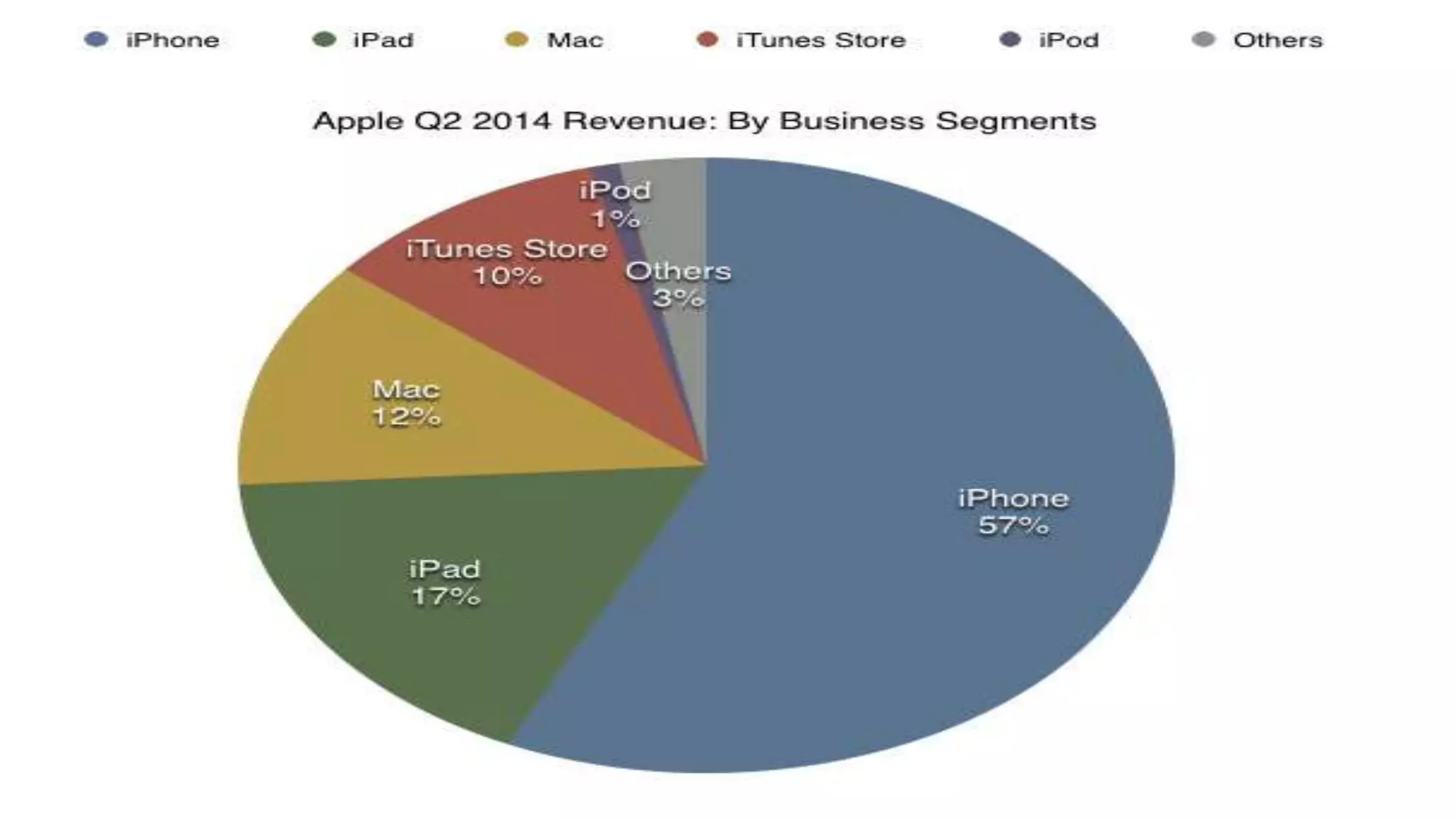
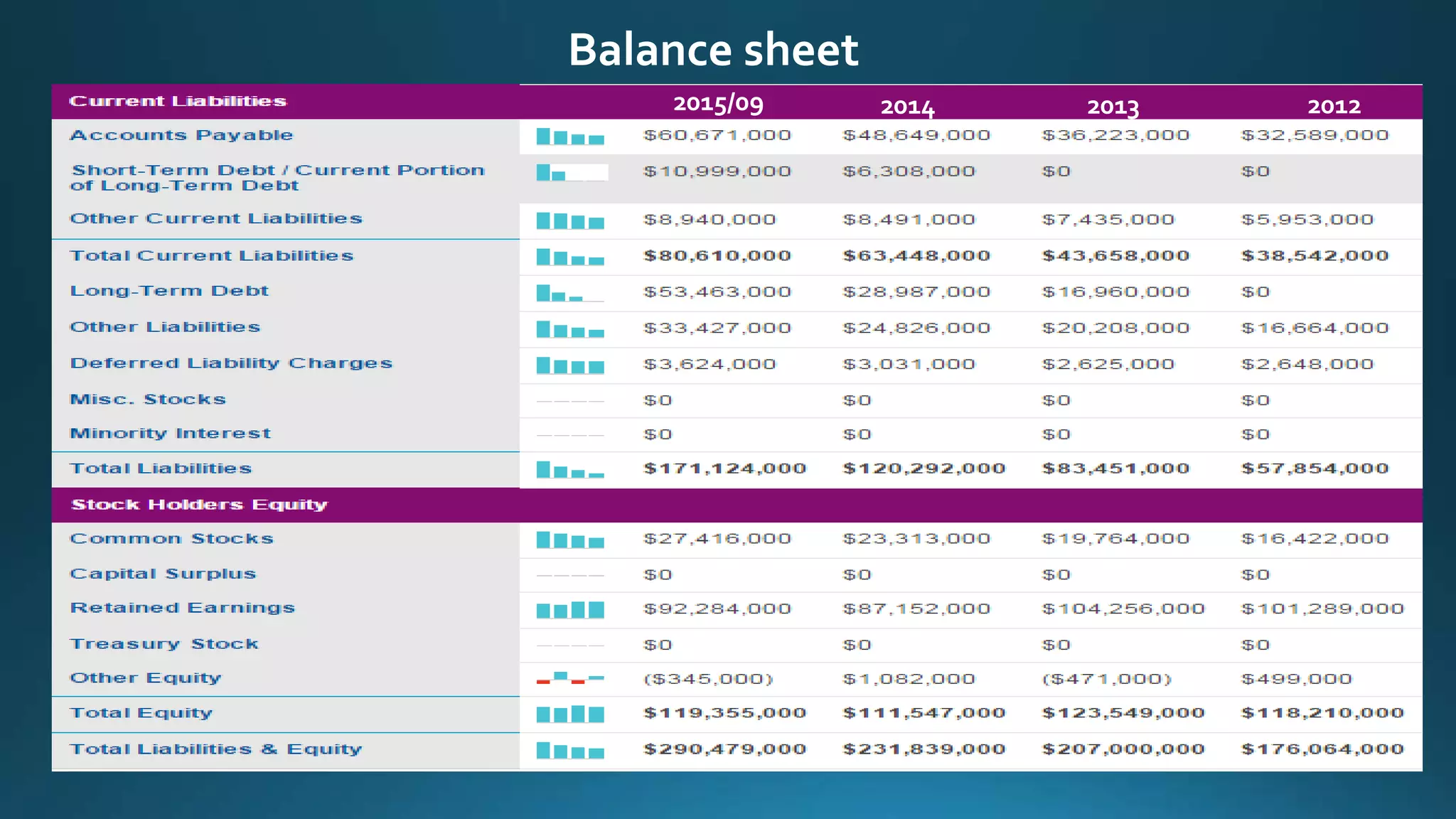
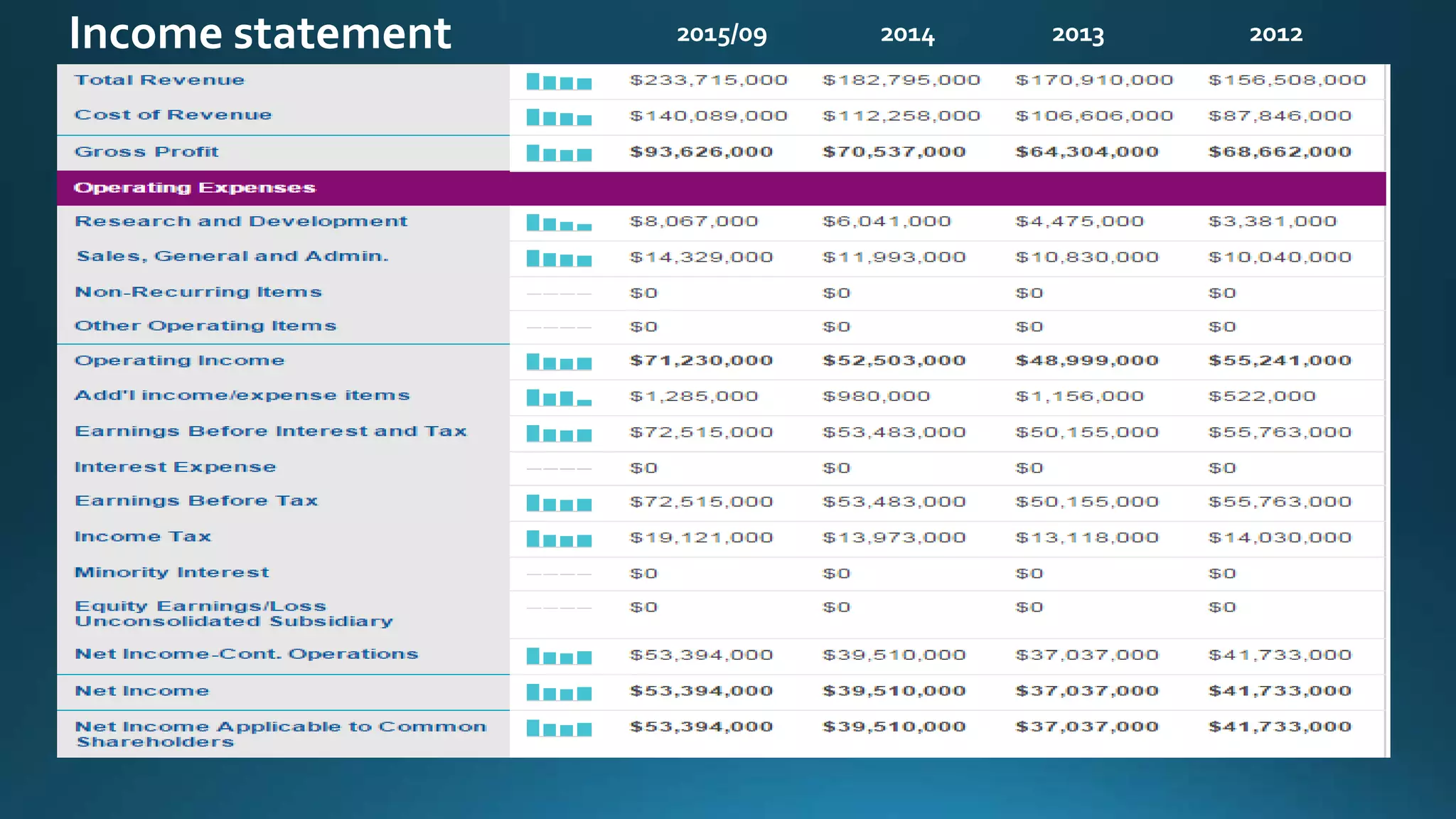
