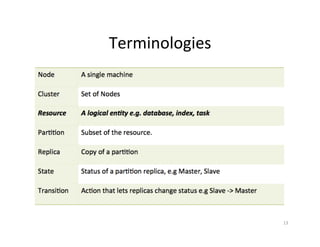
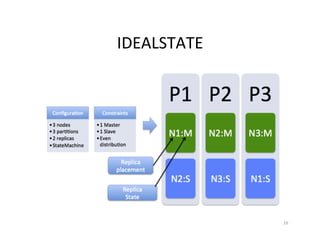
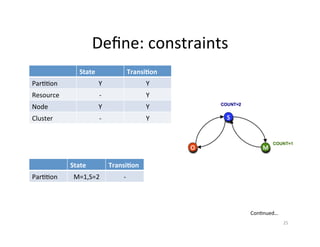
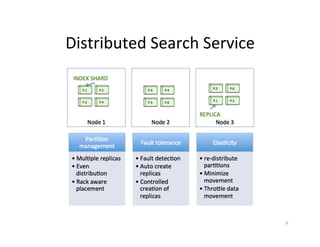
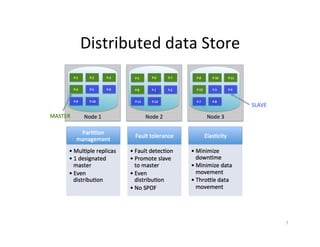
This document provides an overview of Helix, an open source framework for building distributed systems. It describes Helix's architecture, programming model based around state machines, and how systems are defined and configured using Zookeeper. The document also provides examples of how LinkedIn uses Helix to manage various distributed data systems and services.




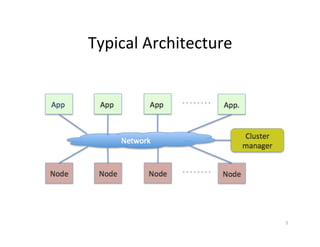
![Message
consumer
group
• Similar
to
Message
groups
in
AcMveMQ
–
guaranteed
ordering
of
the
processing
of
related
messages
across
a
single
queue
–
load
balancing
of
the
processing
of
messages
across
mulMple
consumers
–
high
availability
/
auto-‐failover
to
other
consumers
if
a
JVM
goes
down
• Applicable
to
many
messaging
pub/sub
systems
like
ka]a,
rabbitmq
etc
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachehelixdevopslspeinmeetup06132015-150613131956-lva1-app6891/85/Apache-Helix-DevOps-LSPE-IN-Meetup-8-320.jpg)