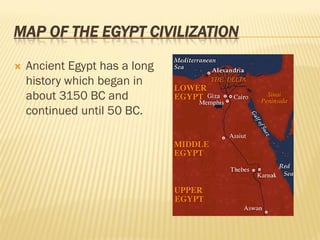
Ancient Egypt had a civilization that began around 3150 BC and lasted until 50 BC. The document provides details about various aspects of ancient Egyptian society such as its social structure, housing, food, family life, education, religion, and arts. It describes how Egyptian social structure was hierarchical with gods and pharaohs at the top and slaves at the bottom. Housing was typically made of mud bricks, while foods varied between rich and poor. Religion played a central role in Egyptian life and they had many gods. The arts included sculpture, painting, music and architecture.