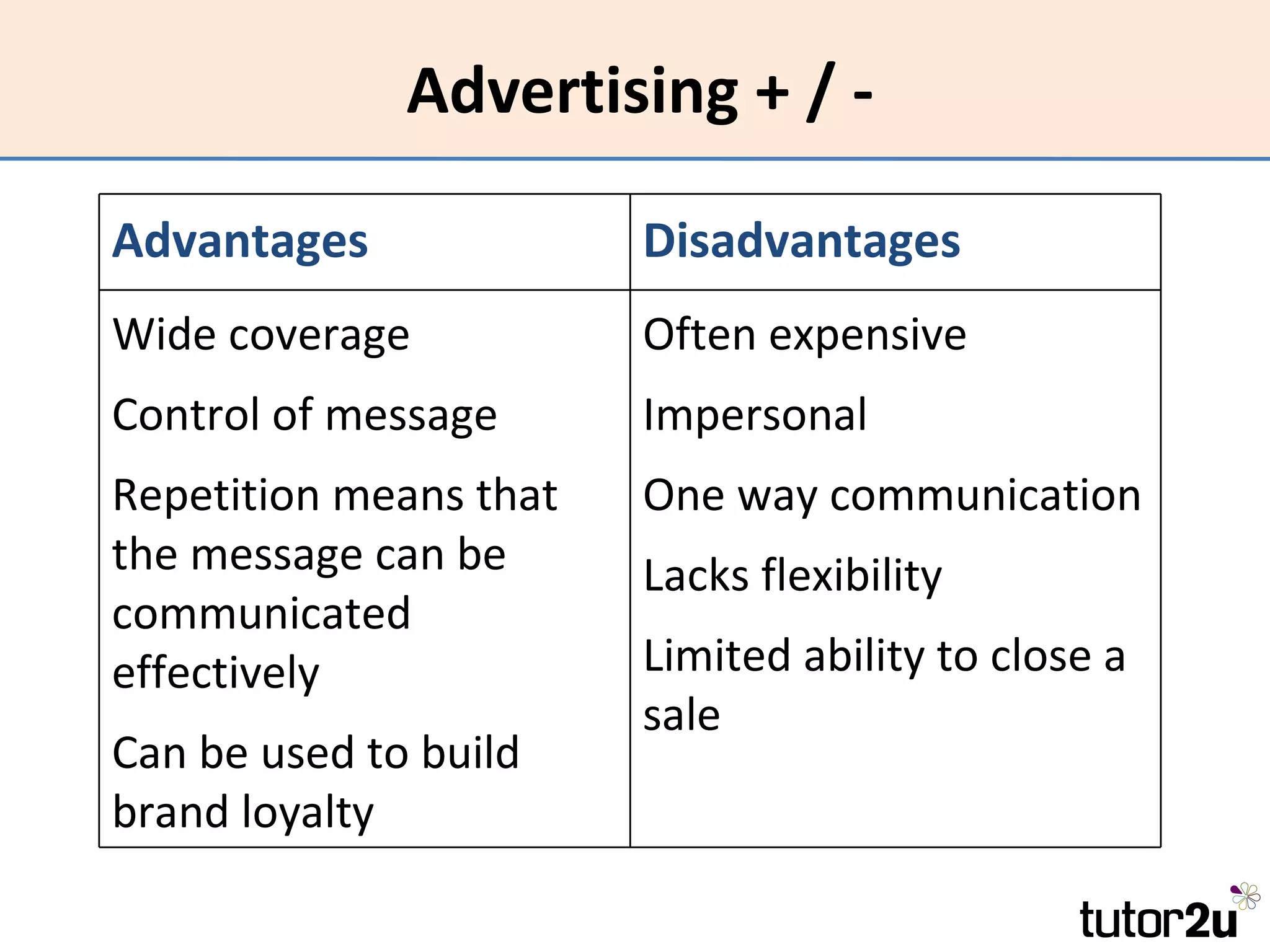
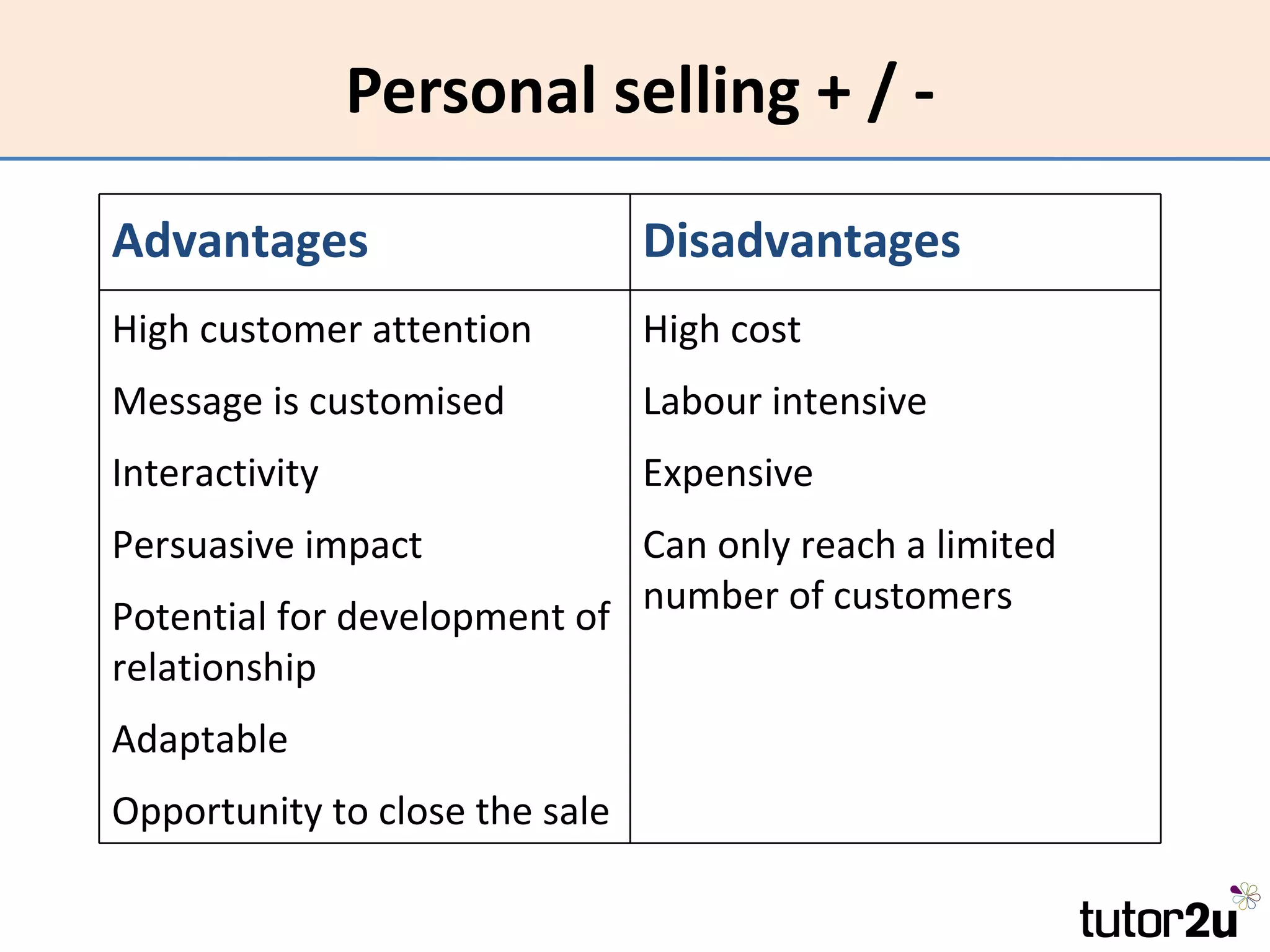
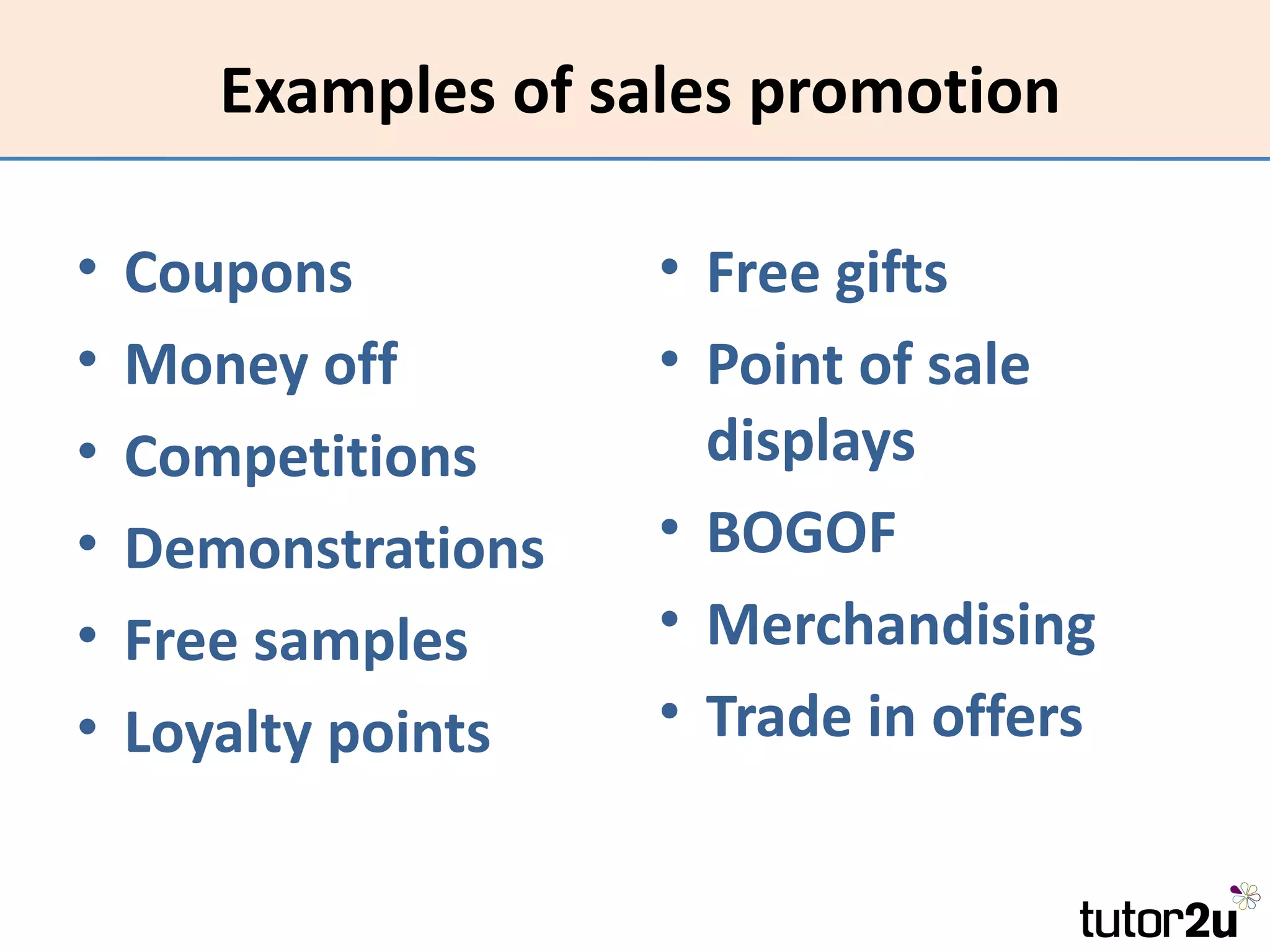
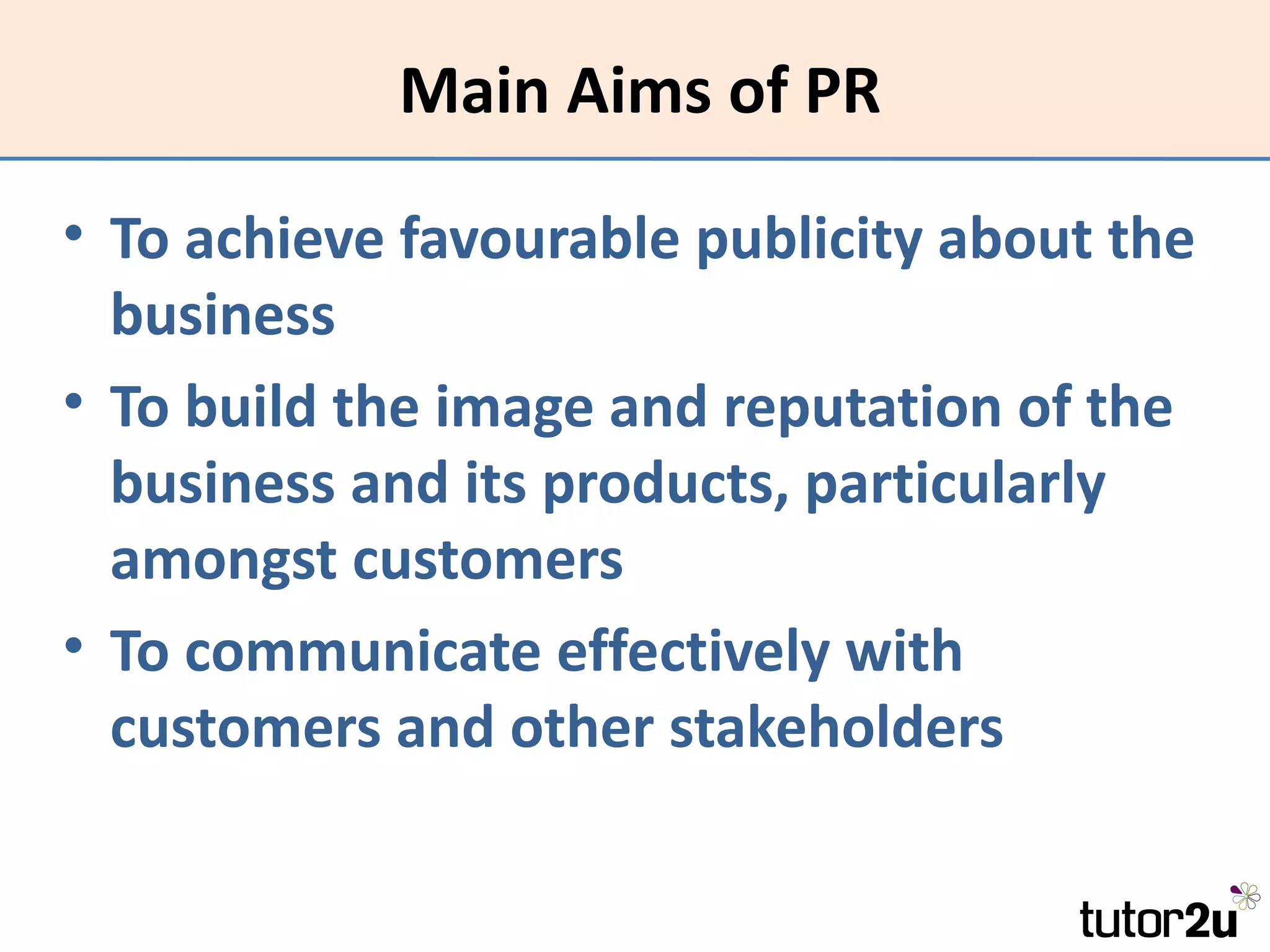
Promotion involves communicating with customers to inform, influence, and persuade them to buy a product. The promotional mix includes advertising, sales promotions, personal selling, public relations, direct marketing, and merchandising. The optimal promotional mix depends on the product's life cycle, nature, competition, marketing budget, strategy, and target market. Promotion aims to increase awareness, change attitudes, and encourage purchase. Effectiveness is measured by whether objectives are achieved, while efficiency considers objectives achieved relative to costs.