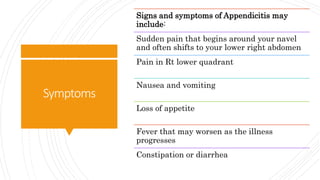
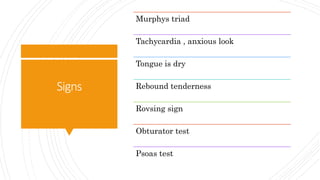
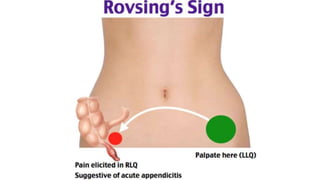
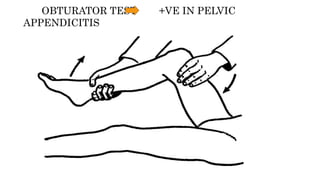
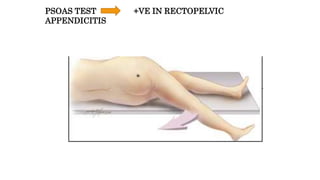
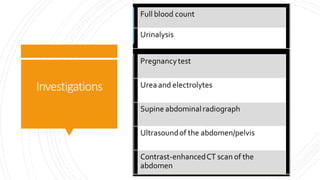
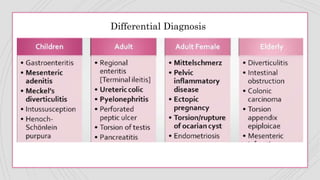
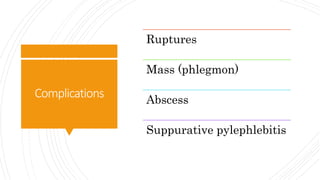
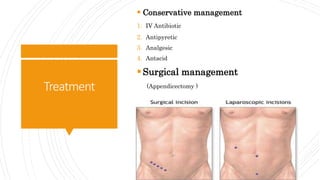
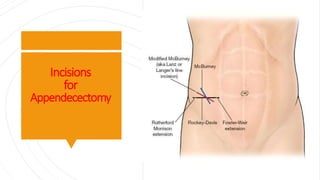
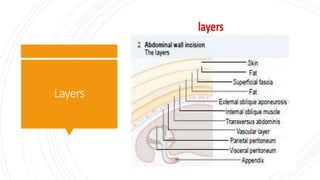
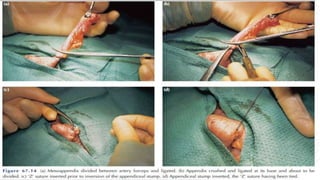
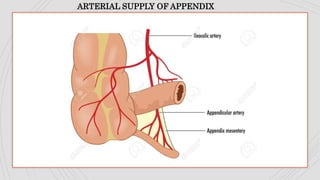
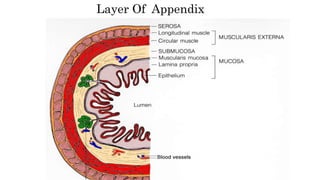
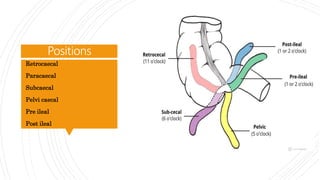
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the vermiform appendix. The appendix is typically 10 cm long and located at the base of the caecum. It receives its blood supply from the appendicular artery. Symptoms of appendicitis include sudden pain in the lower right abdomen that shifts locations, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and signs like rebound tenderness. Treatment involves intravenous antibiotics and analgesics initially, and an appendectomy if symptoms worsen or do not improve. Complications can include rupture, abscess formation, or infection spread.


![pathology
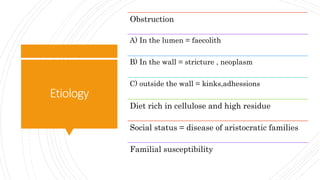
1) OBSTRUCTIVE
A] Mucocele of appendix
B] Vascular congestion of appendix
C] Empyema of appendix
D] Infarcts
2) NON- OBSTRUCTIVE
Inflammation terminates by
Suppuration
Gangrene
Fibrosis
Resolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acasestudyonappendicitis-190829151342/85/appendicitis-9-320.jpg)