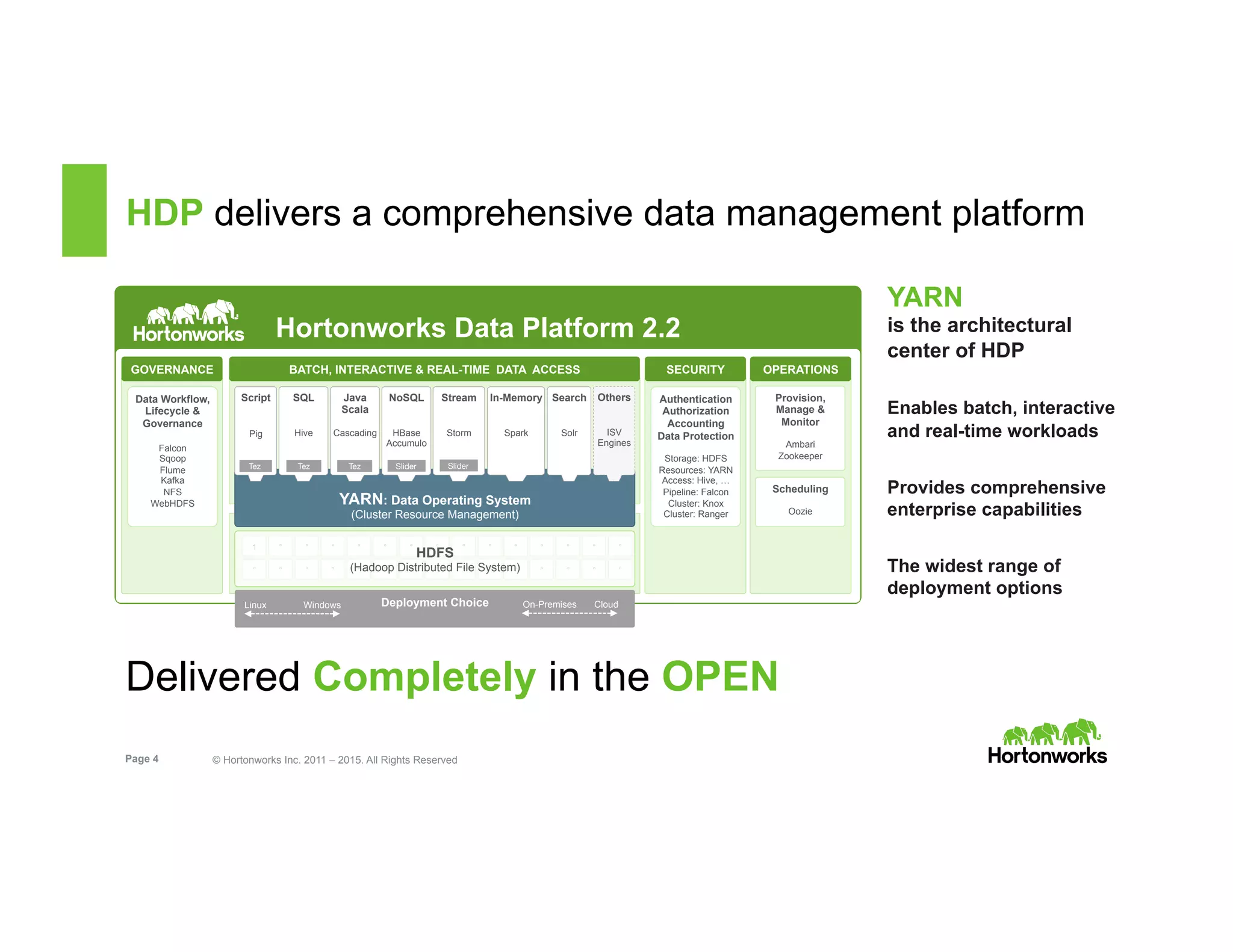
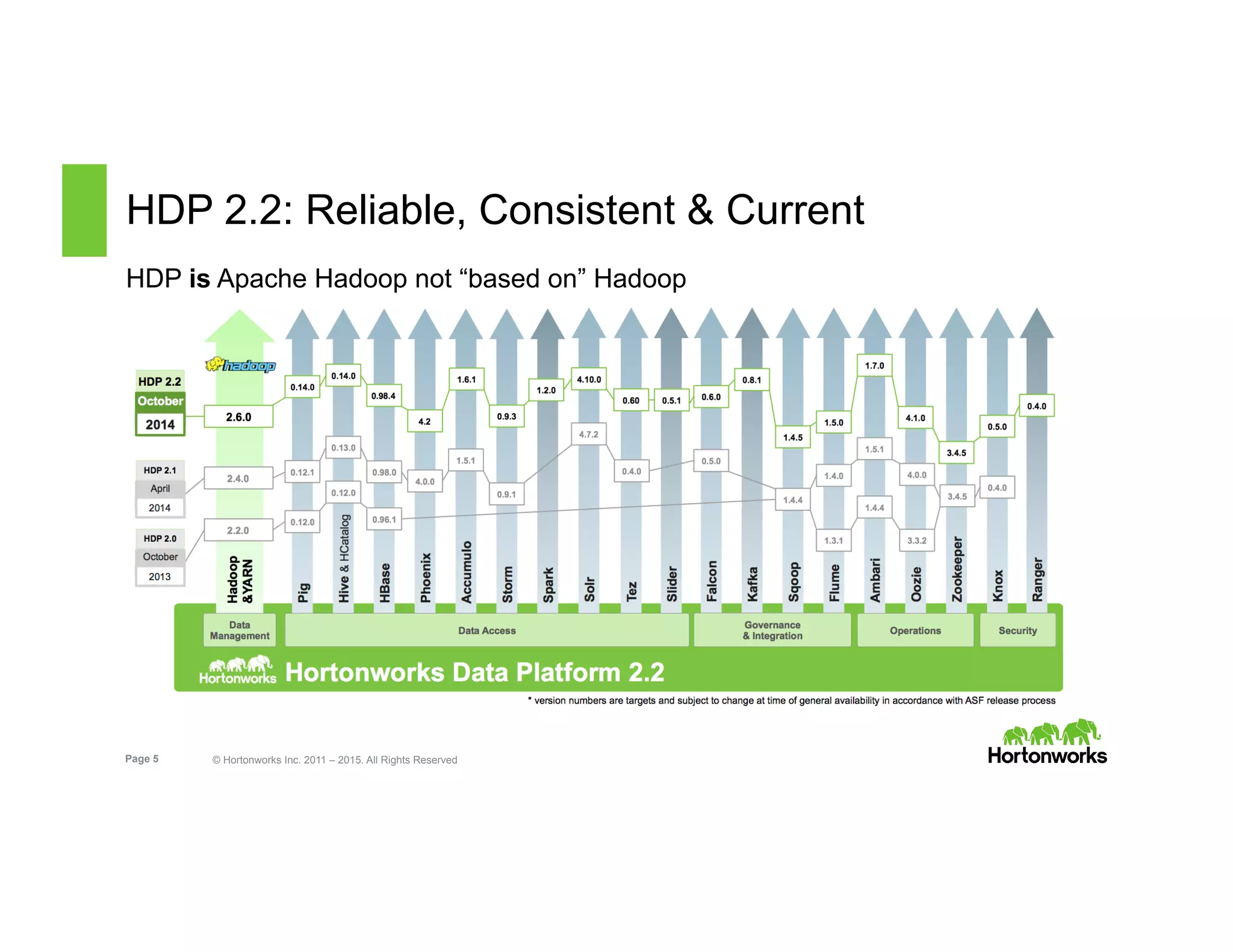