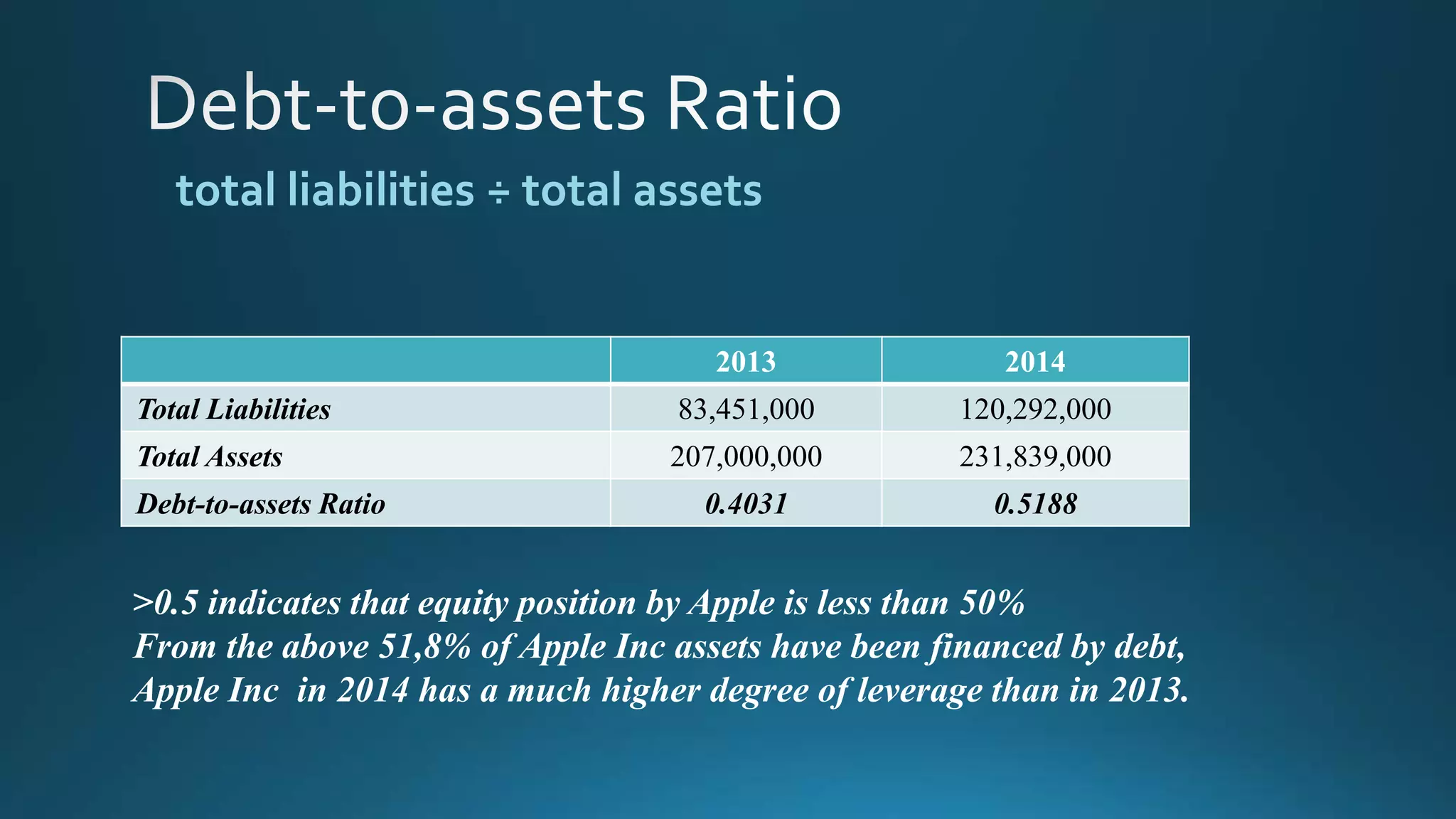
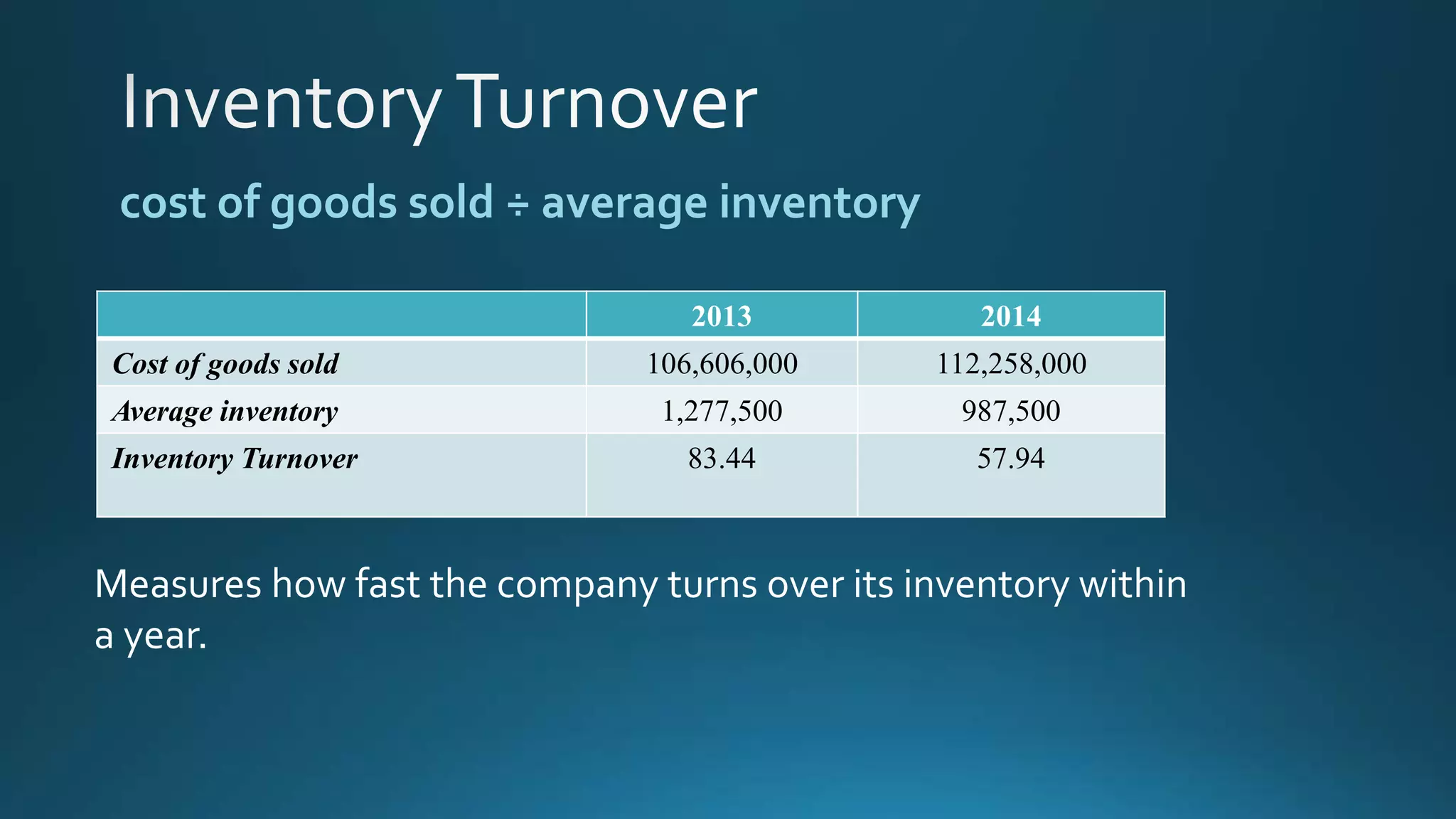
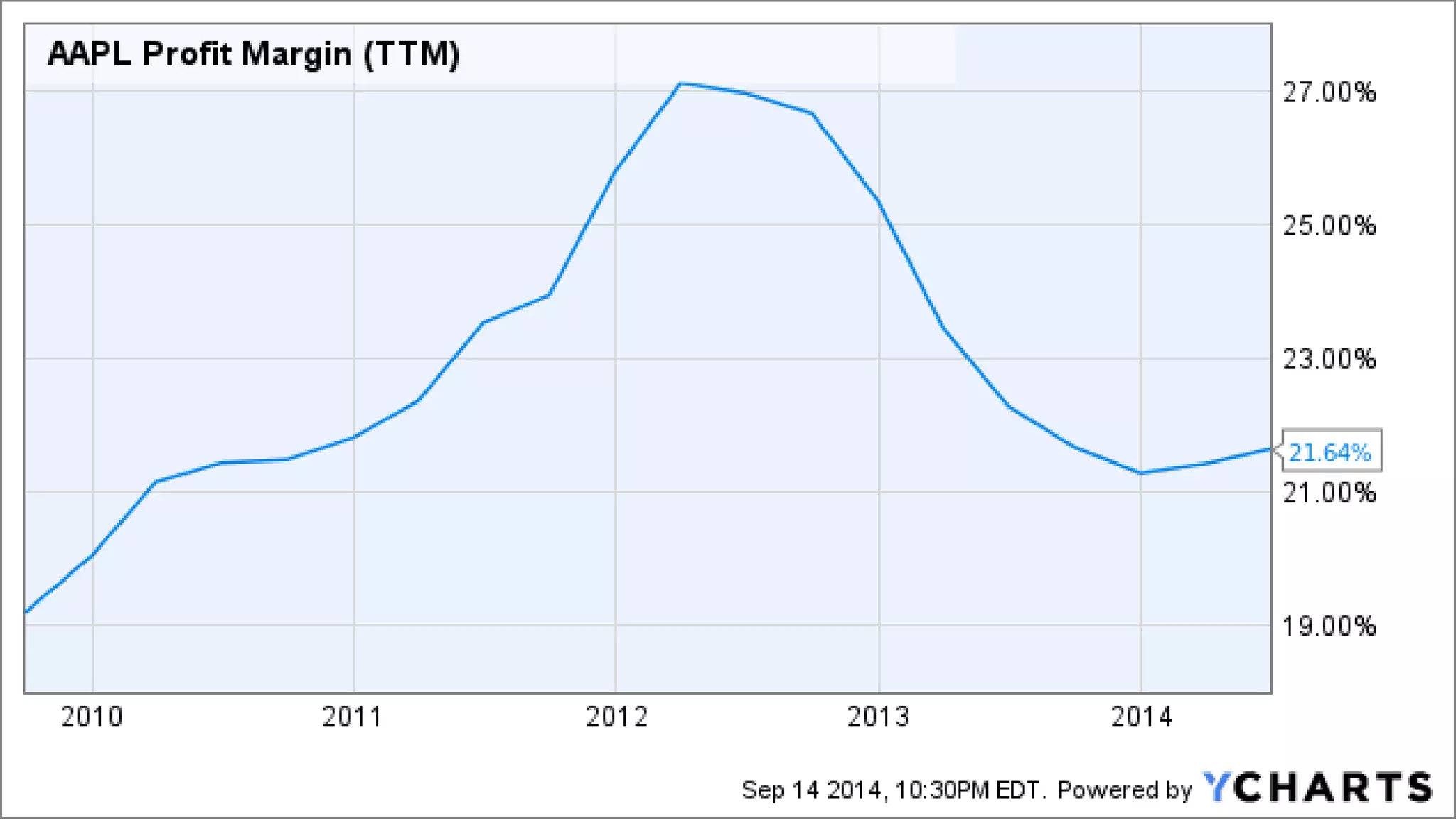
