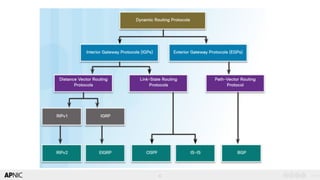
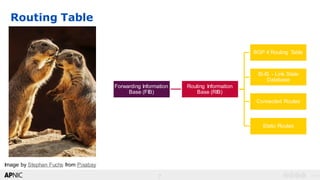
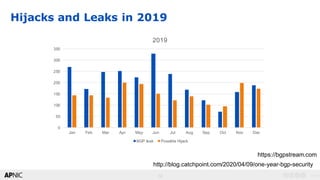
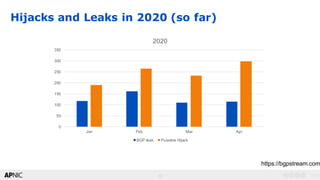
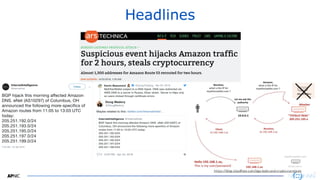
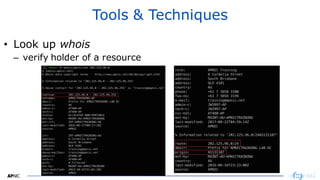
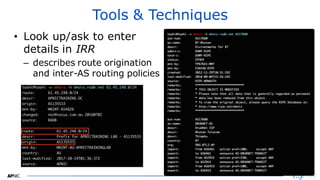
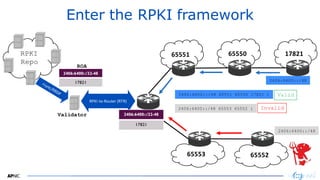
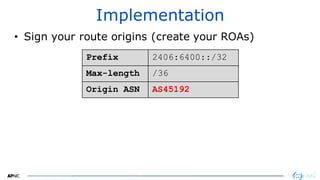
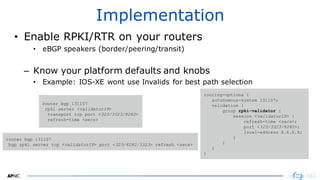
The document provides an introduction to internet routing, BGP hijacking, and the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) system for securing internet routing. It discusses how BGP works and how hijacks can occur when more specific routes are announced. The document then summarizes the RPKI framework for validating route origins using Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) and filtering routes based on their validation state. It provides examples of implementing RPKI on routers to help secure internet routing.



![4
v1.04
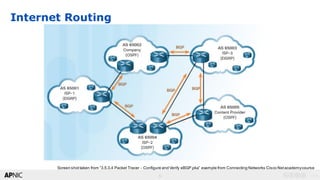
Internet Routing
Google Maps. (2017). Google Maps. [online]Available at: https://goo.gl/maps/Zdw6sruvkb75DiL17 [Accessed 4 Dec.2020].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsidescombined20201211-201221051527/85/BSides-BGP-Hijacking-and-Secure-Internet-Routing-4-320.jpg)
![11
v1.011
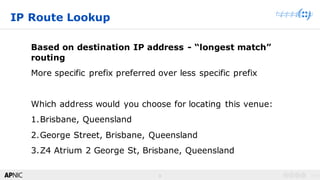
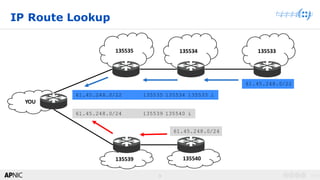
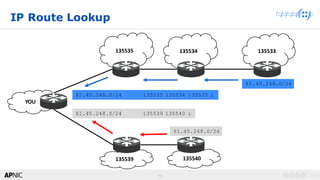
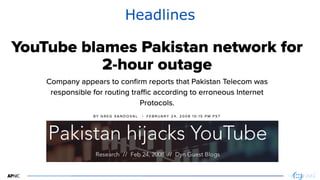
BGP Hijack 101
• Announce a more specific
path
• Announce an IP address
space that is owned by
someone else
Williams, R. (2015). street signs being stolen [Image].
Retrieved from https://media.apnarm.net.au/media/images/2015/02/06/IQT_06-02-2015_NEWS_05_STOLENSIGNS1_t1880.jpg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsidescombined20201211-201221051527/85/BSides-BGP-Hijacking-and-Secure-Internet-Routing-11-320.jpg)














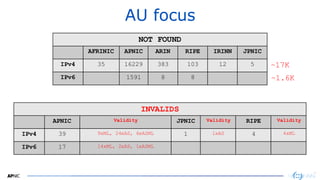
![3636
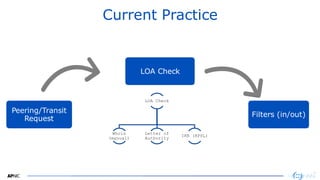
Validation States
• Acting on the Validation states
– Tag & do nothing~ You have downstream/route server @IXPs
– RFC7115 – preference
– Drop Invalids
[Valid (ASN:65XX0), Not Found (ASN:65XX1), Invalid (ASN:65XX2)]
[Valid > Not Found > Invalid]
IPv4 ~ 6K
IPv6 ~ 1K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsidescombined20201211-201221051527/85/BSides-BGP-Hijacking-and-Secure-Internet-Routing-36-320.jpg)