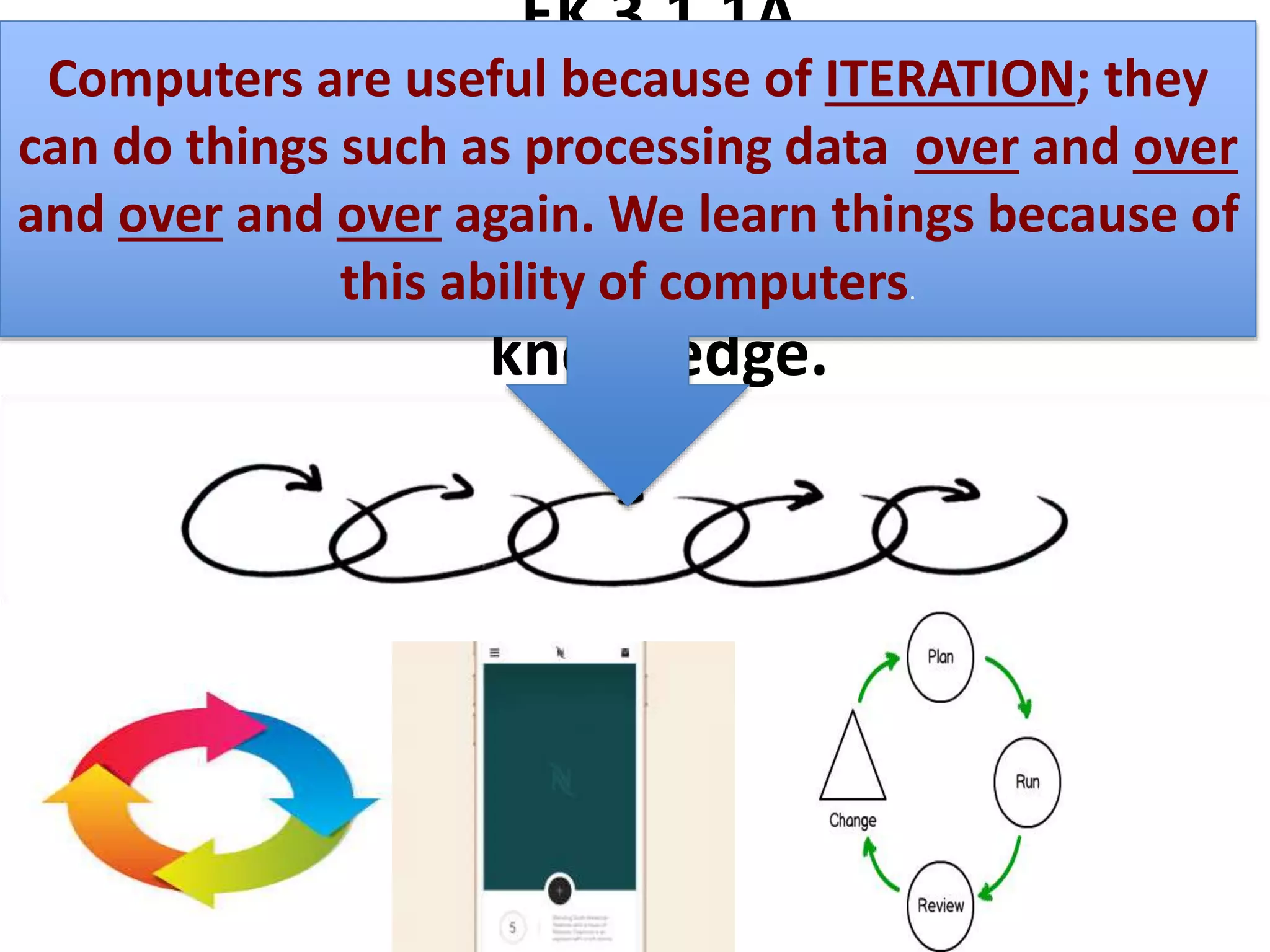
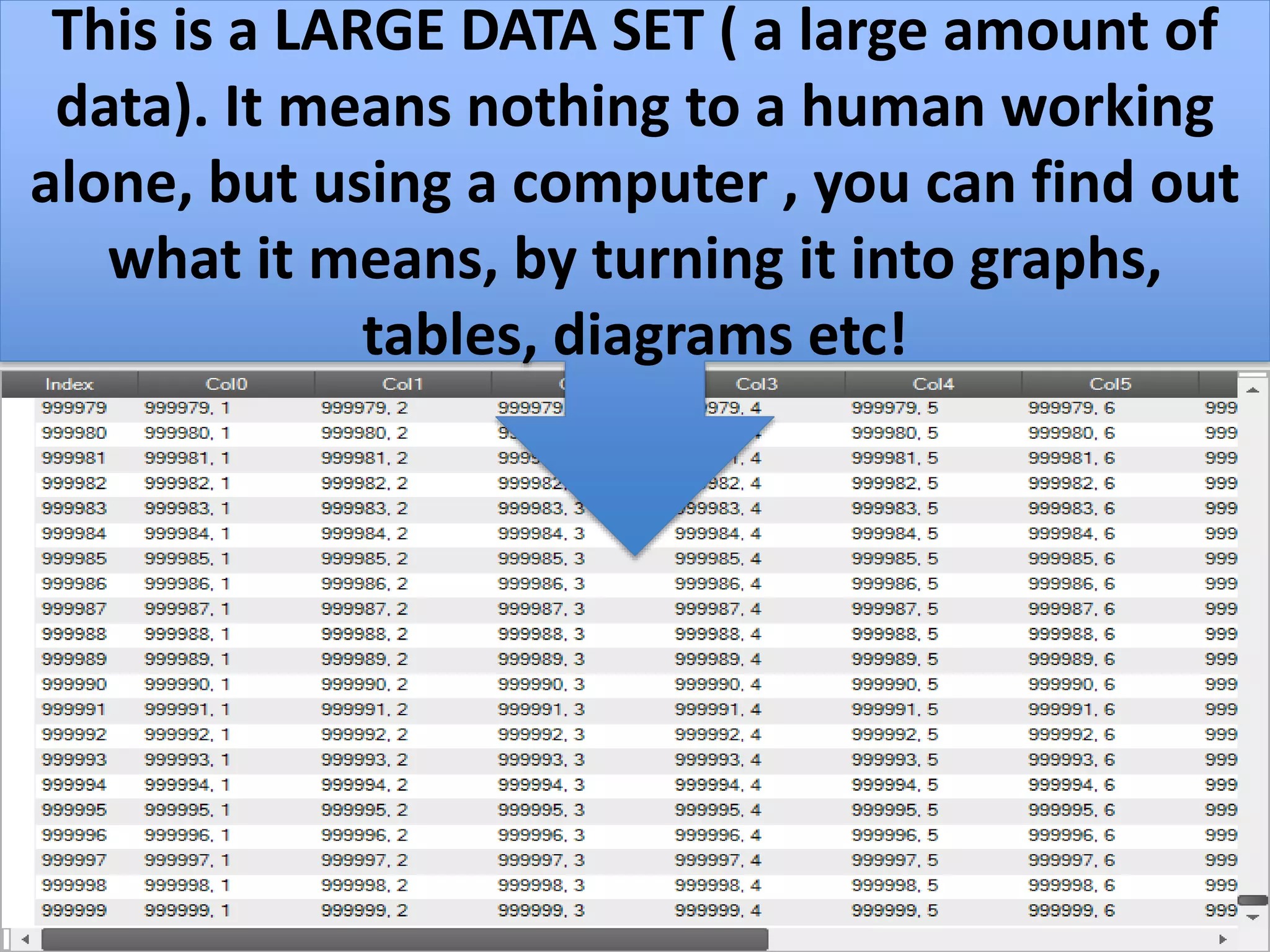
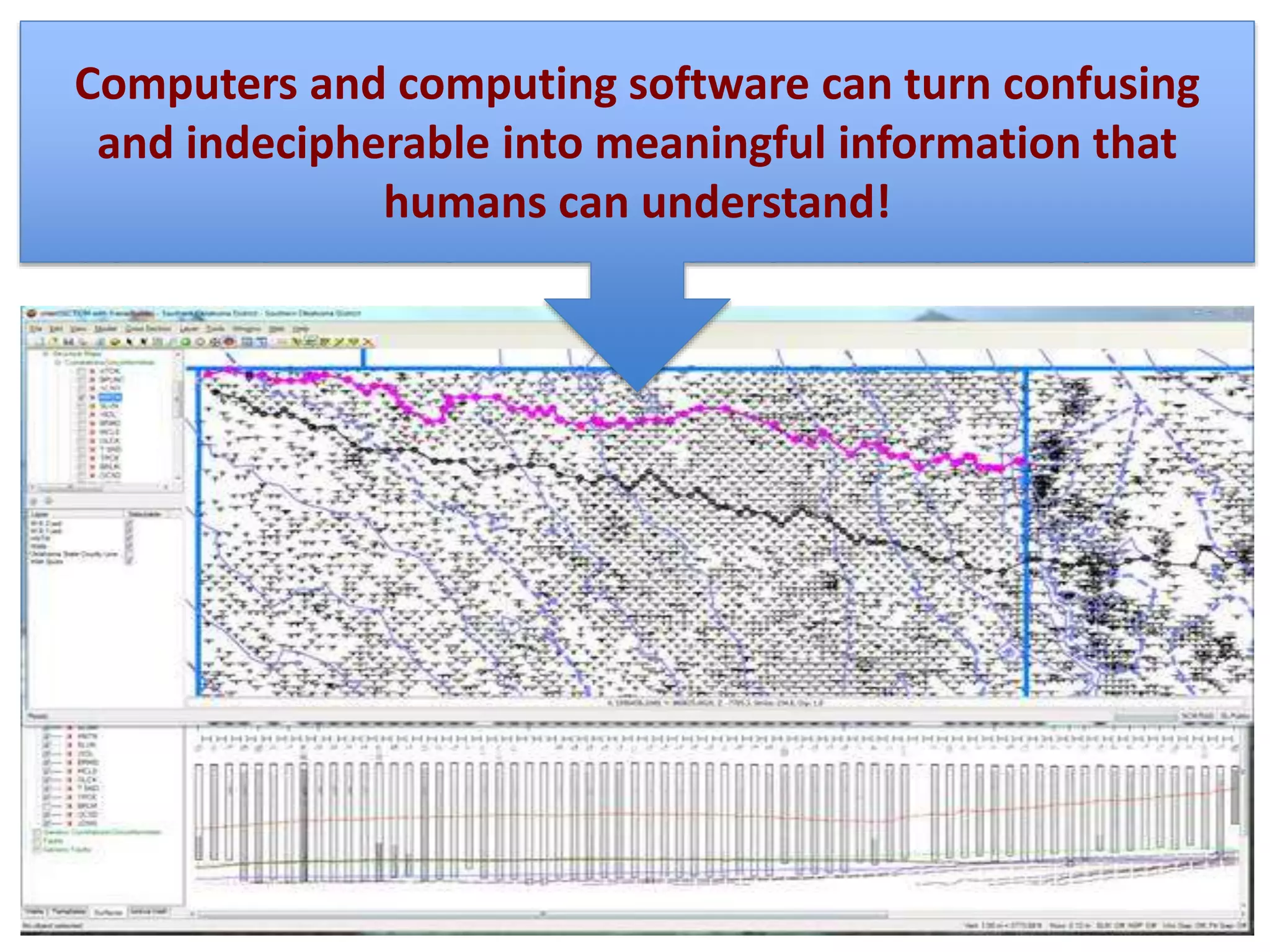
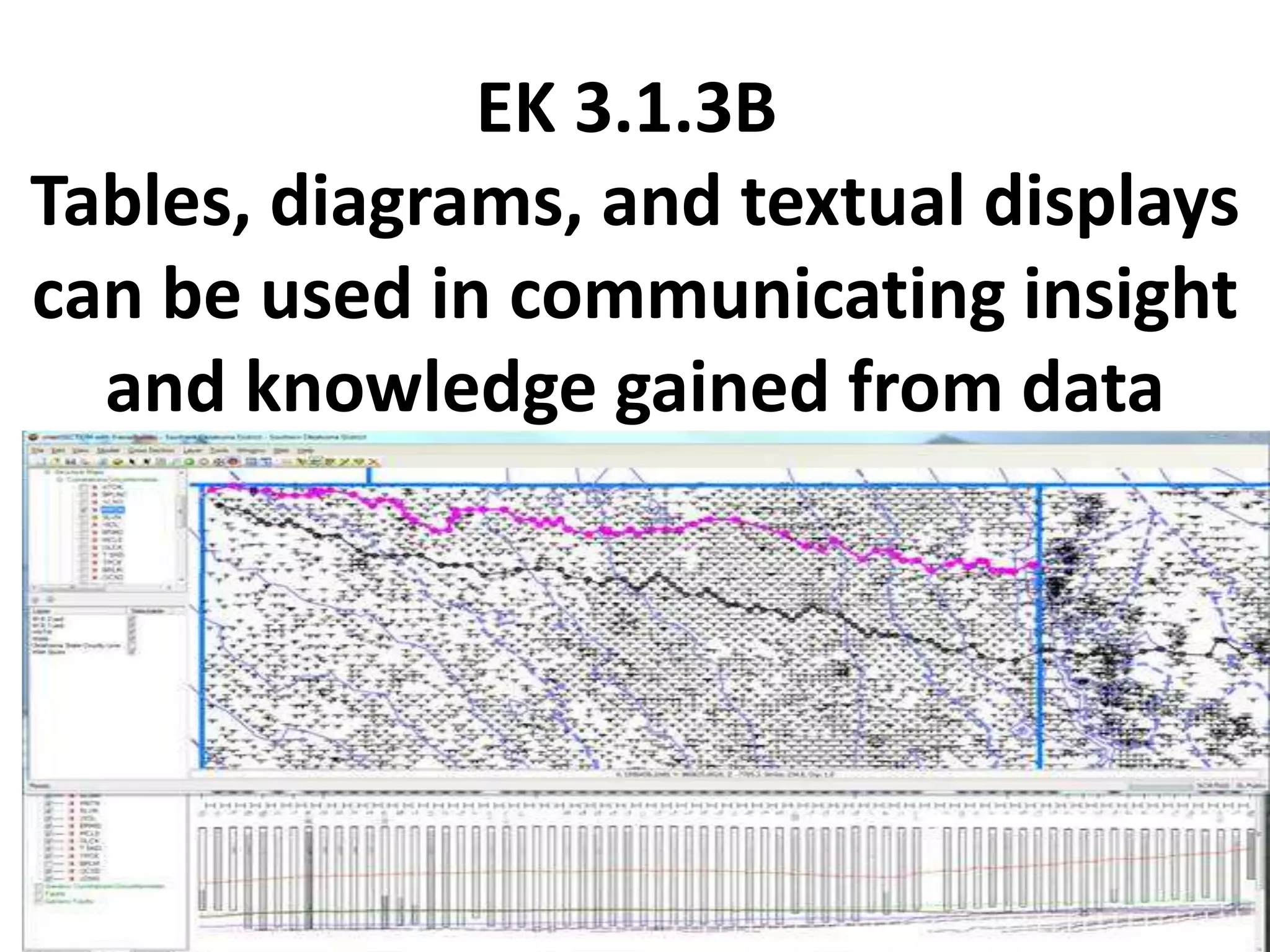
