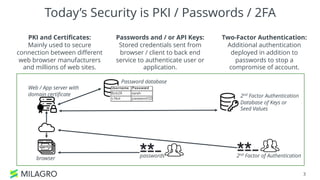
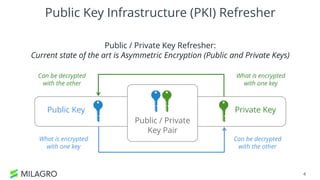
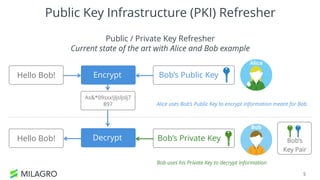
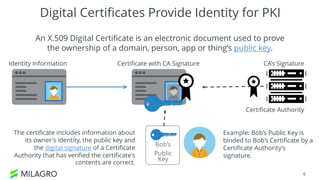
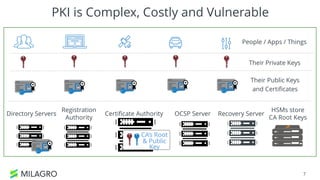
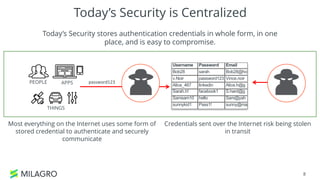
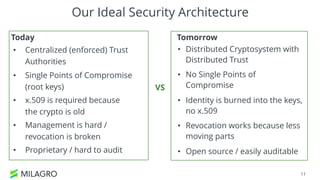
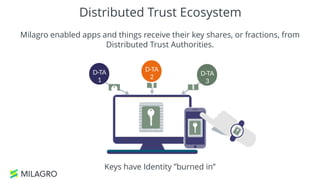
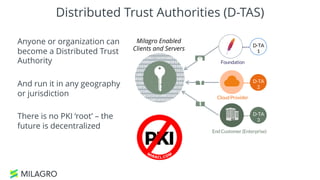
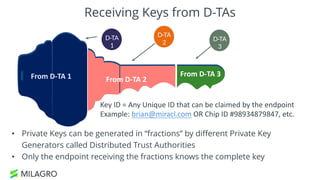
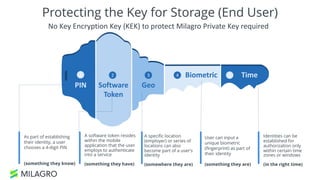
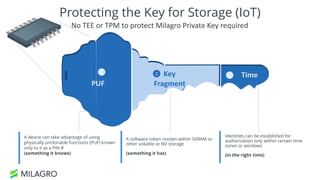
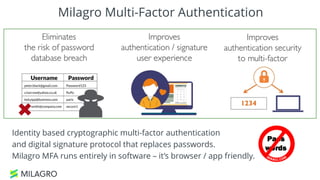
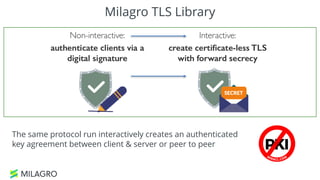
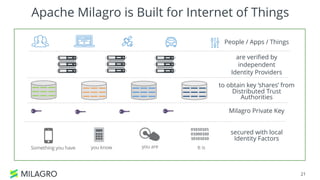
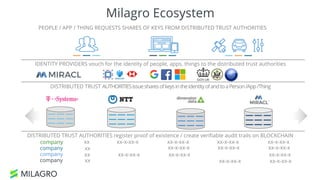
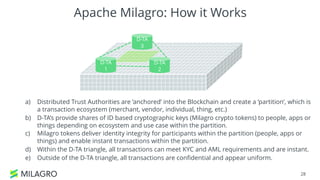
Apache Milagro is an incubating distributed cryptosystem designed to enhance web security by replacing traditional PKI and password-based authentication with an identity-based architecture using distributed trust authorities (DTAs). It leverages pairing cryptography to ensure that private keys are generated in 'fractions,' removing the need for centralized certificate authorities, thus enhancing security and compliance with regulatory standards. The framework aims to facilitate strong authentication and cybersecurity for IoT and blockchain environments, addressing issues of confidentiality, speed, and scalability in cryptocurrency transactions.