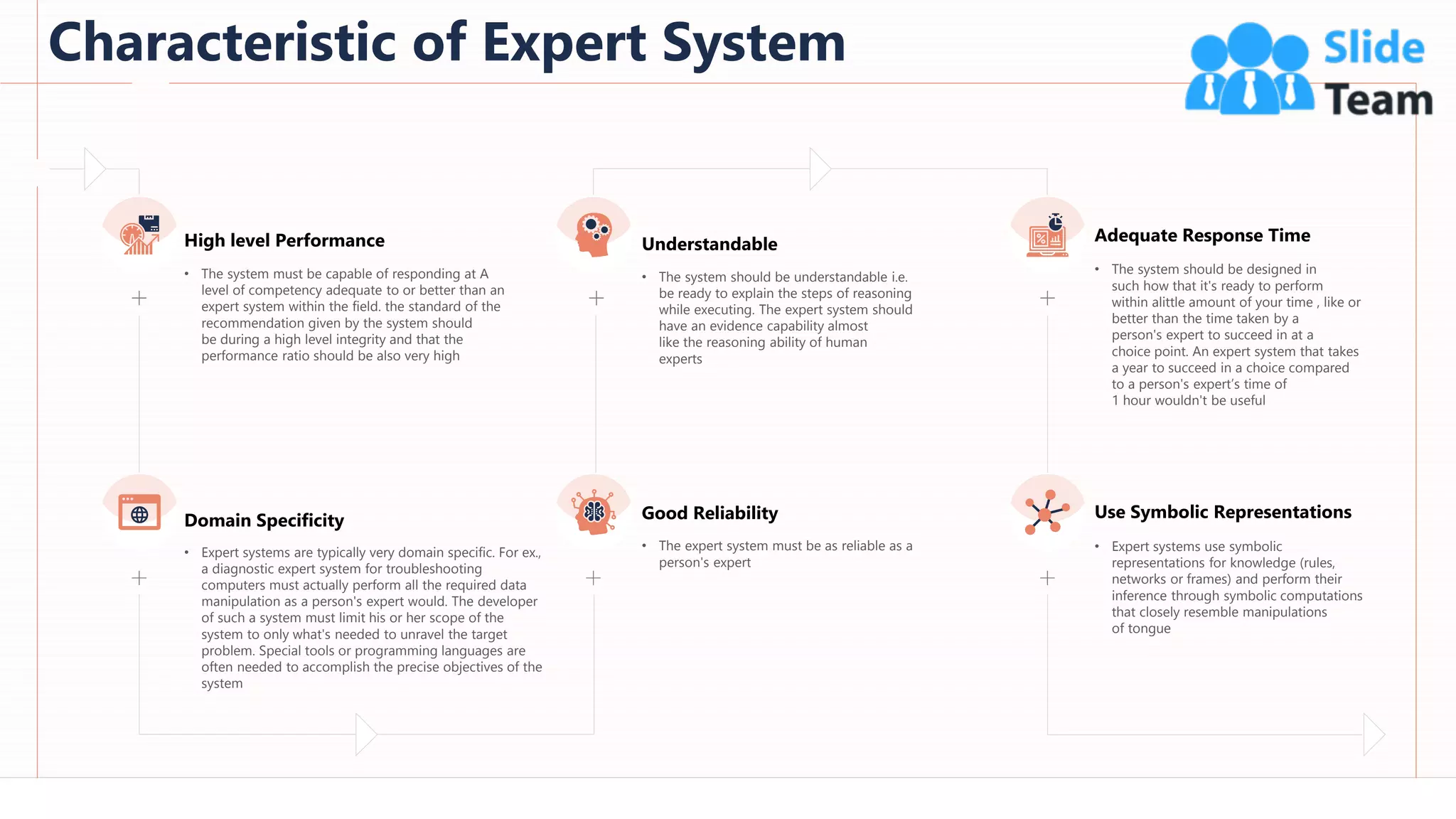
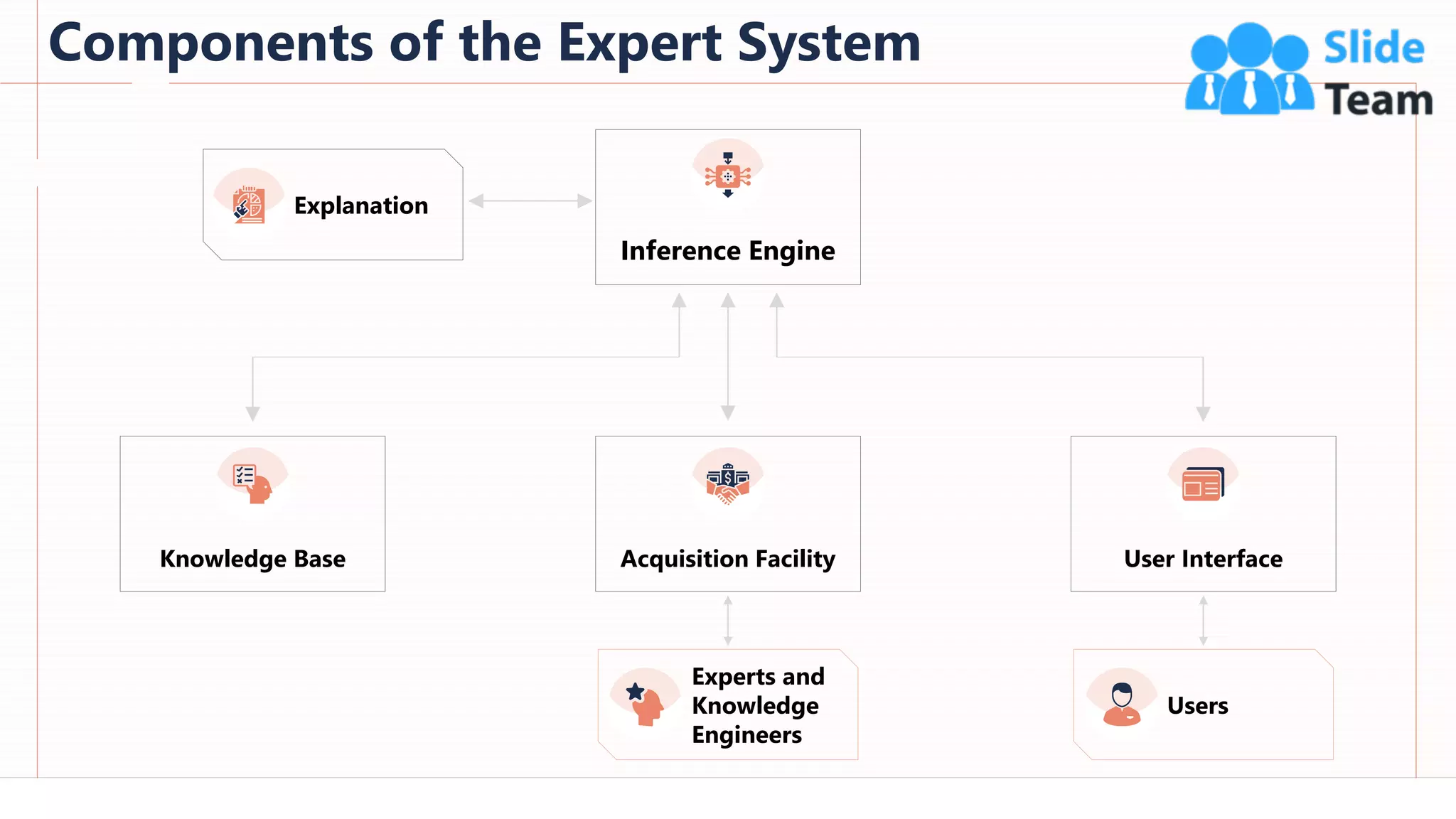
