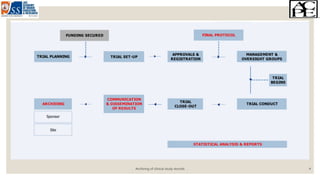
The document discusses the importance and processes involved in the archiving of clinical study records, highlighting regulatory requirements for sponsors to retain essential documents for specific durations. It outlines types of archiving, key documents to be archived, and strategies for effective document management, including disaster recovery plans. The document also mentions various software options for archiving and emphasizes the confidentiality and accessibility of archived materials.