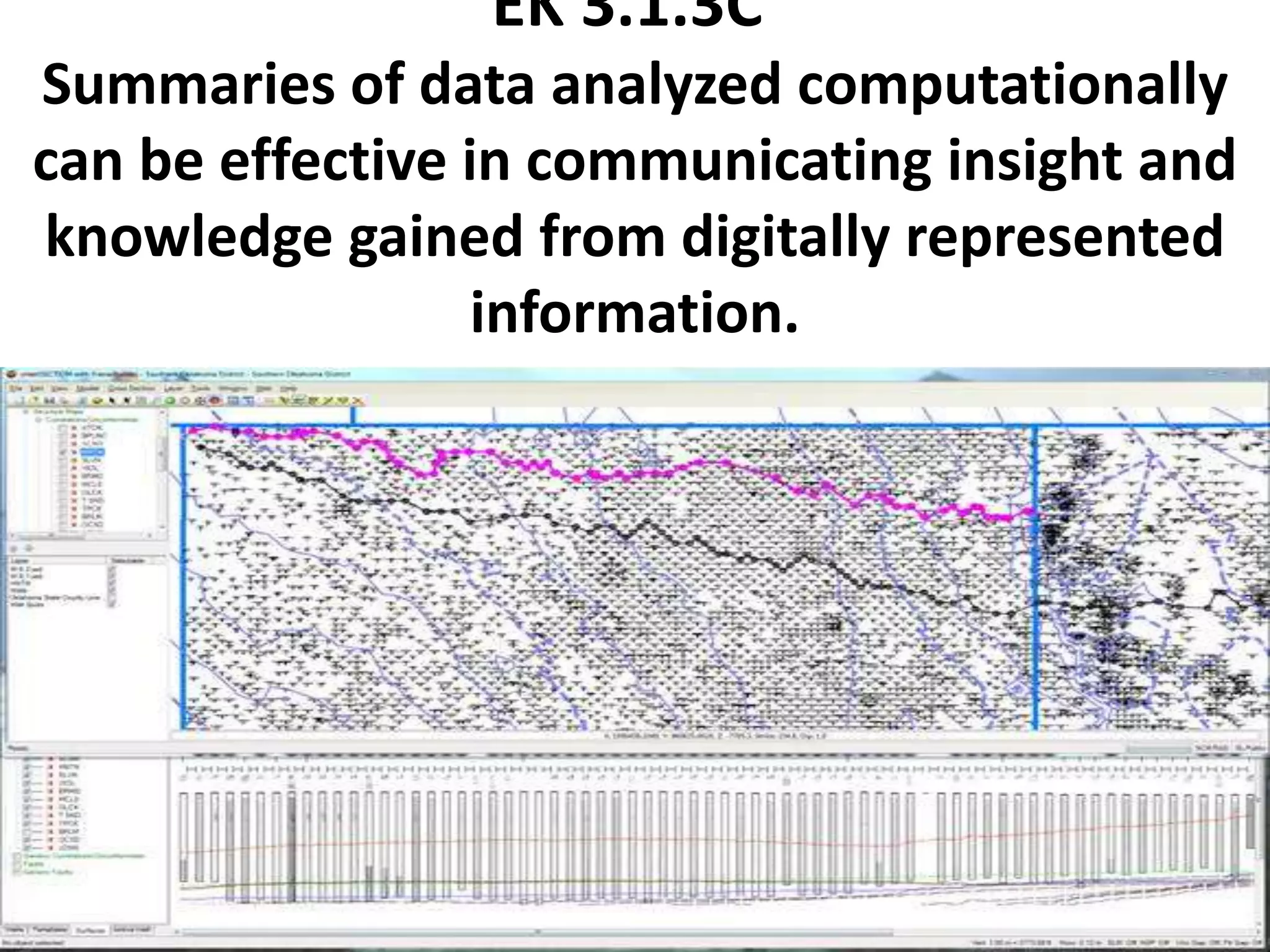
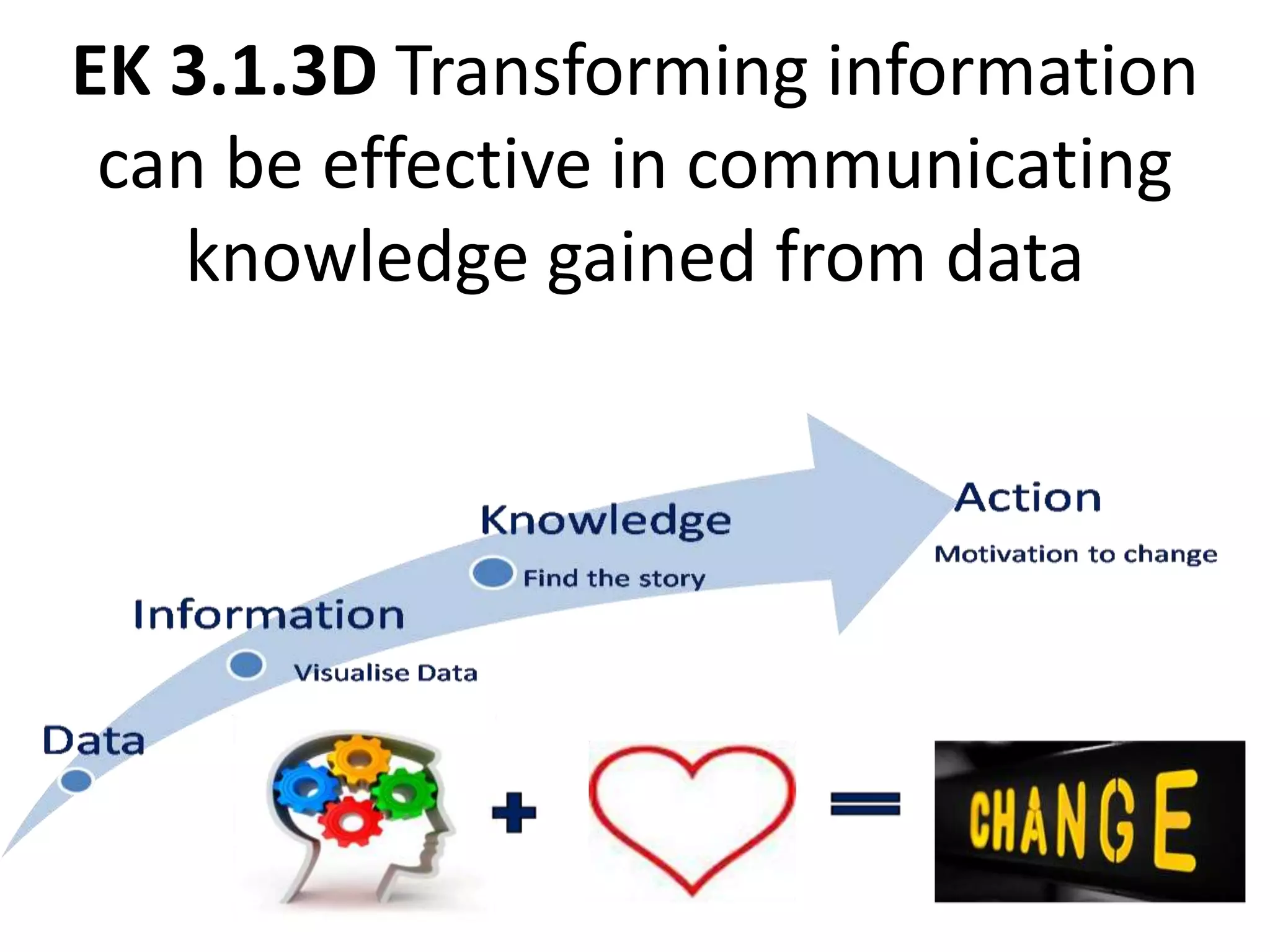
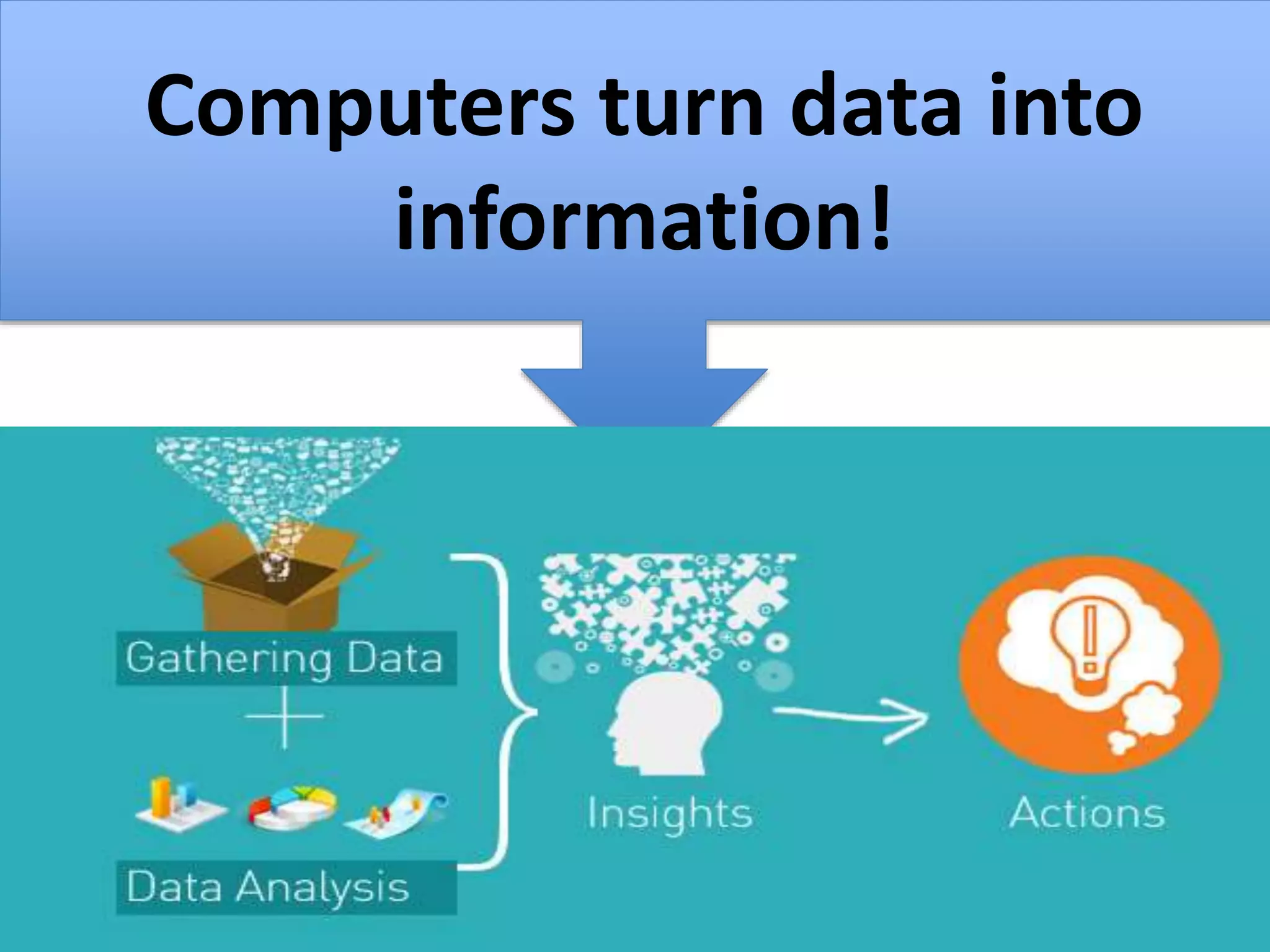
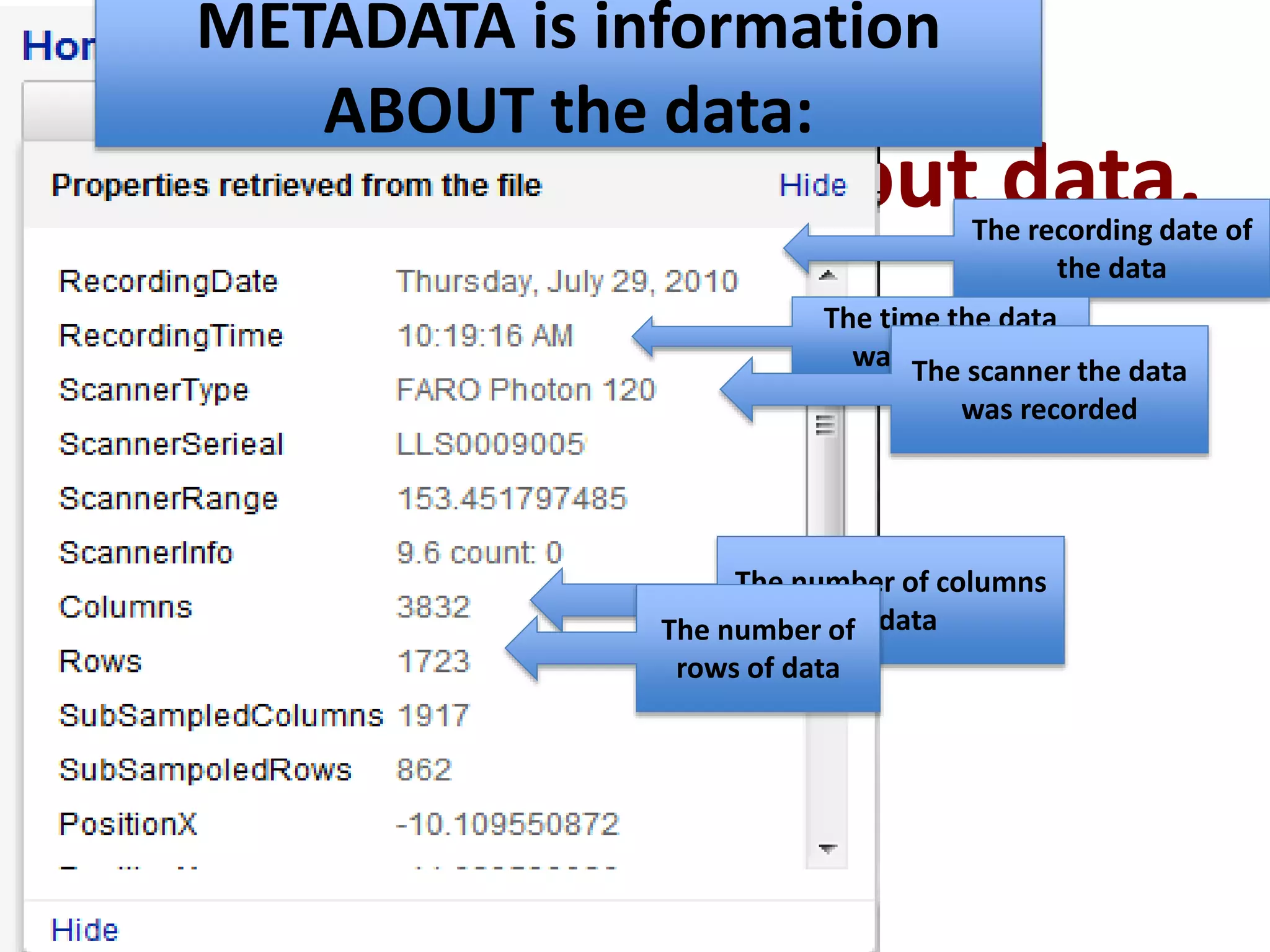
