Recommended
PPT
Cp 50 10-18 1 congenital & acquired ha
PPT
PDF
Clinical practice guideline_of_anemia(cpg)
PPT
PPT
PPT
PDF
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
Cp 50 10-18 4 talk lab - class slide ha
PPT
PDF
PDF
โปรแกรมตรวจสุขภาพ 13 รายการ 999 บาท
PPTX
2010_PMC Cardiovascular-Blood Disorder
PDF
PDF
Compre step 2_2010 si key
PPT
PPT
PPT
Thalassemia screening in pregnancy, Quality improvement and Evidence based pr...
PPT
Transfusion and complications 2011
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
Cpg thalassemia 2014-content
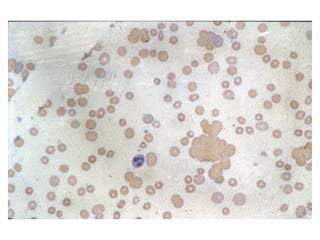
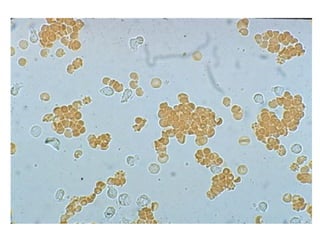
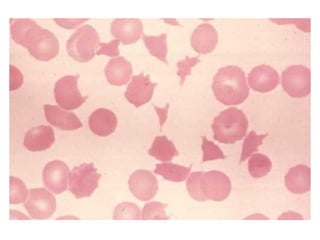
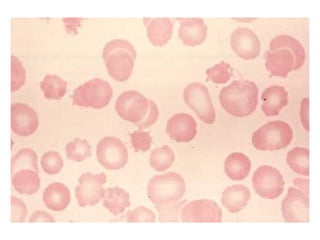
PDF
Cpg thalassemia 2014-content 2
PDF
PDF
More Related Content
PPT
Cp 50 10-18 1 congenital & acquired ha
PPT
PDF
Clinical practice guideline_of_anemia(cpg)
PPT
PPT
PPT
PDF
PPT
Similar to Approach to acute anemia
PPT
PPT
PPT
Cp 50 10-18 4 talk lab - class slide ha
PPT
PDF
PDF
โปรแกรมตรวจสุขภาพ 13 รายการ 999 บาท
PPTX
2010_PMC Cardiovascular-Blood Disorder
PDF
PDF
Compre step 2_2010 si key
PPT
PPT
PPT
Thalassemia screening in pregnancy, Quality improvement and Evidence based pr...
PPT
Transfusion and complications 2011
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
Cpg thalassemia 2014-content
PDF
Cpg thalassemia 2014-content 2
More from Loveis1able Khumpuangdee
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
DOC
PDF
PDF
PDF
PDF
แนวทางการดาเน ํ นงานป ิ องก ้ นควบค ั มการระบาดของโรคม ุ ือ เท้า ปาก สําหรบแพ...
PDF
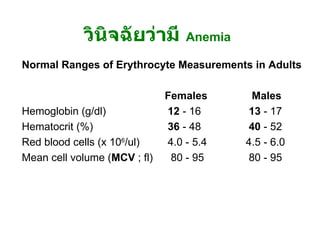
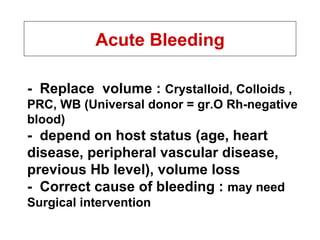
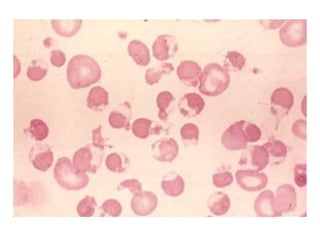
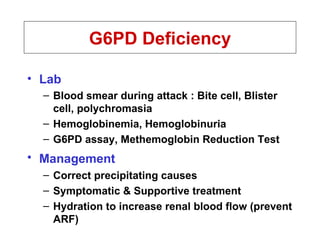
Approach to acute anemia 1. 2. วินิจฉัยว่ามี Anemia อาการ - ซีด เพลีย เหนื่อยง่าย หน้ามืด เวียนศีรษะ ขาดสมาธิ เบื่ออาหาร decreased libido, organ hypoxia (angina in patients with CAD, worsening dementia / intermittent claudication ) อาการแสดง - Pallor of skin & mucous membrane, modest tachycardia, increased pulse pressure, postural hypotension (acute blood loss), systolic ejection murmur, mild peripheral edema, retinal hemorrhage (severe anemia) 3. Normal Ranges of Erythrocyte Measurements in Adults Females Males Hemoglobin (g/dl) 12 - 16 13 - 17 Hematocrit (%) 36 - 48 40 - 52 Red blood cells (x 10 6 /ul) 4.0 - 5.4 4.5 - 6.0 Mean cell volume ( MCV ; fl) 80 - 95 80 - 95 วินิจฉัยว่ามี Anemia 4. ผู้ป่วยหญิงไทยคู่ อายุ 26 ปี ปวดท้อง 1 วัน และมีอาการหน้ามืดคล้ายจะเป็นลม 2 ชั่วโมงก่อนมาโรงพยาบาล ไม่มีเลือดออกที่ใด ผู้ป่วยไม่มีประจำเดือนมา 2 เดือน การตรวจร่างกาย BP 90/60 mmHg, P 120/min GA : drowsiness, markedly pale, mild jaundice, no petechiae or ecchymosis, no cyanosis Abdomen - soft, mildly generalized tenderness, no guarding PR - no melena CBC : Hb 7 g/dL, Hct 21%, Wbc 13,000/mm3, Platelet 260,000/mm3 ; Polychromasia 2+ จงให้การวินิจฉัย และการรักษา 5. Internal Bleeding Abdominal Trauma Tearing or rupture of Liver , spleen Local Intraabdominal pathology Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy Ruptured Hepatoma GI Bleeding Underlying bleeding disorders Retroperitoneal hemorrhage 6. 7. Acute Bleeding - Replace volume : Crystalloid, Colloids , PRC, WB (Universal donor = gr.O Rh-negative blood) - depend on host status (age, heart disease, peripheral vascular disease, previous Hb level), volume loss - Correct cause of bleeding : may need Surgical intervention 8. ผู้ป่วยชายอายุ 22 ปี มีไข้ปวดเมื่อย 5 วัน ปัสสาวะสีเข้ม 3 วัน และเริ่มอ่อนเพลีย เหนื่อยง่าย การตรวจร่างกาย T 38 o c, BP 100/60 , P 110 Alert, moderately pale, mild jaundice, no edema Liver just palpable, spleen not palpable No lymphadenopathy CBC : Hb 5.5 g/dl, Hct 17 %, Wbc 5000 , Platelet 120,000 จงให้การวินิจฉัย และการรักษา 9. 