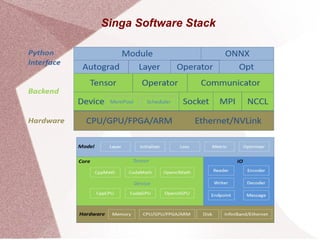
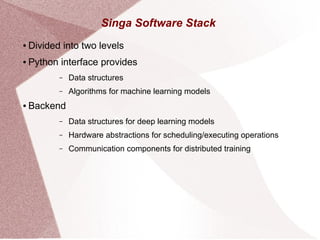
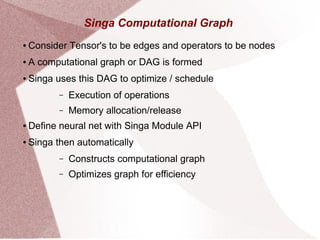
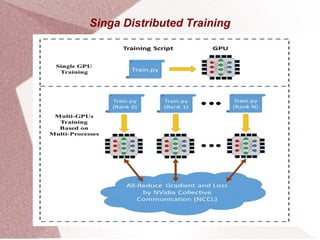
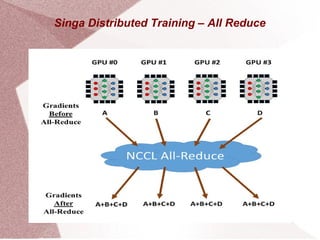
Apache Singa AI is an open-source machine learning system that supports distributed processing and various hardware configurations, optimized for training speed and memory efficiency through computational graphs. It features a Python interface with a backend for deep learning models, allowing for easy scheduling of operations and communication in distributed training setups. Singa employs techniques like lazy allocation and automatic recycling to manage memory effectively while utilizing multiple GPUs for data-parallel training.