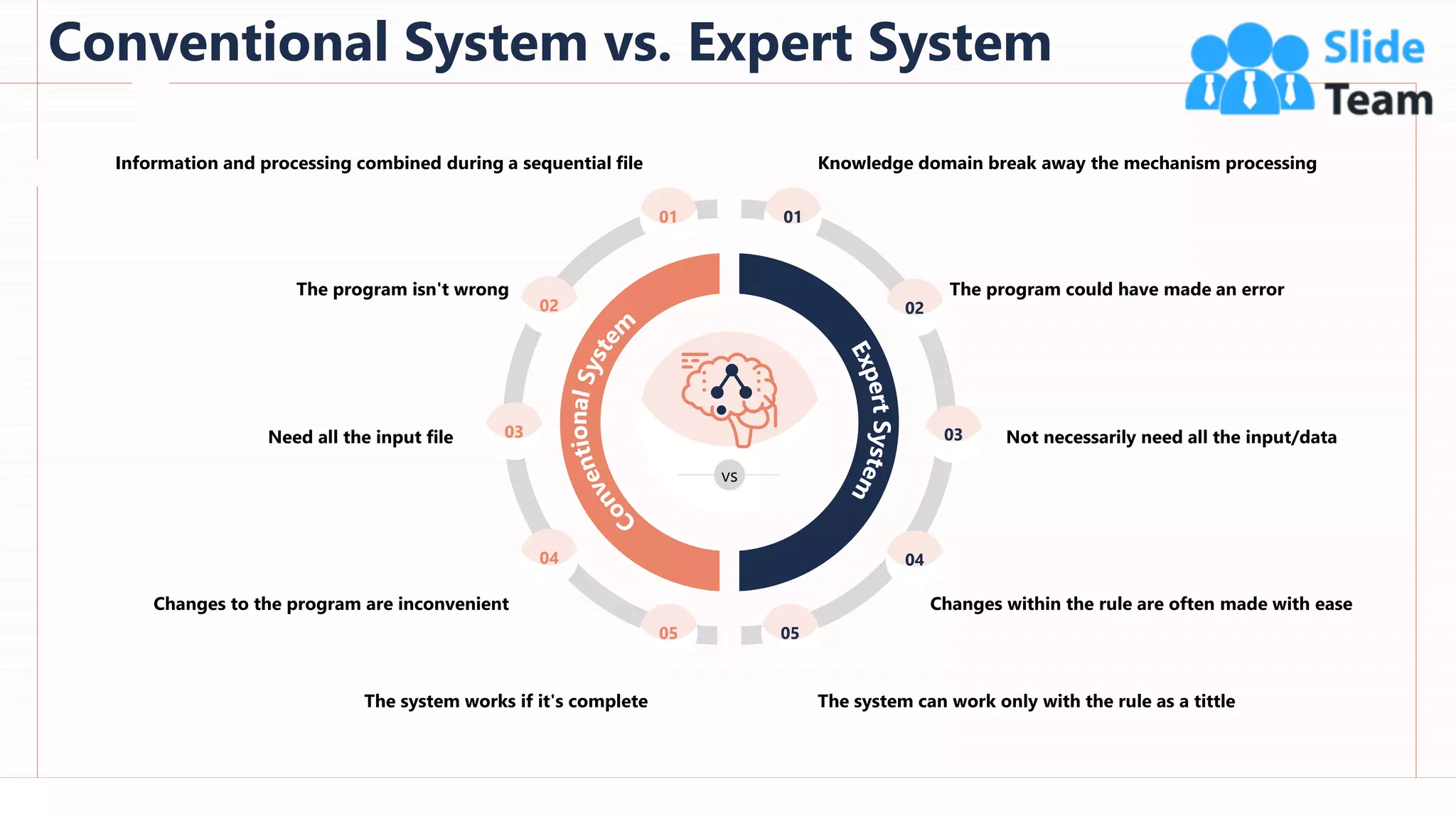
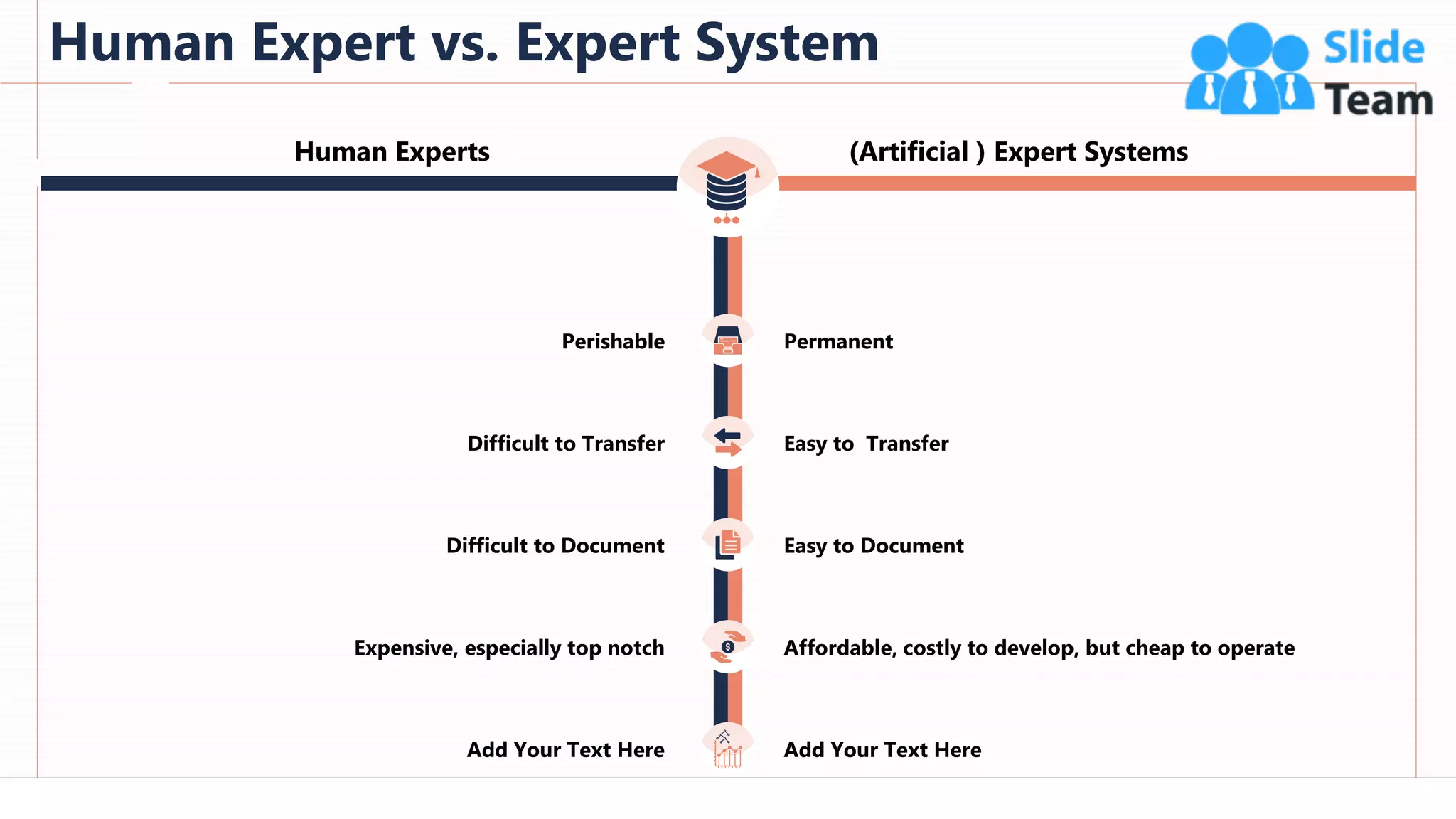
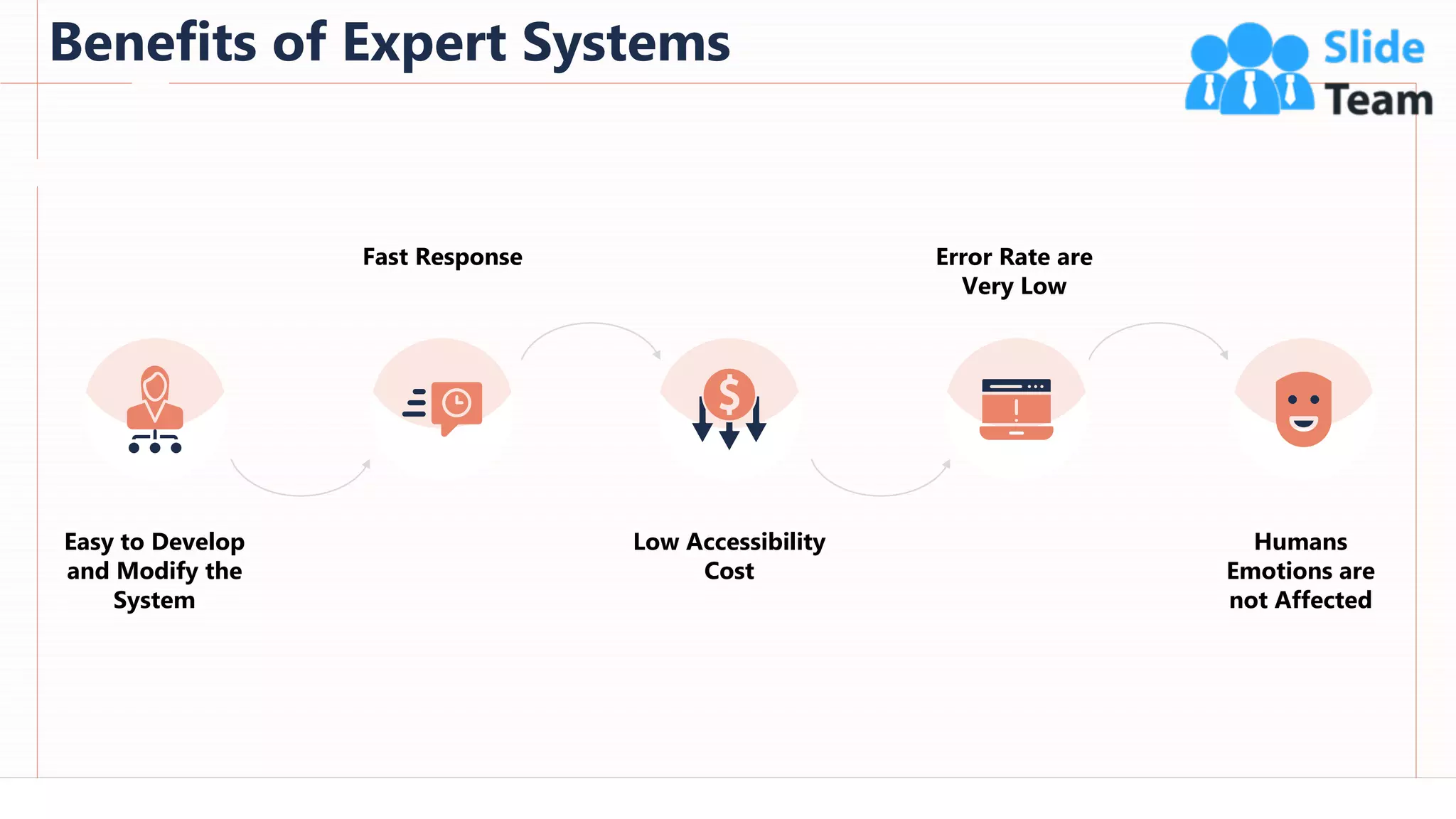