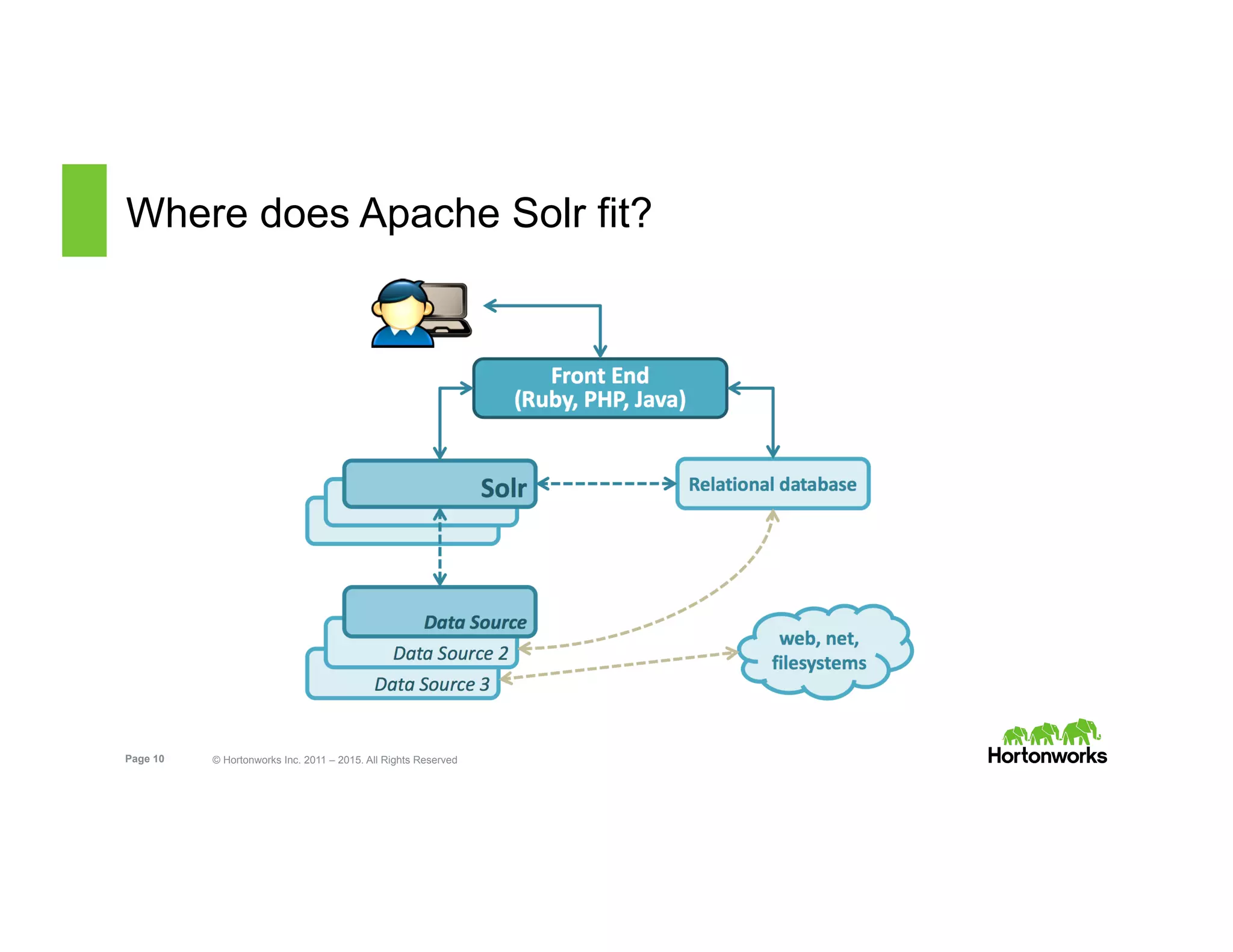
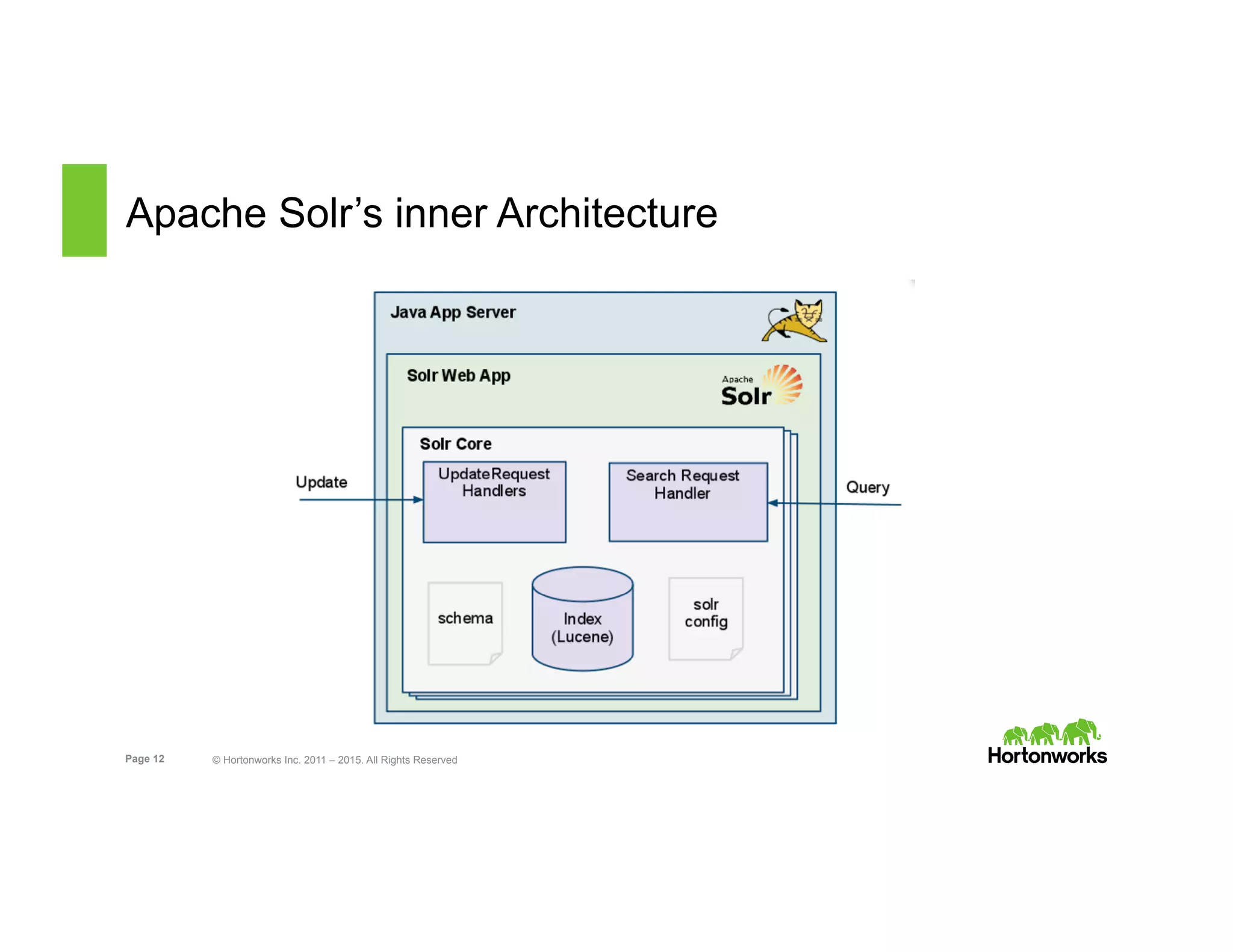
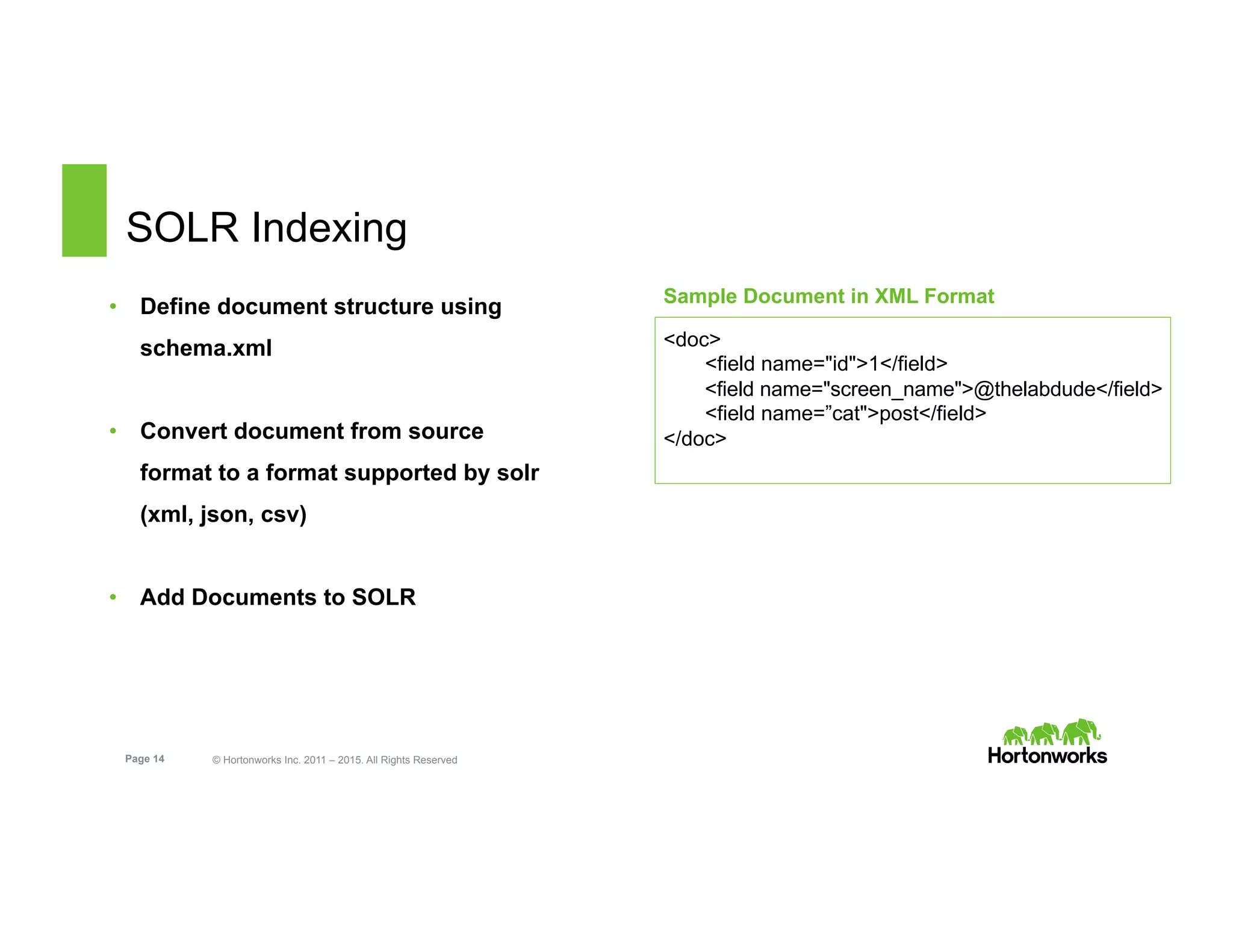