10. G6PD Deficiency X-linked recessive Clinical Neonatal jaundice acute hemolytic anemia : Drug (primaquine, sulfa, dapsone), infection ; beware of acute renal failure Exaggerated jaundice in acute viral hepatitis 11. Lab Blood smear during attack : Bite cell, Blister cell, polychromasia Hemoglobinemia, Hemoglobinuria G6PD assay, Methemoglobin Reduction Test Management Correct precipitating causes Symptomatic & Supportive treatment Hydration to increase renal blood flow (prevent ARF) G6PD Deficiency 12. 13. Clinical approach to patients with suspected hemolysis History Onset/duration (hereditary versus acquired) History of fatigue History of jaundice Abdominal pain/ cholelithiasis (chronic hemolysis) Medications (may exacerbate enzyme def.) Travel (consider malaria) Infection Vascular/cardiac surgery History of blood transfusion Blood loss (DDx of anemia with reticulocytosis) Discolored urine Complete family history (jaundice, gall stone, splenectomy, hereditary anemia) 14. History Physical Exam Pallor Increased temperature Rapid pulse Jaundice Thalassemic face Mechanical click from prosthetic valve SLE signs Splenomegaly Clinical approach to patients with suspected hemolysis 15. History & Physical Exam Screening Lab CBC , blood smear , Absolute reticulocyte count Haptoglobin (decreased), LDH (elevated), Indirect bilirubin Clinical approach to patients with suspected hemolysis 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. History & Physical Exam Screening Lab CBC , blood smear , Absolute reticulocyte count Haptoglobin (decreased), LDH (elevated), Indirect bilirubin Further lab Direct Coombs’ test, Inclusion body (HbH) Intravascular – Hemoglobinemia, Hb.uria, Hemosiderinuria G6PD, osmotic fragility, Blood bank consultation Clinical approach to patients with suspected hemolysis 22. 23. Conditions mistaken for hemolytic anemia Anemia and unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia without reticulocytosis Internal bleeding Ineffective erythropoiesis 24. 25. Conditions mistaken for hemolytic anemia Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia without anemia or reticulocytosis Gilbert syndrome Crigler-Najjar Neonates 26. 27. Conditions mistaken for hemolytic anemia Anemia and reticulocytosis without unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia Bleeding Recovery from aplastic or nutritional anemia (iron, vit.B12, folate) 28. Myobloginuria Dark urine No hemoglobinemia Normal haptoglobin Elevated muscle enzyme: CPK Conditions mistaken for hemolytic anemia 29. 30. หาสาเหตุของ Anemia การแบ่งชนิดของ Anemia * แบ่งตาม pathogenesis - Disorders of erythrocyte production - Acute bleeding - Hemolysis * แบ่งตามขนาดเม็ดเลือดแดง - Microcytic anemia (MCV < 80 fl) - Normocytic anemia (MCV 80-100 fl) - Macrocytic anemia (MCV > 100 fl) 31. แบ่งตาม pathogenesis Disorders of RBC production Hypoproliferative anemia Stem cell : aplastic anemia(AA), pure red cell aplasia(PRCA), Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) drug, chemicals, radiation ขาดสารกระตุ้น เช่น Chronic renal failure, hypothyroidism Myelophthisis - leukemia, lymphoma, metastatic tumor, disseminated