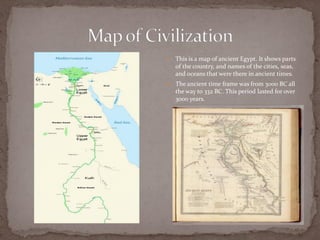
Ancient Egypt was famous for mummifying their kings and important people to preserve their bodies for the afterlife. They built elaborate pyramids, like the Great Pyramid of Giza, to serve as tombs for pharaohs and other nobles. Egyptian society was strictly stratified, with pharaohs and nobles at the top, peasants and slaves at the bottom. Women had some rights but less opportunities than men. Children learned skills from their parents to take on roles in society, and the ancient Egyptians had rich cultural and religious practices that lasted for over 3000 years.