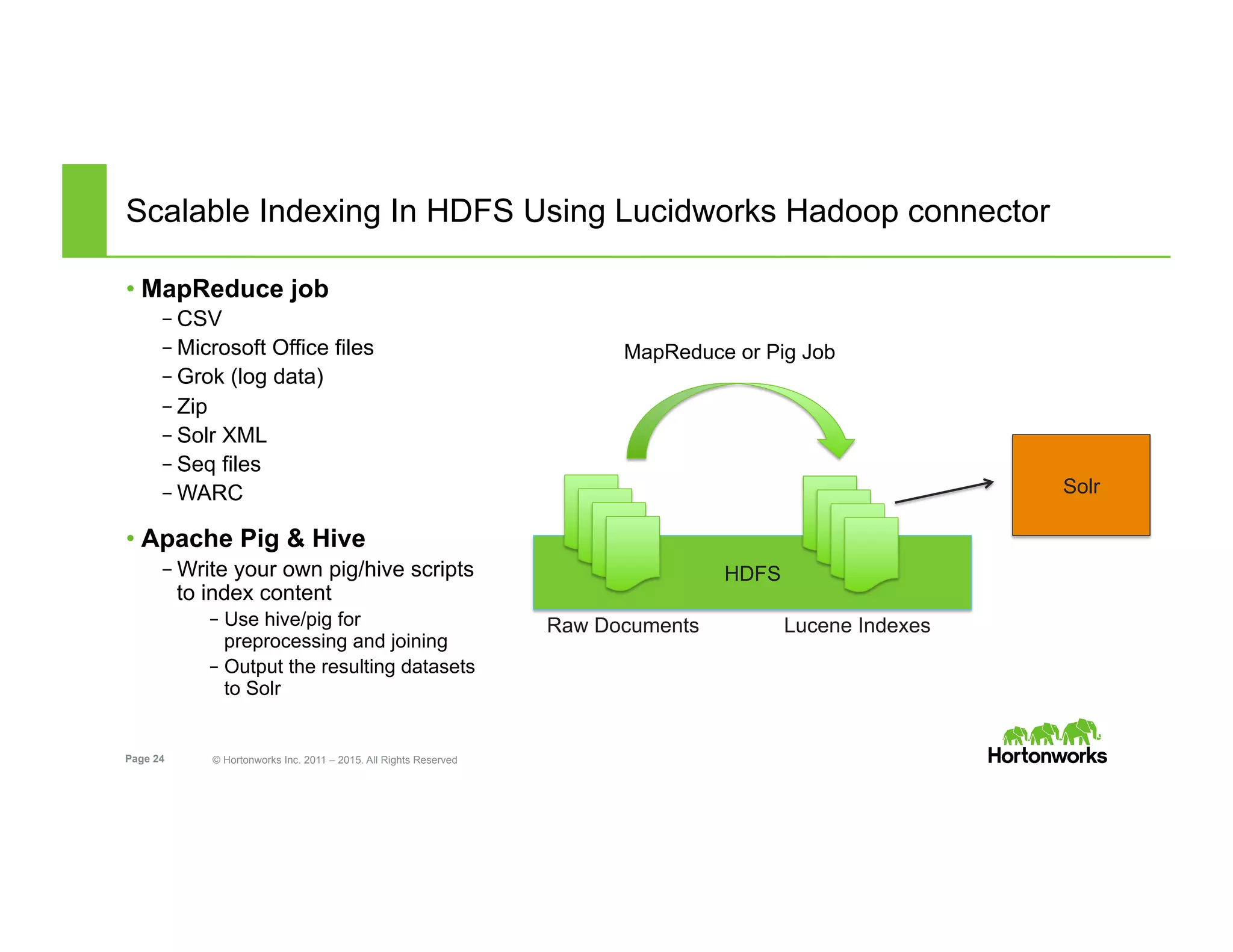
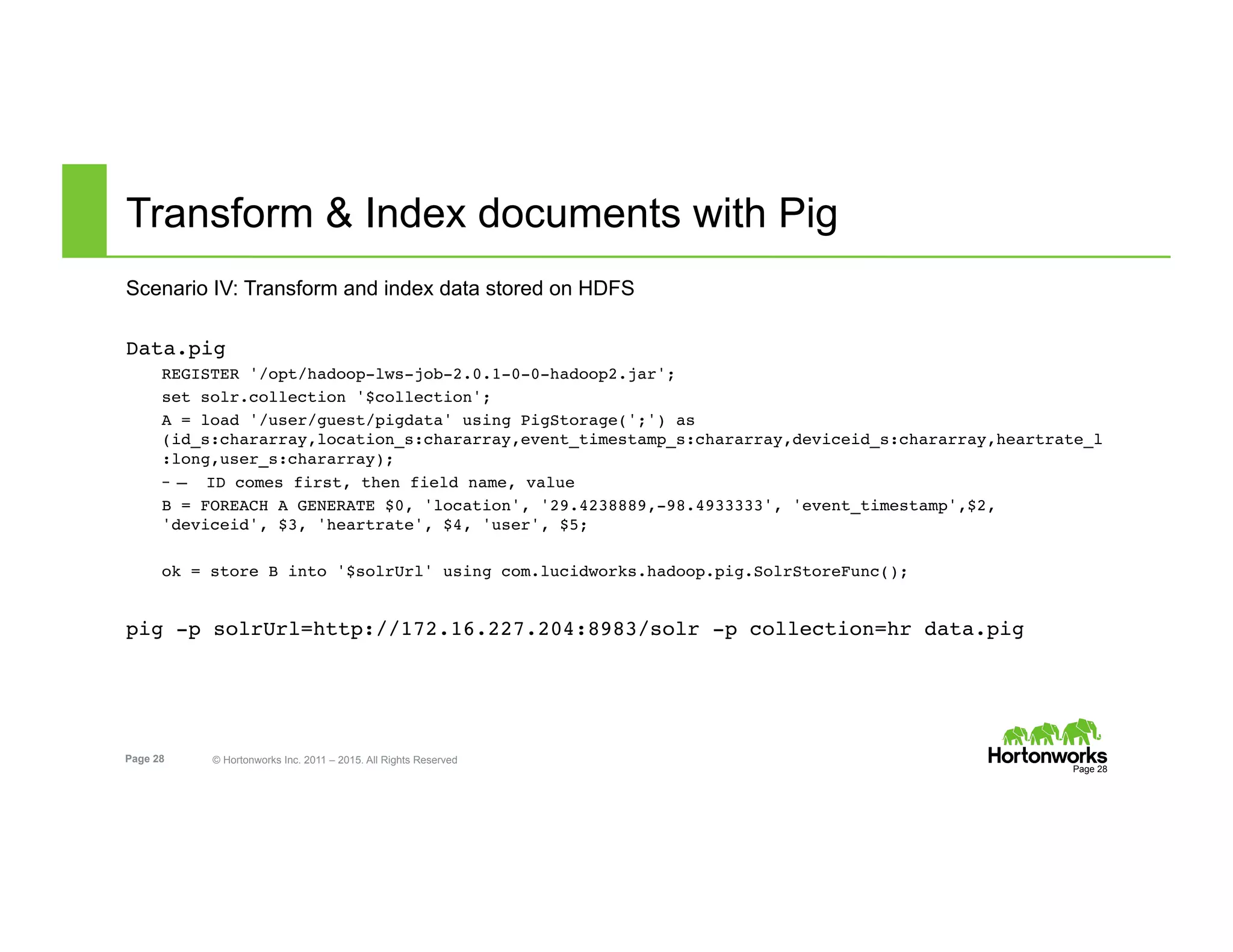
The document outlines the features and functionalities of Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP) 2.2, focusing on Apache Solr integration for text search and indexing. It covers the architecture of Solr, how to index and query documents, and deployment options for utilizing Solr with Hadoop. The document also discusses best practices for managing and scaling Solr installations within HDP.