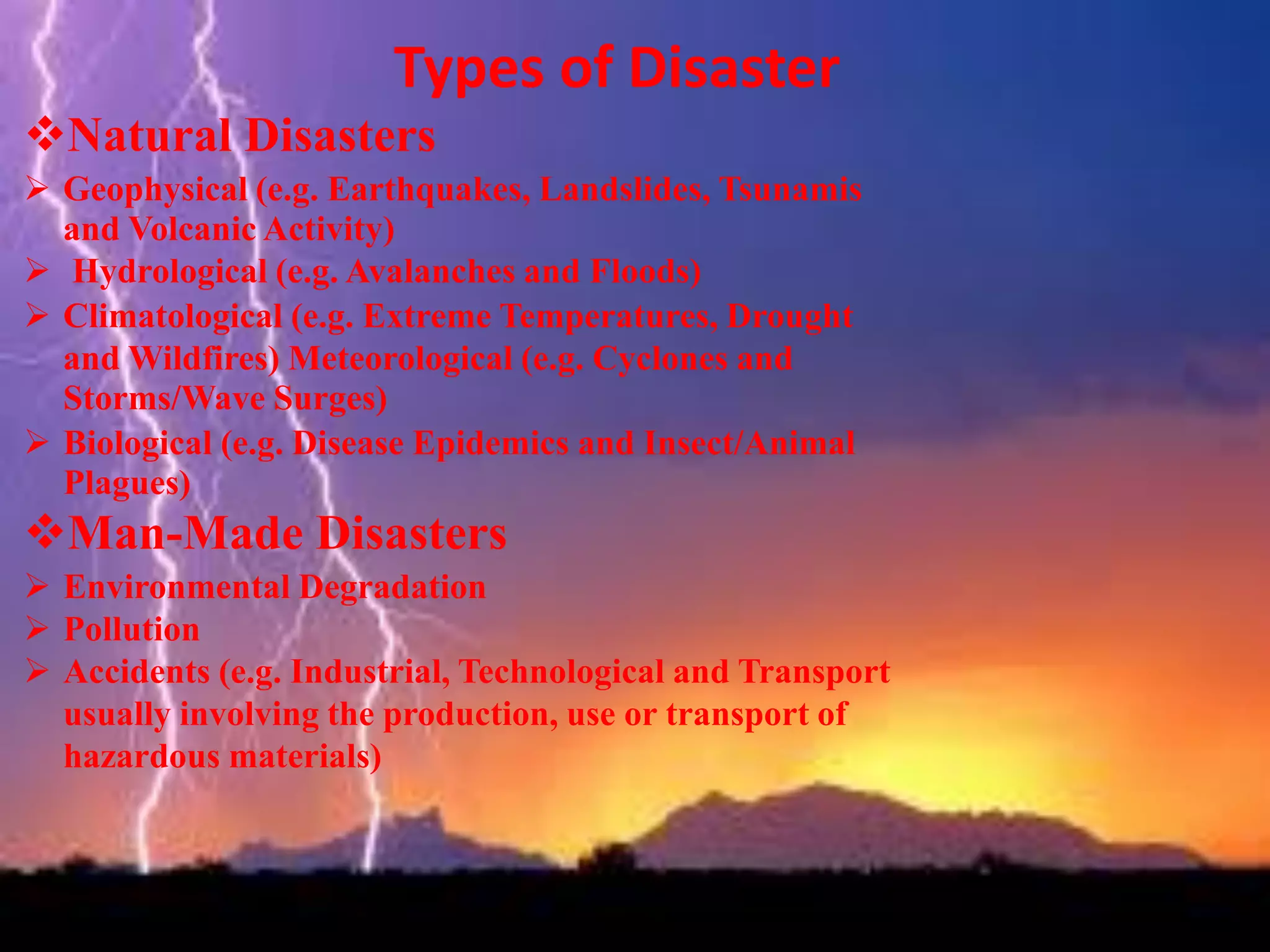
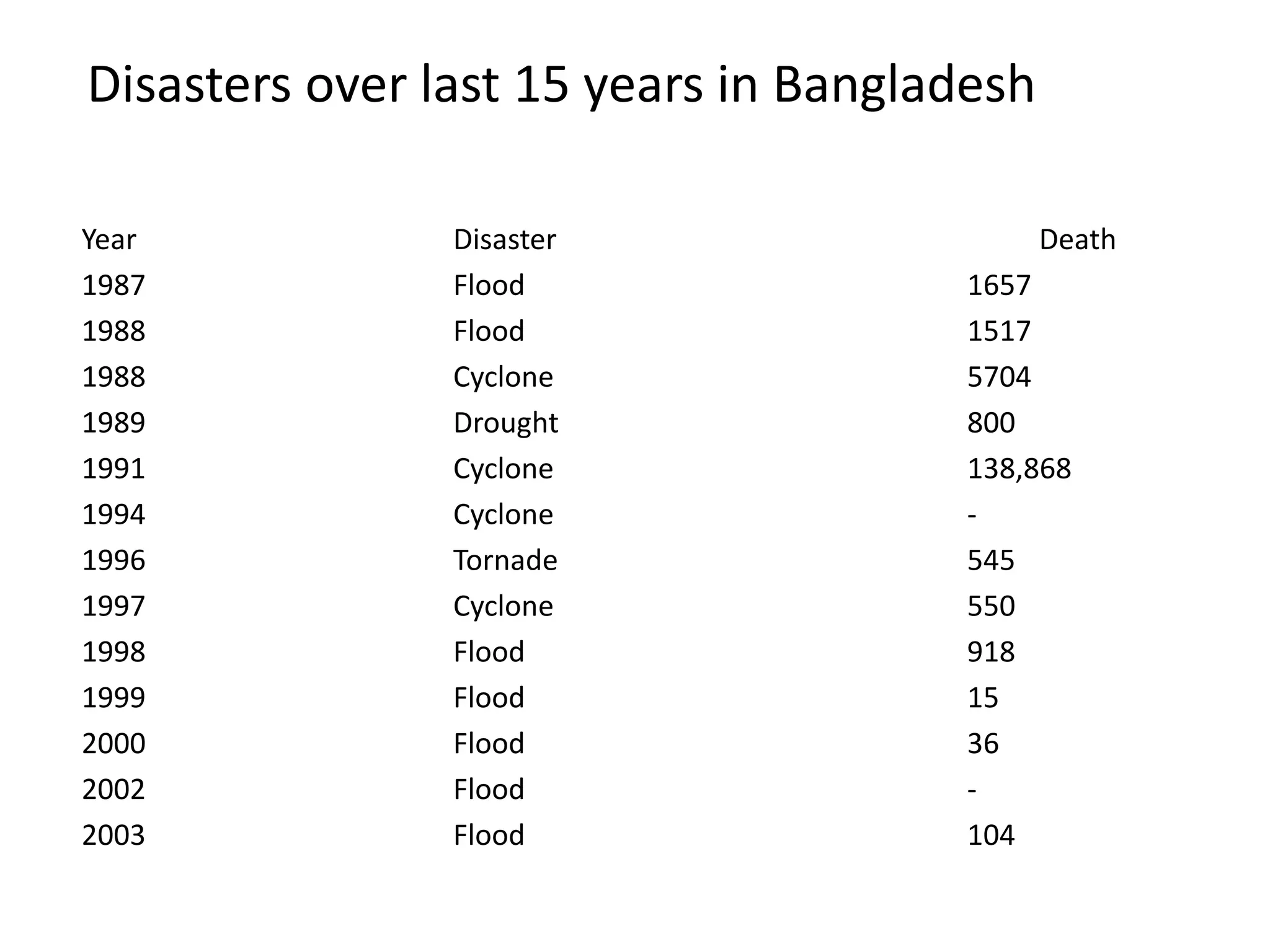
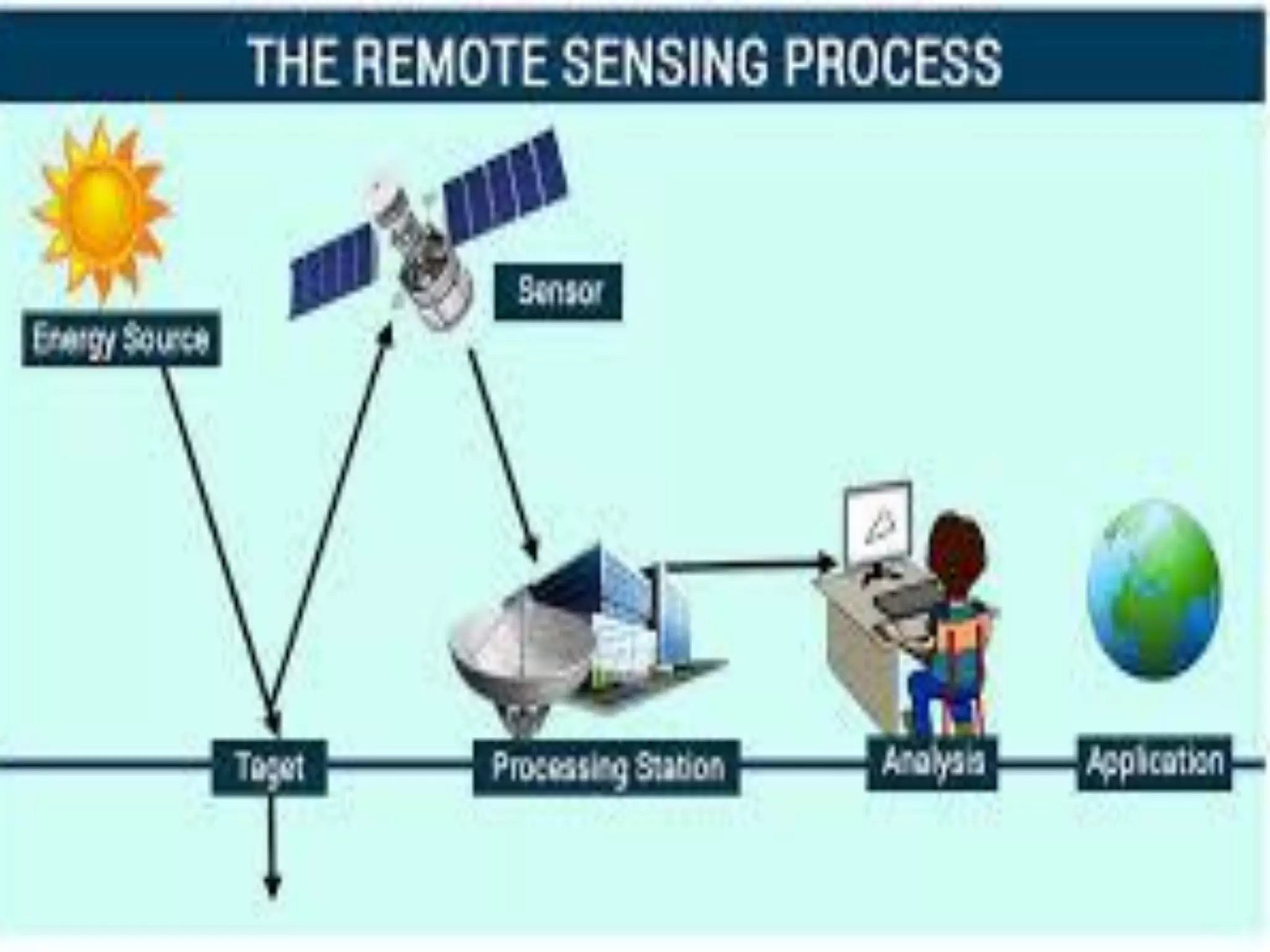
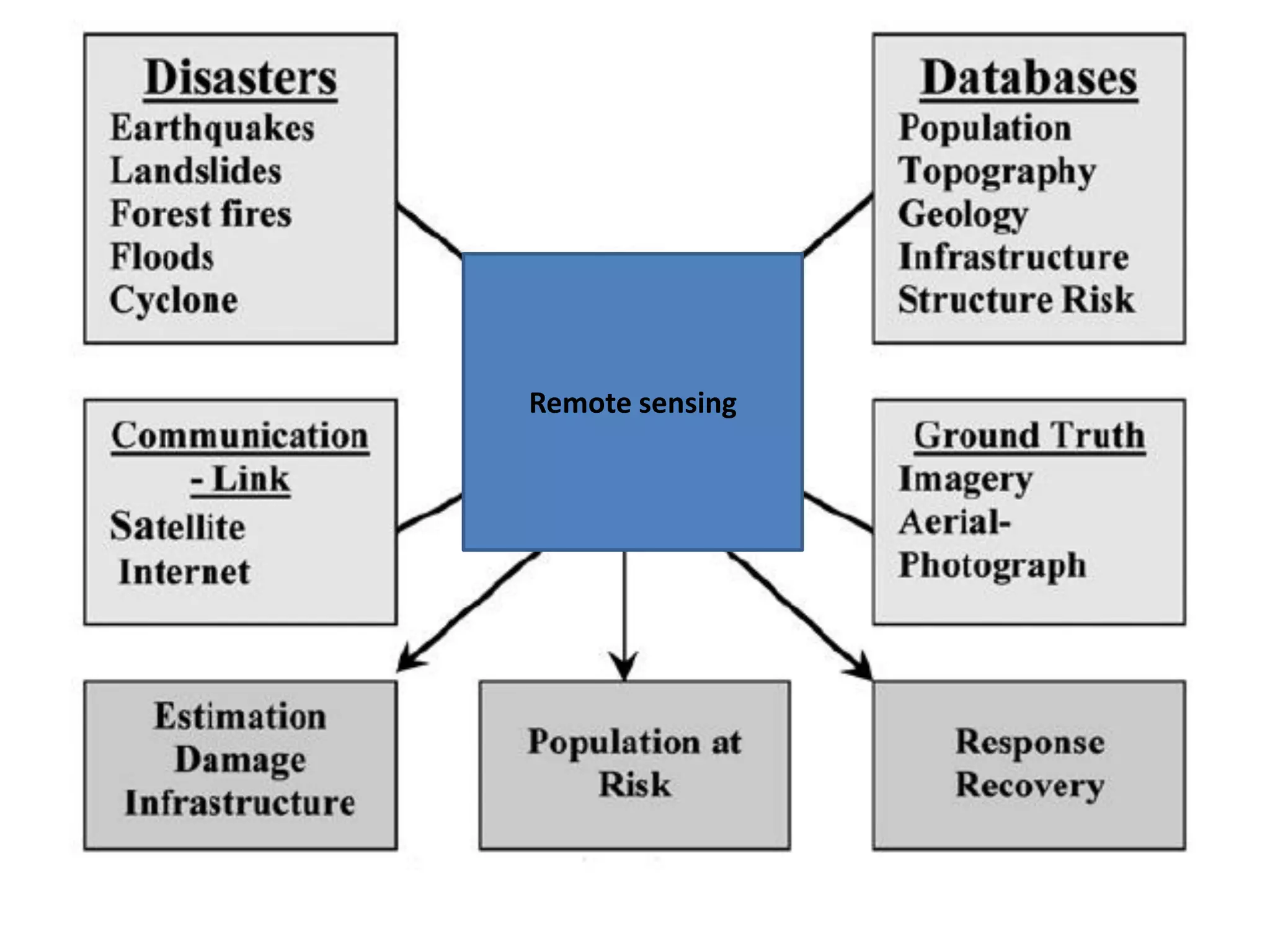
