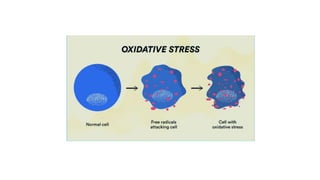
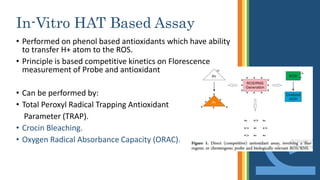
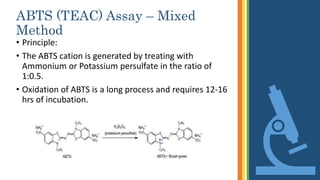
This document discusses various assays used to measure antioxidant activity. It begins by explaining that free radicals are produced during metabolic processes and can damage cells, but antioxidants terminate these reactions. Common antioxidants include vitamins C and E. Assays are used to quantitatively measure antioxidant potential and are based on hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) or electron transfer (ET) reactions. Examples of specific assays described include DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, catalase, and superoxide dismutase assays. Procedures for each assay are provided. The document emphasizes the importance of safety during experimental procedures.