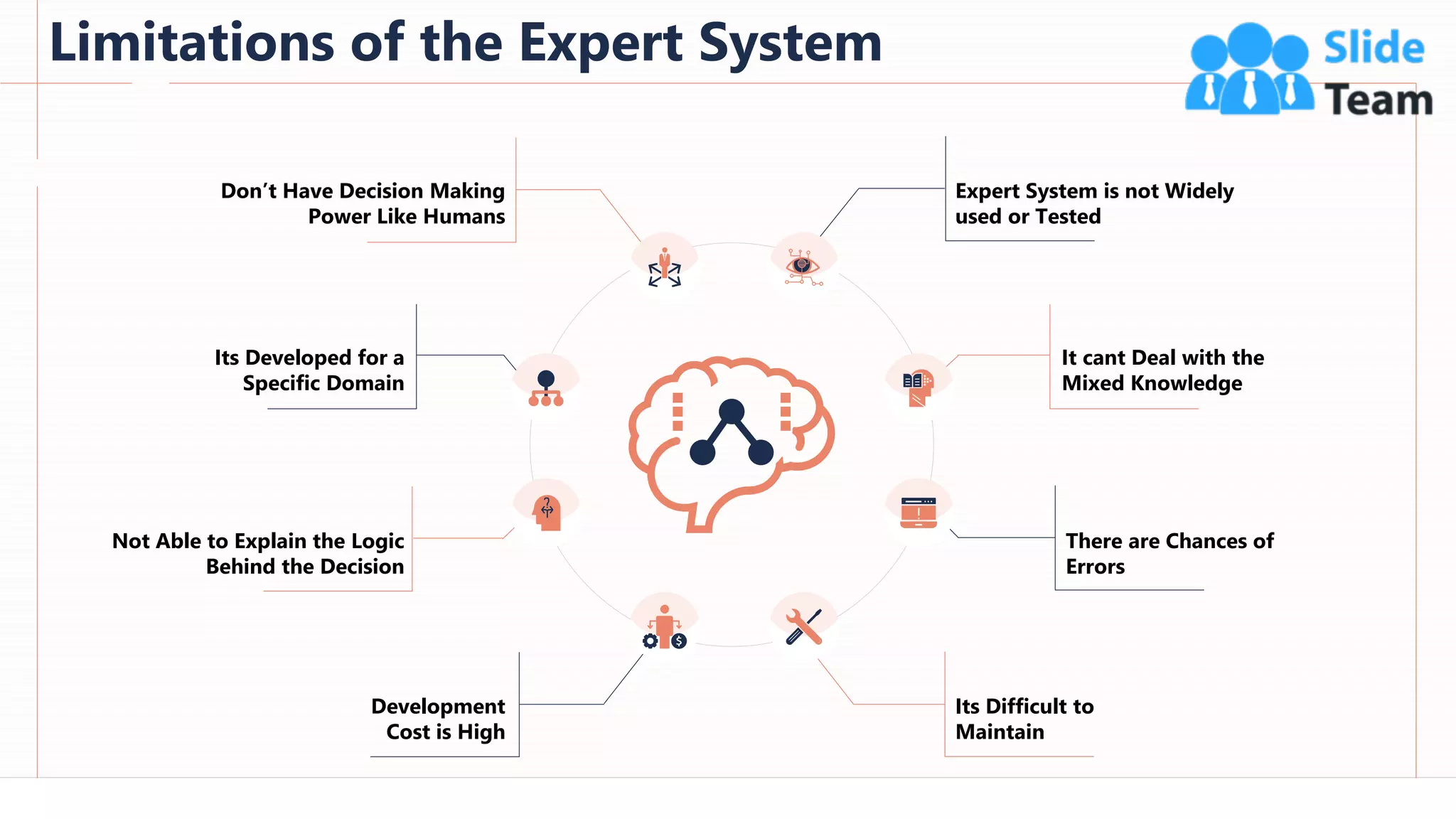
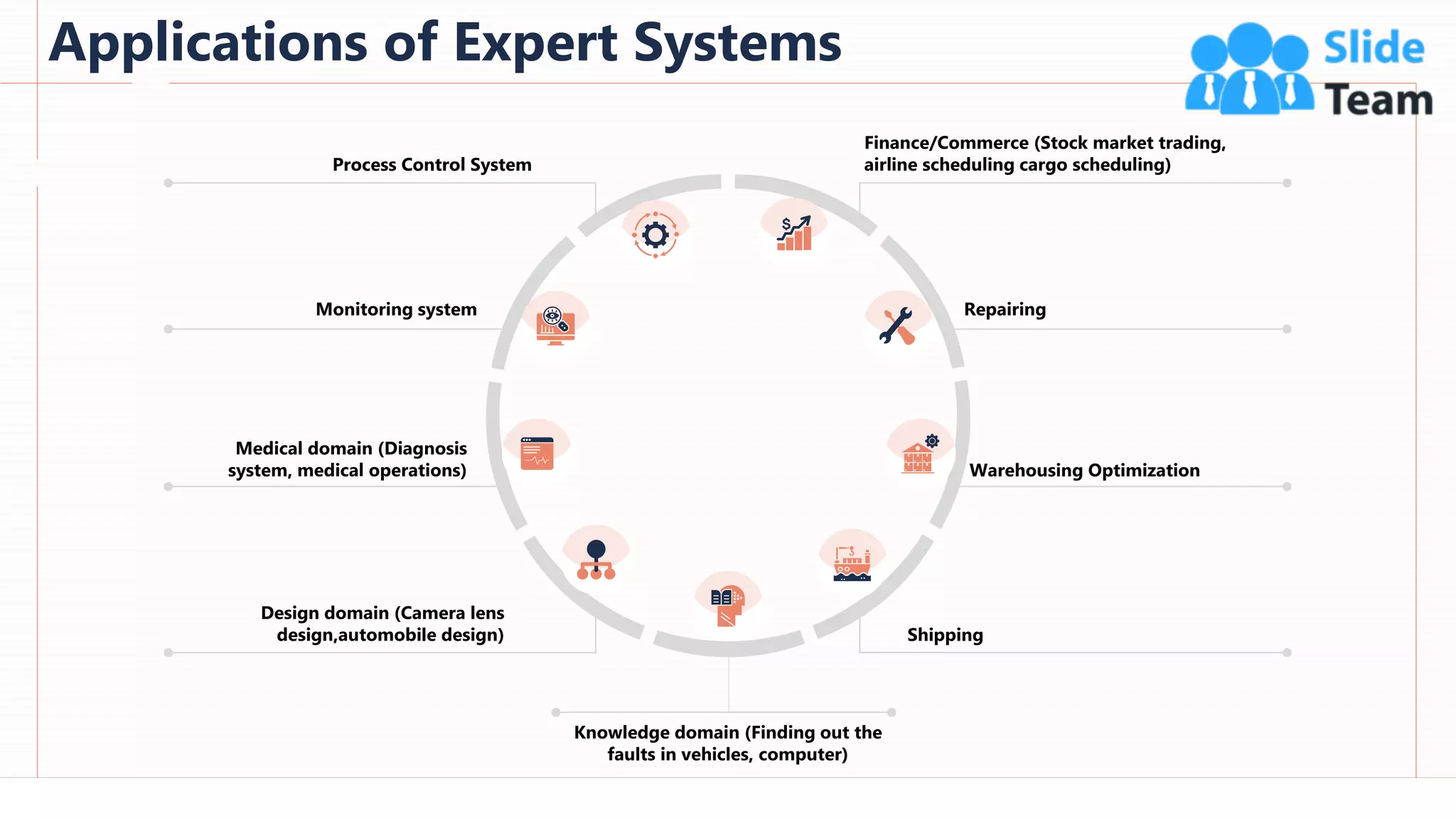