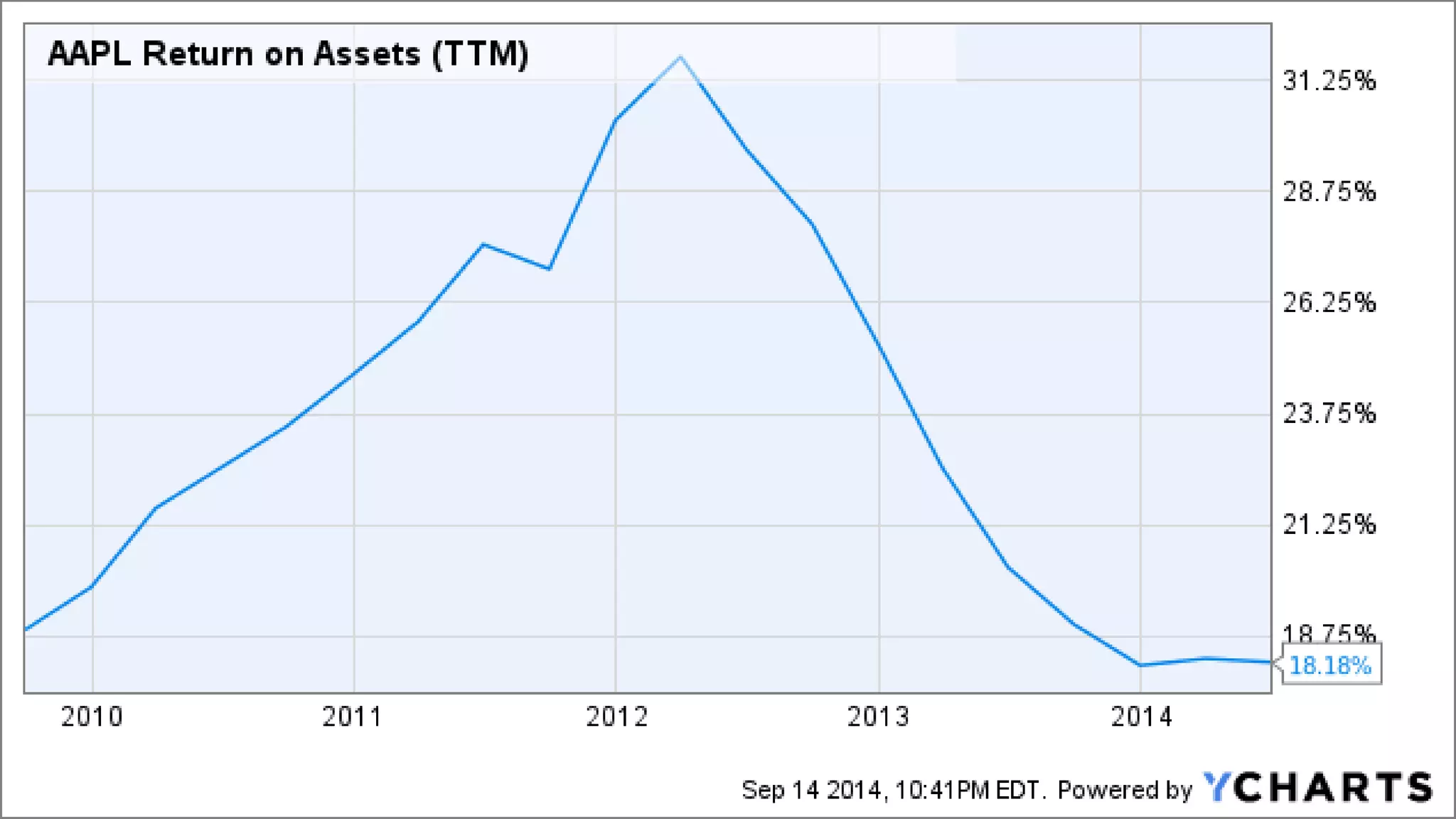
This document analyzes financial ratios for Apple from 2013-2014. It calculates ratios in five categories: liquidity, leverage/solvency, turnover/activity, profitability, and efficiency. The ratios show that Apple's liquidity decreased from 2013-2014 while its debt levels and profitability increased slightly. Key metrics include a current ratio of 1.08 in 2014, days accounts payable of 0.001187309, and return on equity of 0.354. Overall the analysis indicates that Apple's financial position remained strong from 2013-2014.