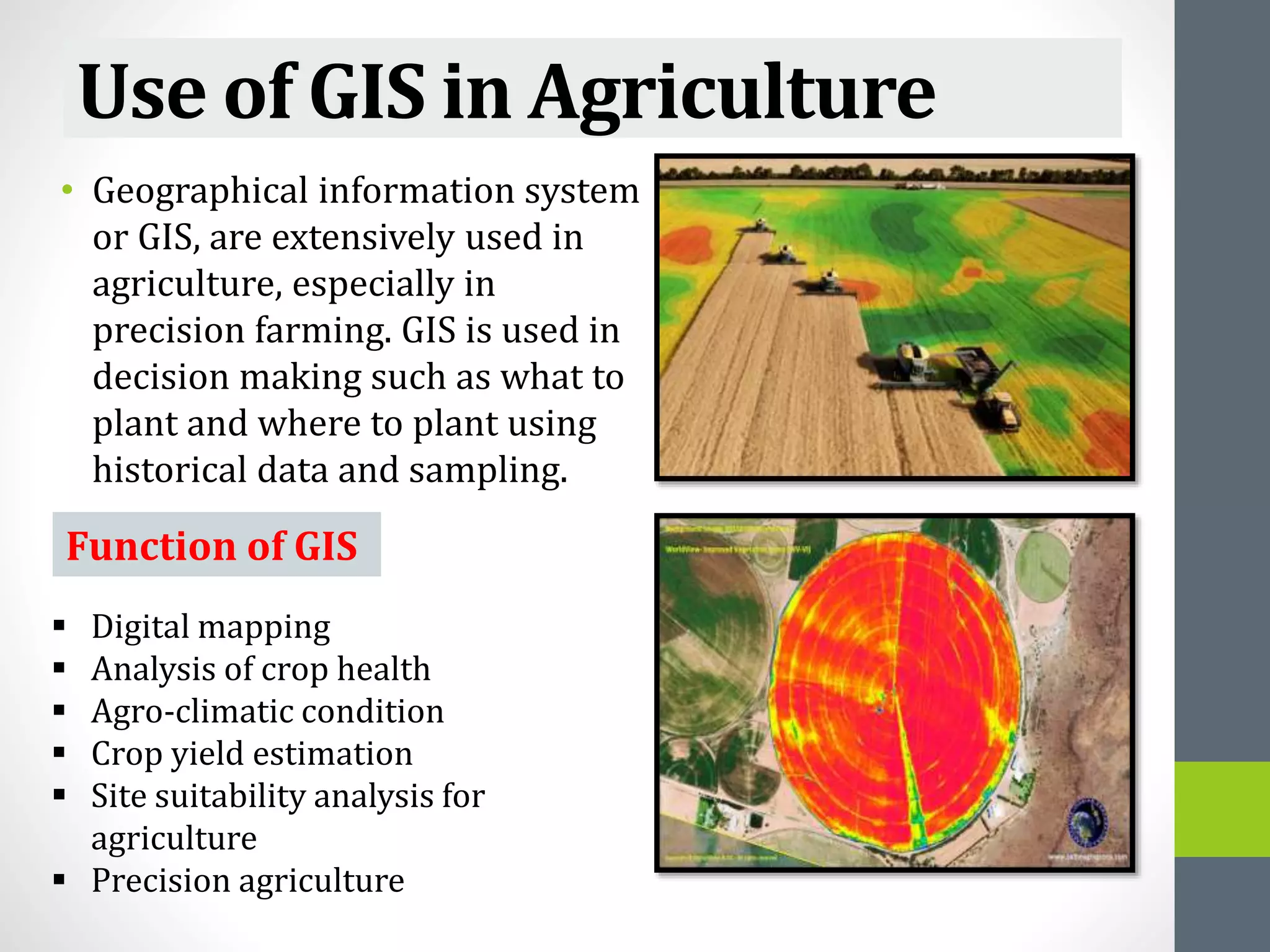
The document discusses the application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Indian agriculture, highlighting its importance in precision farming and addressing challenges like poor seed quality and inadequate water supply. It presents how GIS technologies enhance crop mapping, resource management, and decision-making while also noting obstacles such as connectivity issues and literacy levels among farmers. The conclusion emphasizes GIS's potential to improve farm management, market exposure, and incomes.