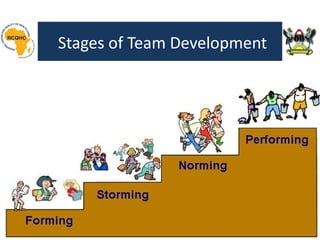
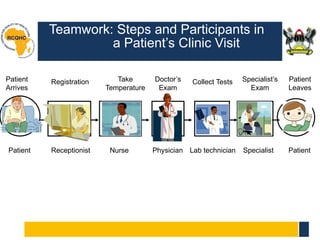
The document outlines the four stages of team development—forming, storming, norming, and performing—highlighting the characteristics and critical skills needed at each stage. It emphasizes the importance of teamwork in healthcare for quality improvement and outlines considerations for selecting team members and the roles of leaders. Additionally, the document details responsibilities for leaders before, during, and after quality improvement projects to ensure team effectiveness and integration of changes.