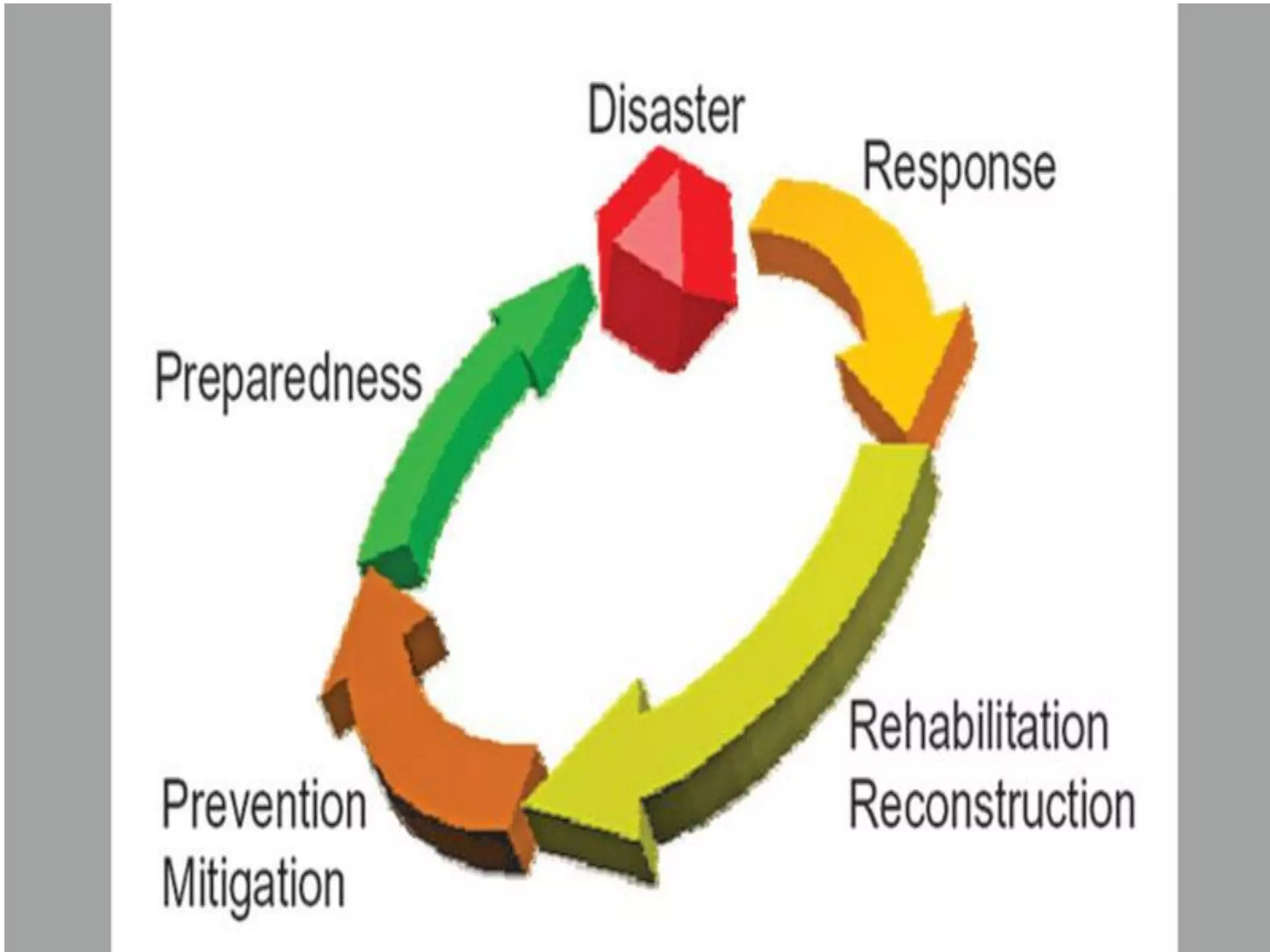
This document discusses the application of remote sensing in disaster management in Bangladesh. It outlines the types of natural and man-made disasters that occur in Bangladesh, including cyclones, floods, droughts and pandemics. It describes how remote sensing can be used for hazard mapping, early warning systems, monitoring of volcanoes and landslides, wildfire detection and disaster response and recovery efforts. Specific examples of remote sensing applications for cyclone and flood management in Bangladesh are provided.