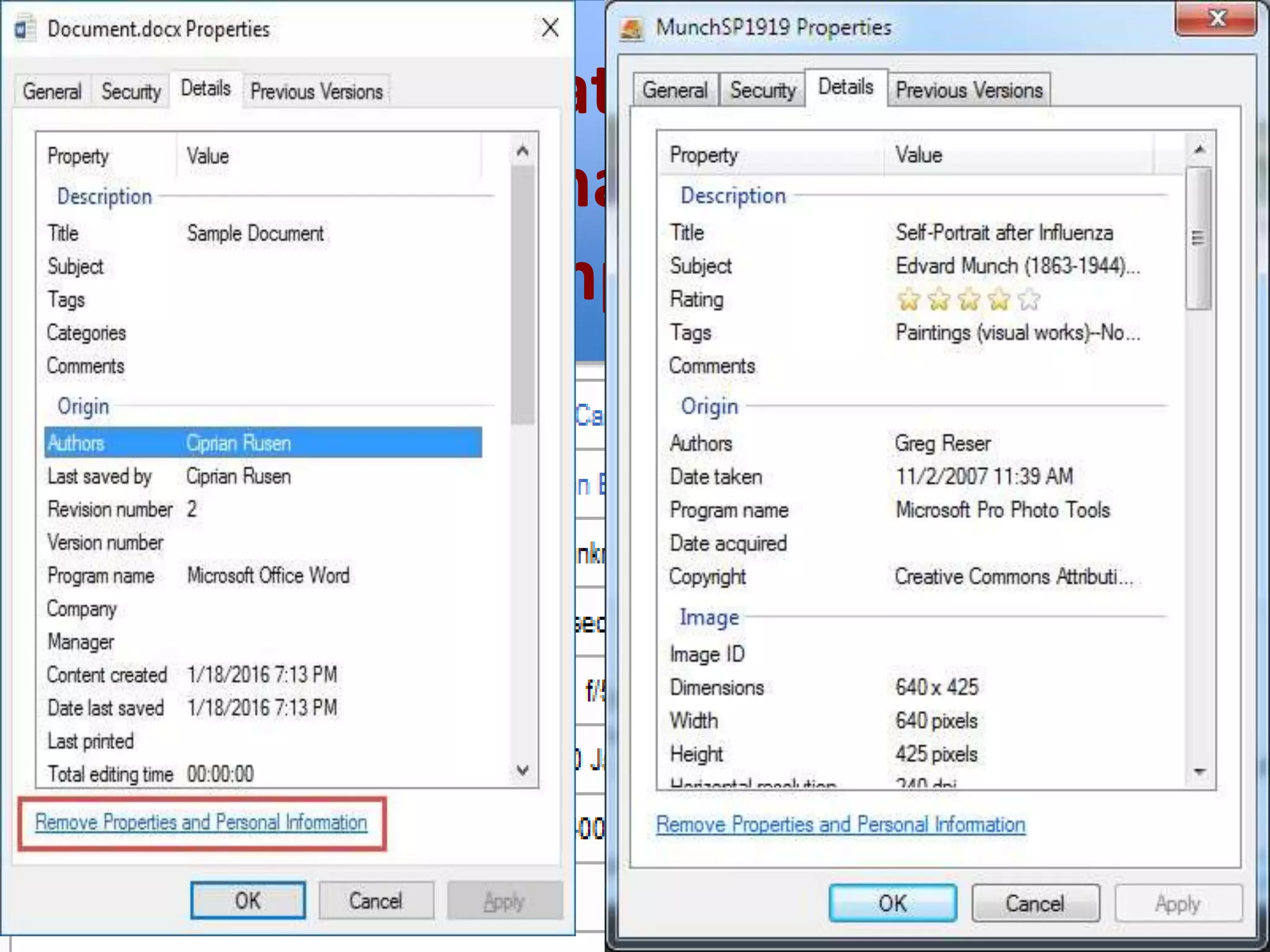
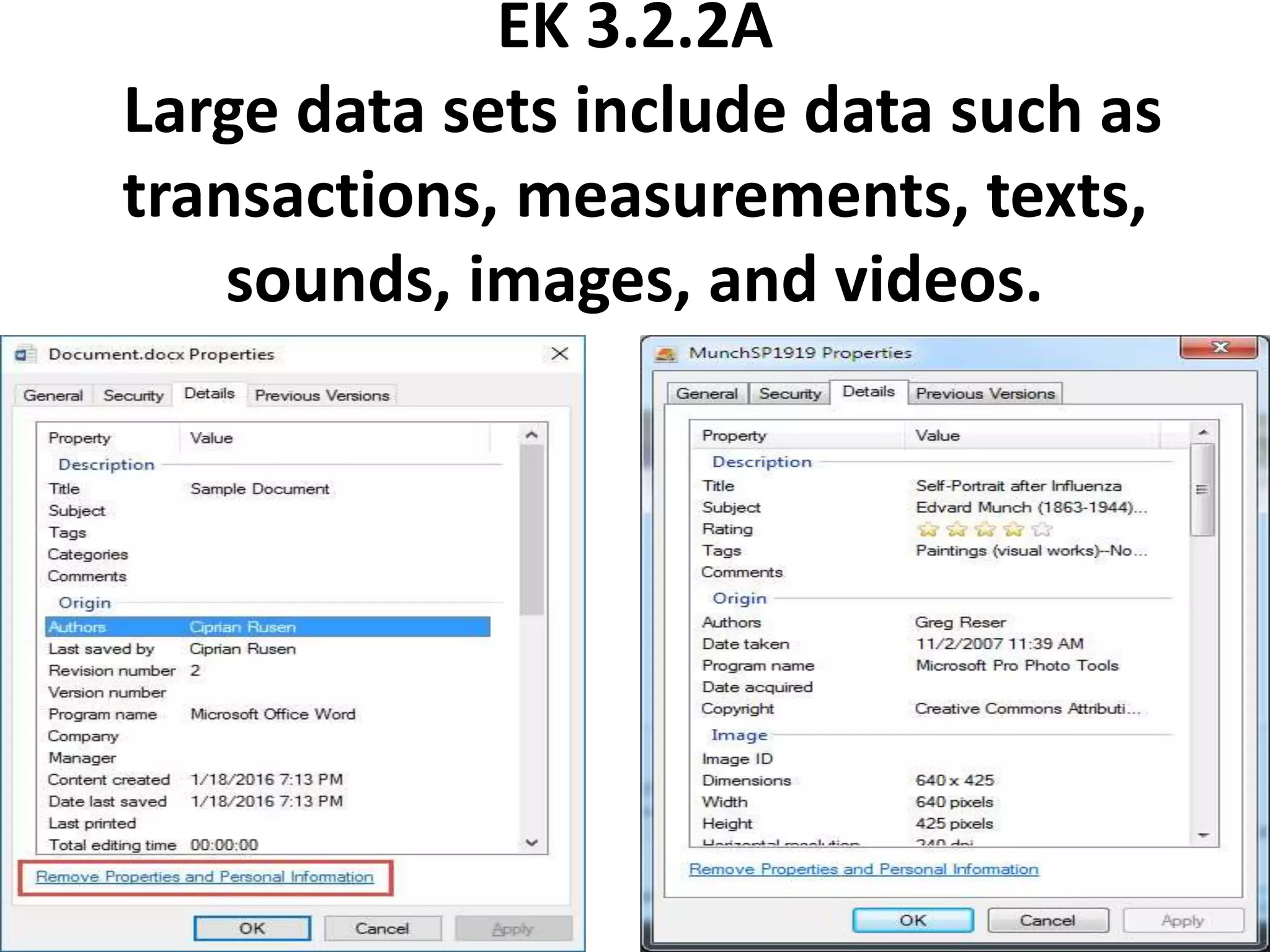
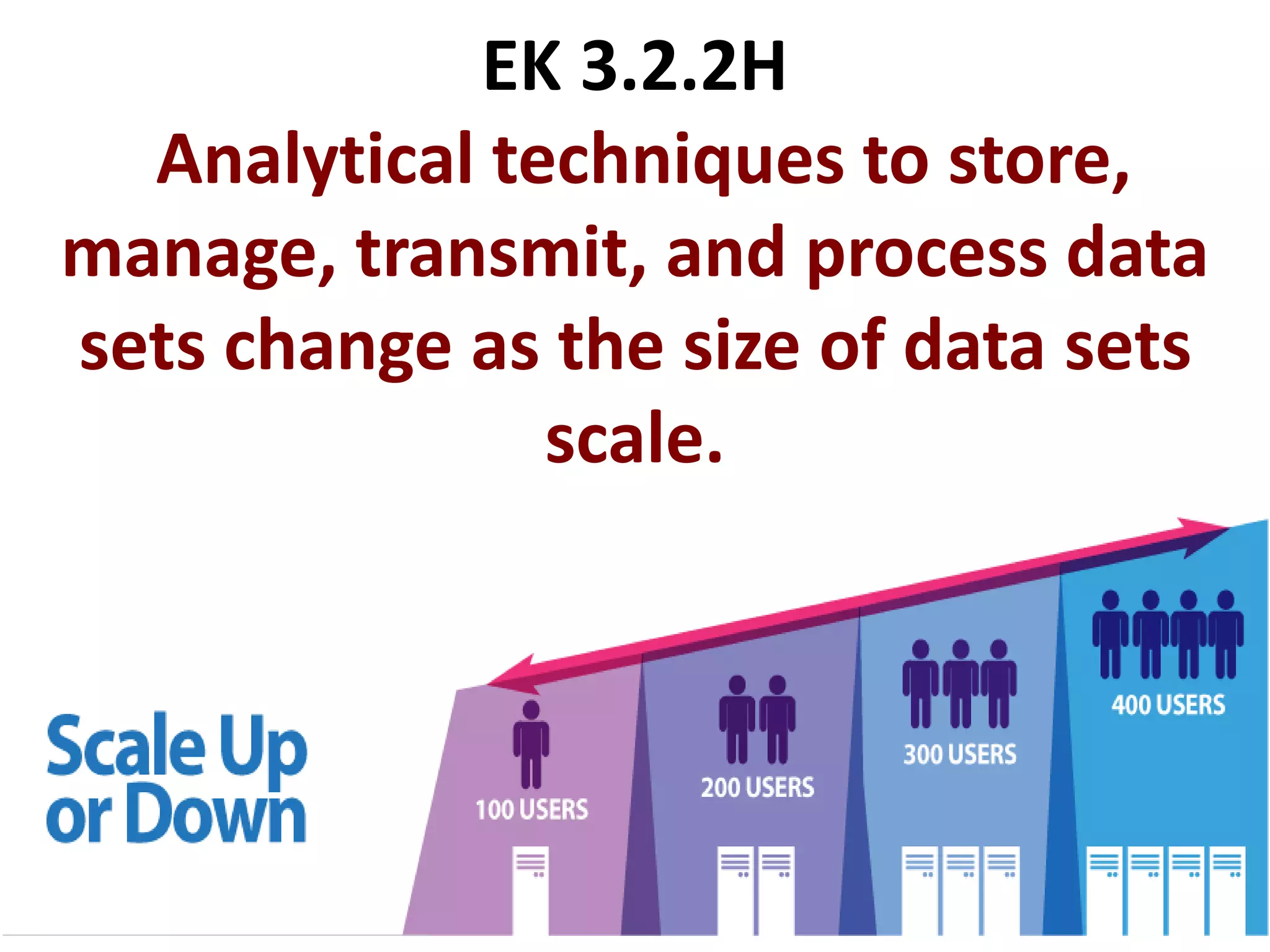
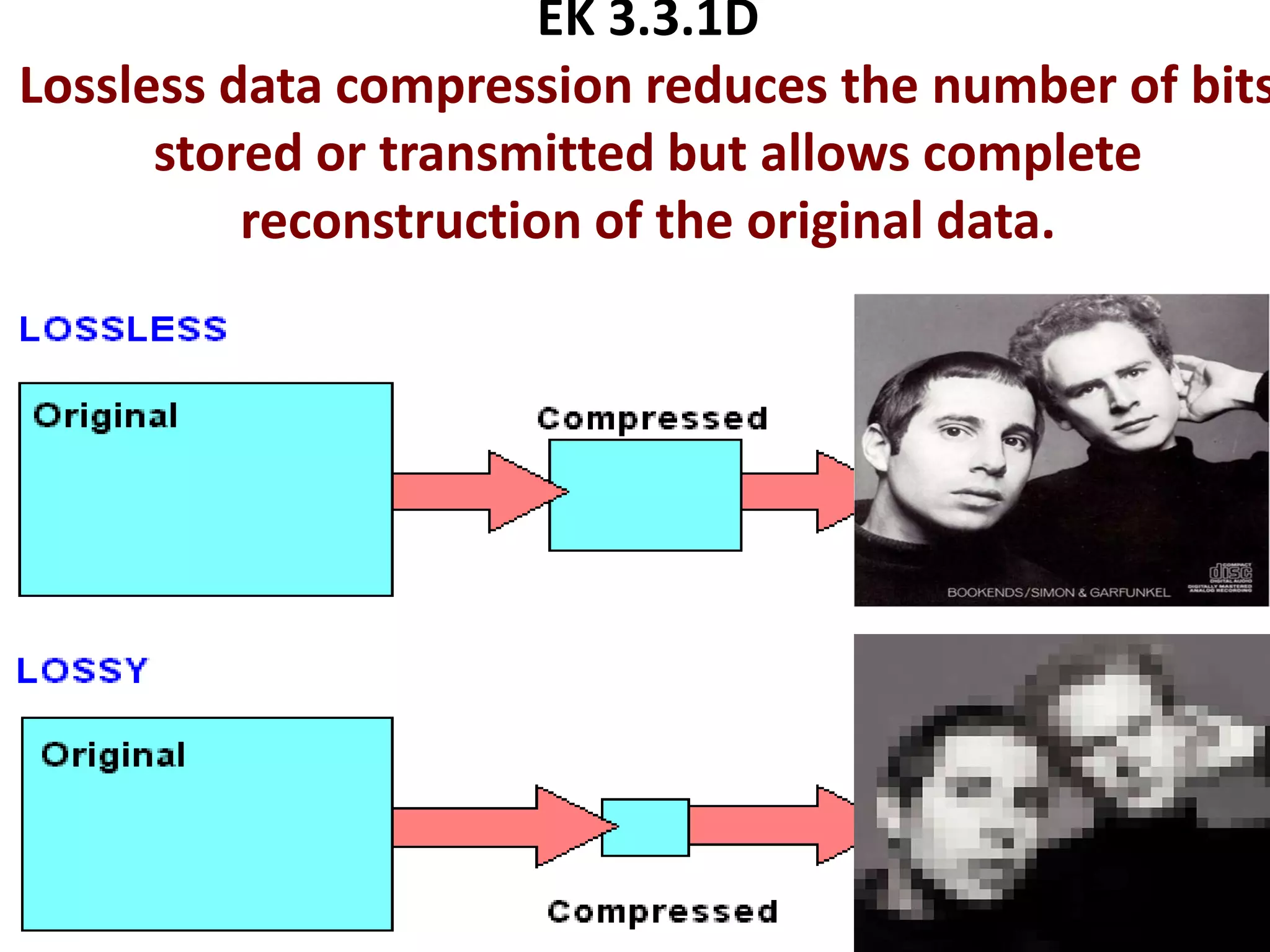
This document provides explanations and examples for key concepts related to using computers to process digital information and gain insight and knowledge from data. It discusses how computers can iteratively process data to learn things, filter and clean digital information, combine and classify data, and help patterns emerge. It also addresses how collaboration helps solve data-driven problems by bringing different perspectives and skills, and how visualizing and communicating data through tables, diagrams and summaries helps convey insights gained from computational analysis of large datasets. The document notes challenges around structuring, storing, maintaining privacy and scaling large datasets, as well as tradeoffs around data storage formats, compression techniques, and security versus privacy.