TB/Fungus, myelofibrosis (MF) Iron deficiency, anemia of inflammation Maturation defects Thalassemias, sideroblastic anemia Megaloblastic anemia ( ขาด folate, vitamin B12 ) 32. Acute bleeding Hemolysis Intracorpuscular defects Hereditary - Membrane defects : hereditary spherocytosis - Enzyme defects : G-6PD deficiency - Globin defects : Thalassemia, Hemoglobinopathy Acquired : PNH ( paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria ) Extracorpuscular defects Immune hemolysis : AIHA, hemolytic transfusion reaction Infections : malaria, clostridial infection Microangiopathy : TTP / HUS Drug or chemicals : lead poisoning แบ่งตาม pathogenesis 33. Microcytic anemia Iron def., Thalassemia, anemia of chronic disease ( บางราย ), sideroblastic anemia Normocytic anemia Primary marrow disorders (AA, PRCA,MDS,Myelophthisis,MF), anemia of chronic disease, CRF, Mild iron deficiency, acute bleeding, hemolysis ( ยกเว้น thalassemia), endocrine disorders Macrocytic anemia Megaloblastic anemia, liver disease, alcoholism, reticulocytosis, primary marrow disorders บางราย , drugs(AZT,MTX,chemotherapy), hypothyroidism บางราย แบ่งตามขนาดเม็ดเลือดแดง (MCV) 34. แบ่งชนิด Anemia ตาม Onset Acute anemia ( ภายใน 1 สัปดาห์ ) Acute blood loss Acute hemolysis Chronic anemia Iron def. anemia, megaloblastic anemia Anemia of chronic disease, CRF, hypothyroidism Primary marrow disorders Thalassemia, PNH 35. การซักถามประวัติเพื่อหาสาเหตุ ข้อมูลทั่วไป - เพศ , อายุ , อาชีพ , เศรษฐฐานะ Onset of anemia : acute , chronic , การได้รับเลือดในอดีต ประวัติชี้แนะสาเหตุ anemia Blood loss : melena, hematemesis, hemorrhoids, hypermenorrhea Precipitating : fever -> anemia, ปัสสาวะสีเข้ม , jaundice (HbH,HS,G-6 PD def.) WBC ต่ำ , Plt. ต่ำ : จุดจ้ำเลือด , ติดเชื้อบ่อย , bleeding (BM dis.,SLE,HIV,TTP) อาการของ anemia บางชนิด : dark urine (G-6 PD def, PNH), แสบลิ้น ( glossitis) อาการของโรคระบบต่างๆ : CRF, SLE, Hypothyroidism, TB, Cancer , MM Drug : induce PU, hemolysis in G-6 PD def, Alcohol การผ่าตัดทางเดินอาหาร / chronic diarrhea - vit.B12, Iron, folate def. ประวัติซีดในครอบครัว : Thalassemia 36. การตรวจร่างกาย V/S : postural hypotension (acute bl. loss), hypertension (CRF), Fever (Inf.,leukemia,SLE), bradycardia (hypothyroidism) GA : Jaundice (hemolysis,liver dis), Thalassemic facies, edema(CRF,CHF), koilonychia (Fe def), myxedema, malar rash/DLE /oral ulcer/polyarthritis (SLE), oral thrush/OHL/PPE (HIV), Glossitis (Fe, B12 def), petechiae (plt ต่ำ ) , signs of chronic liver disease splenomegaly (extravascular hemolysis, portal hypertension, Inf.,leukemia) Lymphadenopathy (HIV, neoplasm, SLE, TB) PR - melena, rectal shelf, hemorrhoids, prostate gland 37. CBC & Blood smear MCV Reticulocyte count Blood smear - blast cell, leukoerythroblastic blood picture, fragmented red cell, spherocyte, autoagglutination, macro-ovalocyte, hypersegmented neutrophil, burr cell, target cell, tear drop cell, polychromasia, malaria 38. Further investigations Serum ferritin, Iron study - Fe def anemia -> หาสาเหตุ Fe def LDH, serum B12 level, folate level - Megaloblastic anemia LDH, Bilirubin, haptoglobin - hemolysis Coombs’ test - AIHA -> ANA Calcium, globulin, BUN/Cr, Urine Bence Jones, BM study, Film skull - Multiple myeloma Hemoglobin typing - thalassemia disease BUN / Cr , urine exam - CRF 39. Approach to Anemia History Physical examination CBC , MCV Blood smear Reticulocyte count Clinical diagnosis & decision making & initial management Further investigation