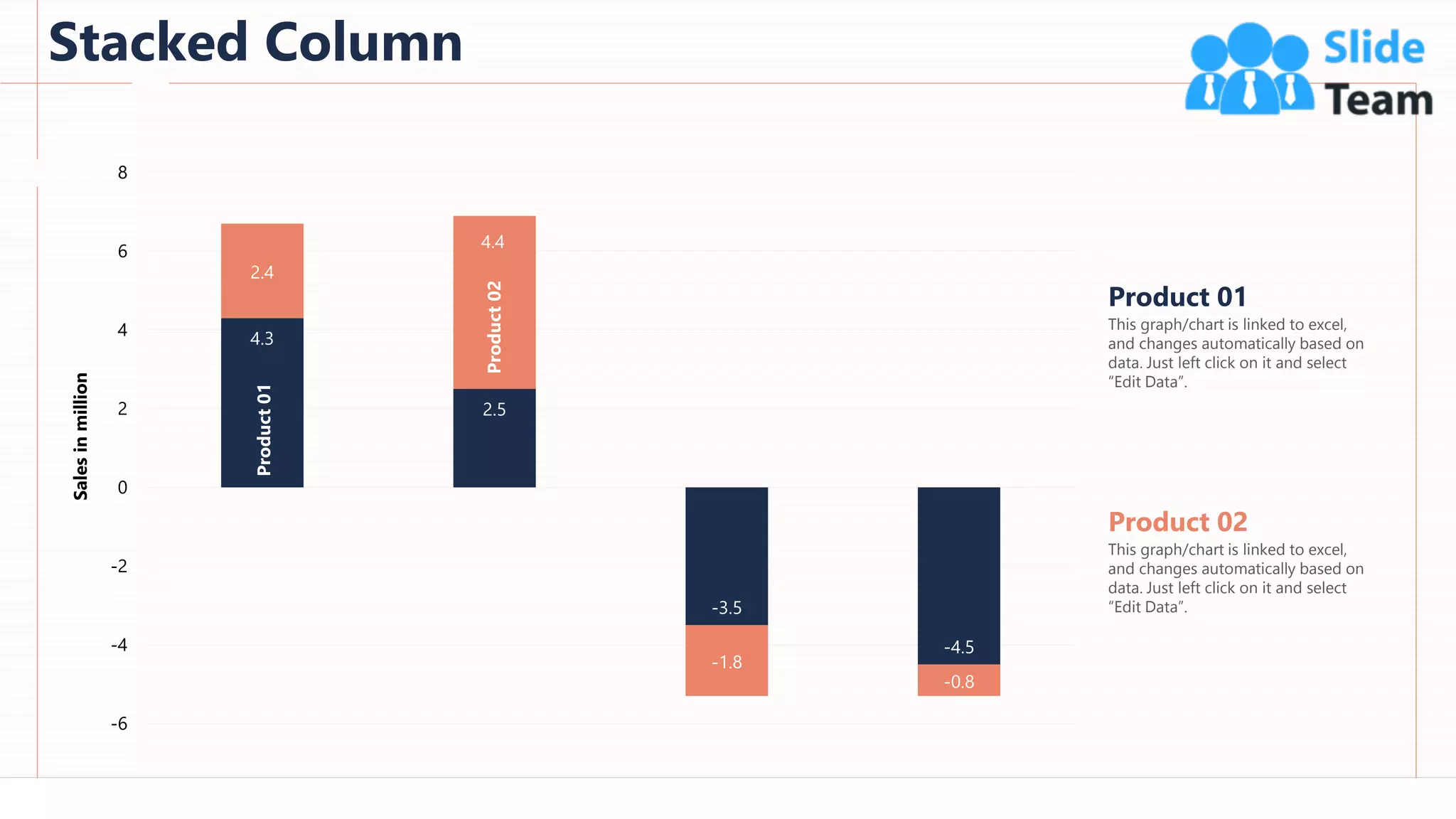
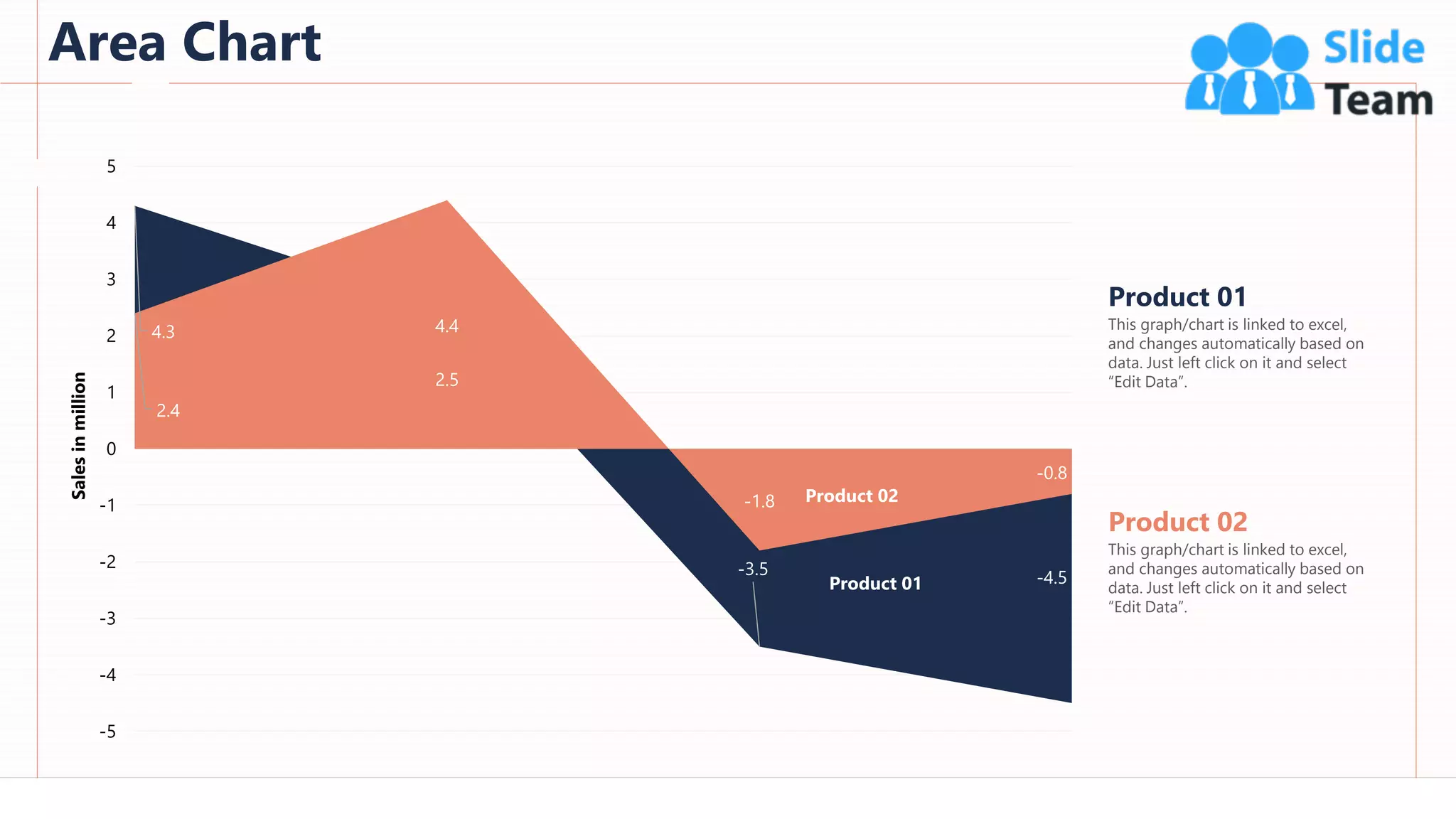
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL), covering definitions, processes, algorithms, and applications in various fields. It details the concepts of supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, comparing traditional programming with machine learning approaches. Additionally, it discusses the importance of AI and its trends, particularly in the context of advancements seen in 2020.