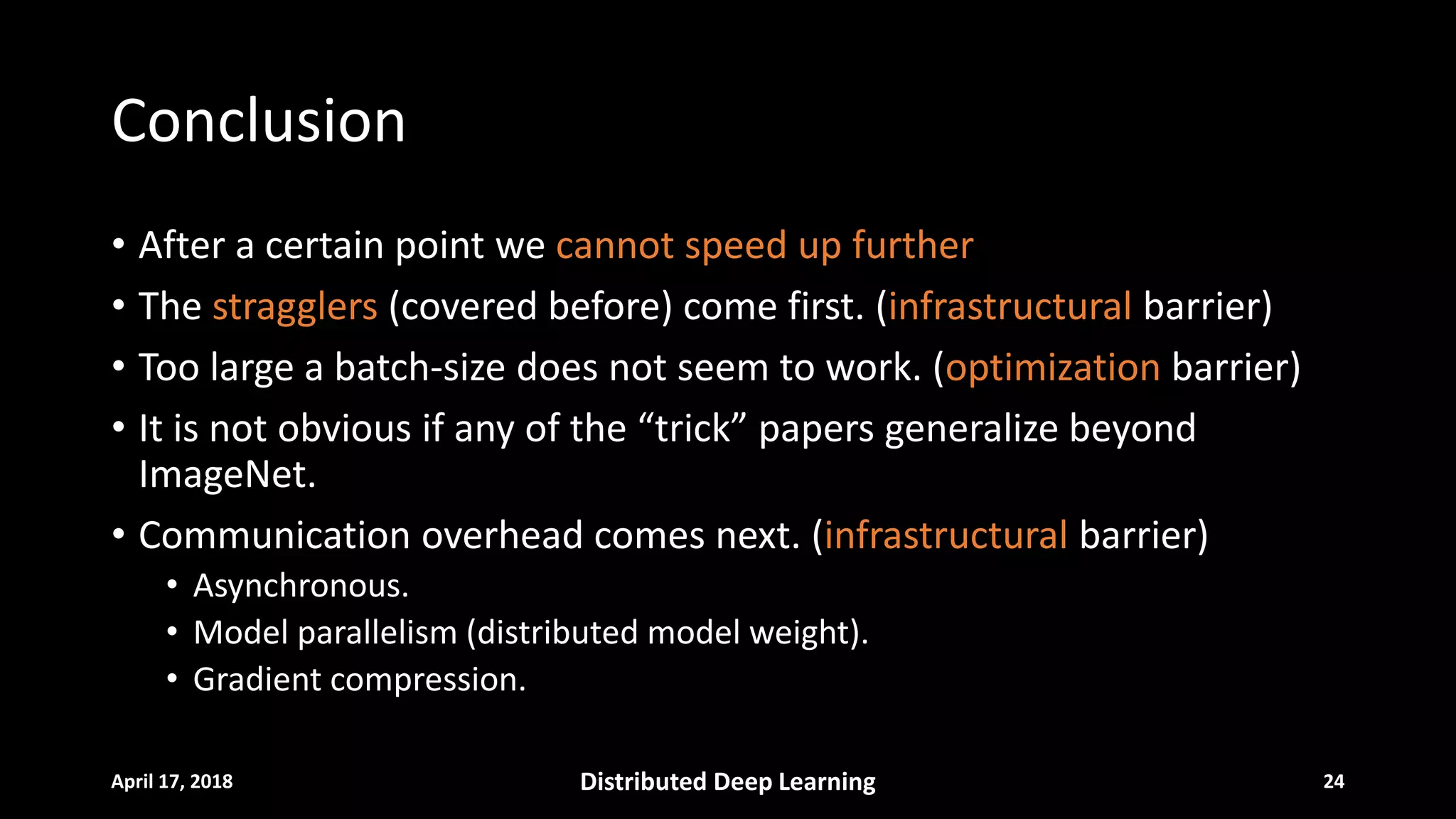
The document discusses strategies for distributed deep learning including data and model parallelism as well as synchronous and asynchronous optimization. It outlines challenges such as communication overhead, long-tail latency, and programming barriers. It then summarizes several papers that improved the speed of training on ImageNet through techniques like larger batch sizes, model distillation, and gradient compression. The conclusion notes that while scaling has limitations due to infrastructure and optimization barriers, asynchronous methods and gradient compression can help address communication overhead.

![Strategies
• Parallelisms: data parallelism vs. model parallelism.
• Optimization: synchronous vs. asynchronous.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 2
Source [5]Source [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-2-2048.jpg)
![Challenges
• Infrastructural barriers
• Communication overhead.
• Long-tail machine/network latency.
• Optimization barriers
• Synchronous: batch-size trade-off.
• Asynchronous: gradient interference.
• Programming barriers
• Error prone pipelines.
• After 128 GPUs there’s no point [1].
April 17, 2018 3Distributed Deep Learning
Source [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-3-2048.jpg)

![Downpour SGD, Sandblaster LBFGS [5]
• Run on CPU (2012!).
• Downpour SGD: Asynchronous SGD, basically HOGWILD on multiple
machines.
• Sandblaster LBFGS: Simple distributed version of LBFGS.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-5-2048.jpg)
![Downpour SGD, Sandblaster LBFGS [5]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-6-2048.jpg)
![ImageNet in one hour [3]
• Using synchronous SGD and a linear scaling rule increase the mini-
batch size.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-7-2048.jpg)
![ImageNet in one hour [3]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-8-2048.jpg)
![ImageNet in one hour [3]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-9-2048.jpg)
![ImageNet in one hour [3]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-10-2048.jpg)
![ImageNet in 15 minutes [4]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-11-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
• Based on knowledge distillation (KD) [2]:
1. Train a high-capacity teacher model.
2. Train a low-capacity student model + distillation loss.
• KD better generalization, model compression.
• When cannot scale up, train an ensemble in parallel.
• Merge the ensembles into a single model with KD.
• Instead of a two-phase training, do it at the same time.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-12-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-13-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
• Unlike distributed SGD, using stale 𝜃𝜃𝑖𝑖’s does not hurt performance.
• The change in weights does not make a significant change in predictions.
• The synchronization can be at the model level or prediction level.
• Each model can be trained on a partition of the dataset.
• Each model can be trained in a distributed way.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-14-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-15-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-16-2048.jpg)
![Co-distillation / Online Distillation [1]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-17-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
• Gradient compression ratio 300x to 600x without losing accuracy.
• ResNet-50 from 97MB to 0.35MB.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-18-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
• Gradient compression ratio 300x to 600x without losing accuracy.
• ResNet-50 from 97MB to 0.35MB.
• Local gradient clipping: accumulate small gradients, broadcast the
rest.
• Momentum correction: take momentum into account.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-19-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-20-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
• Gradient compression ratio 300x to 600x without losing accuracy.
• ResNet-50 from 97MB to 0.35MB.
• Local gradient clipping: accumulate small gradients, broadcast the
rest.
• Momentum correction: take momentum into account.
• Momentum factor masking.
• Momentum warm-up training.
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-21-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-22-2048.jpg)
![Deep Gradient Compression [7]
April 17, 2018 Distributed Deep Learning 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributeddeeplearning-180418211211/75/Distributed-deep-learning-23-2048.jpg)