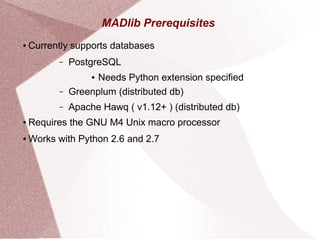
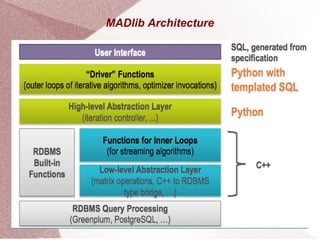
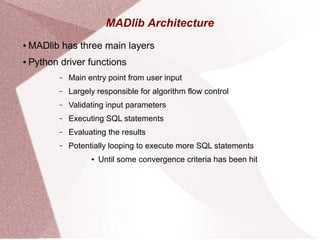
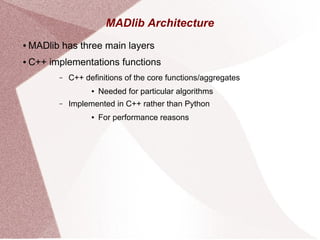
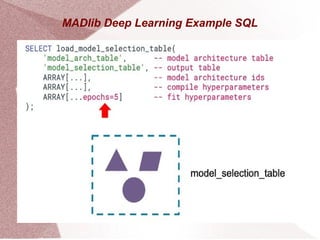
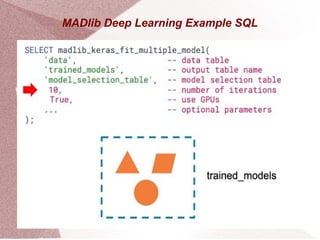
Apache MADlib is an open-source library for scalable in-database analytics and machine learning in SQL, supporting both structured and unstructured data. It features a layered architecture involving Python drivers, C++ implementations, and a database abstraction layer, enabling various statistical and machine learning functions including deep learning and time series analysis. Additionally, it provides utilities for data transformation and model selection, and is compatible with databases like PostgreSQL and Greenplum.