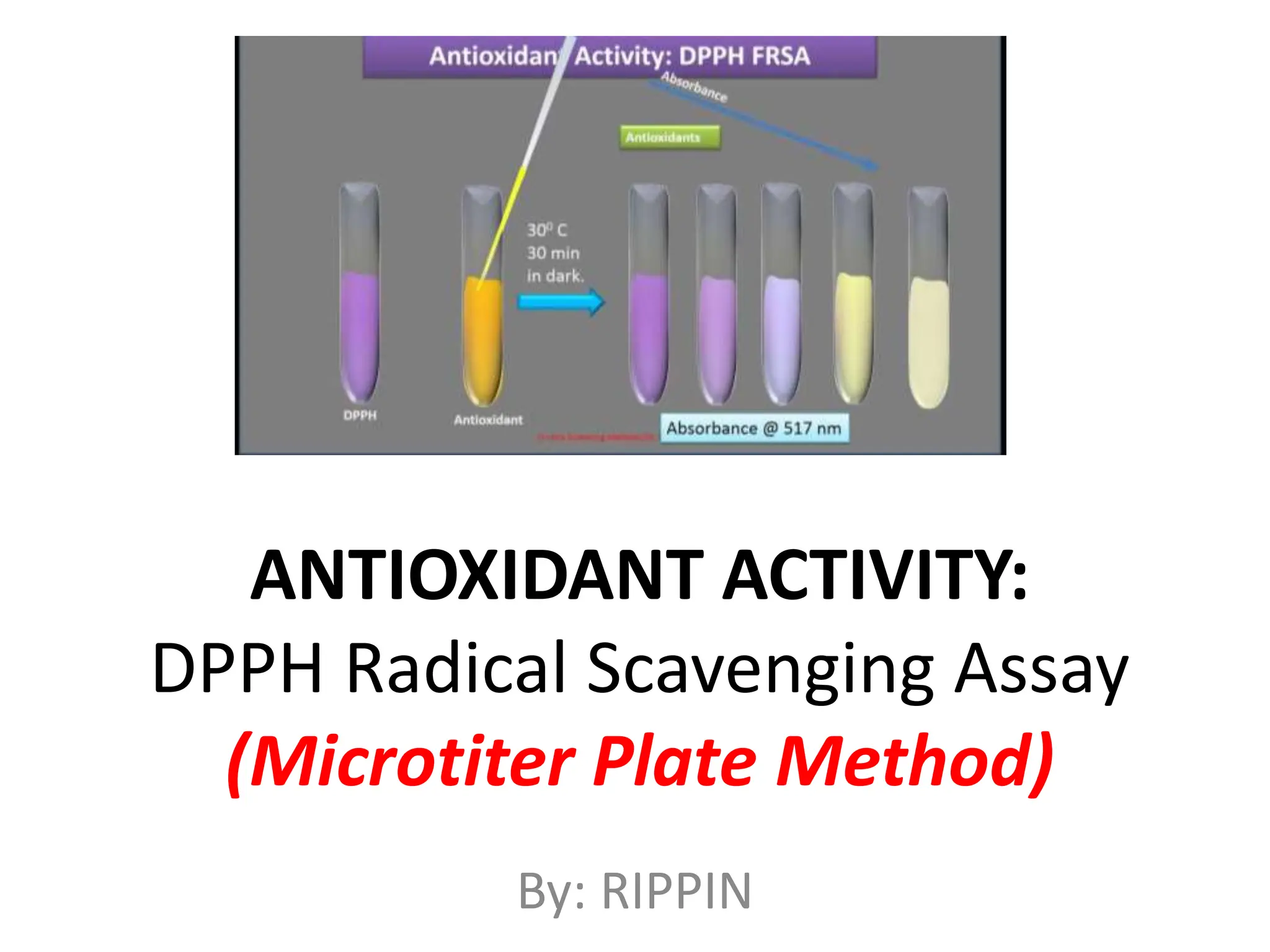
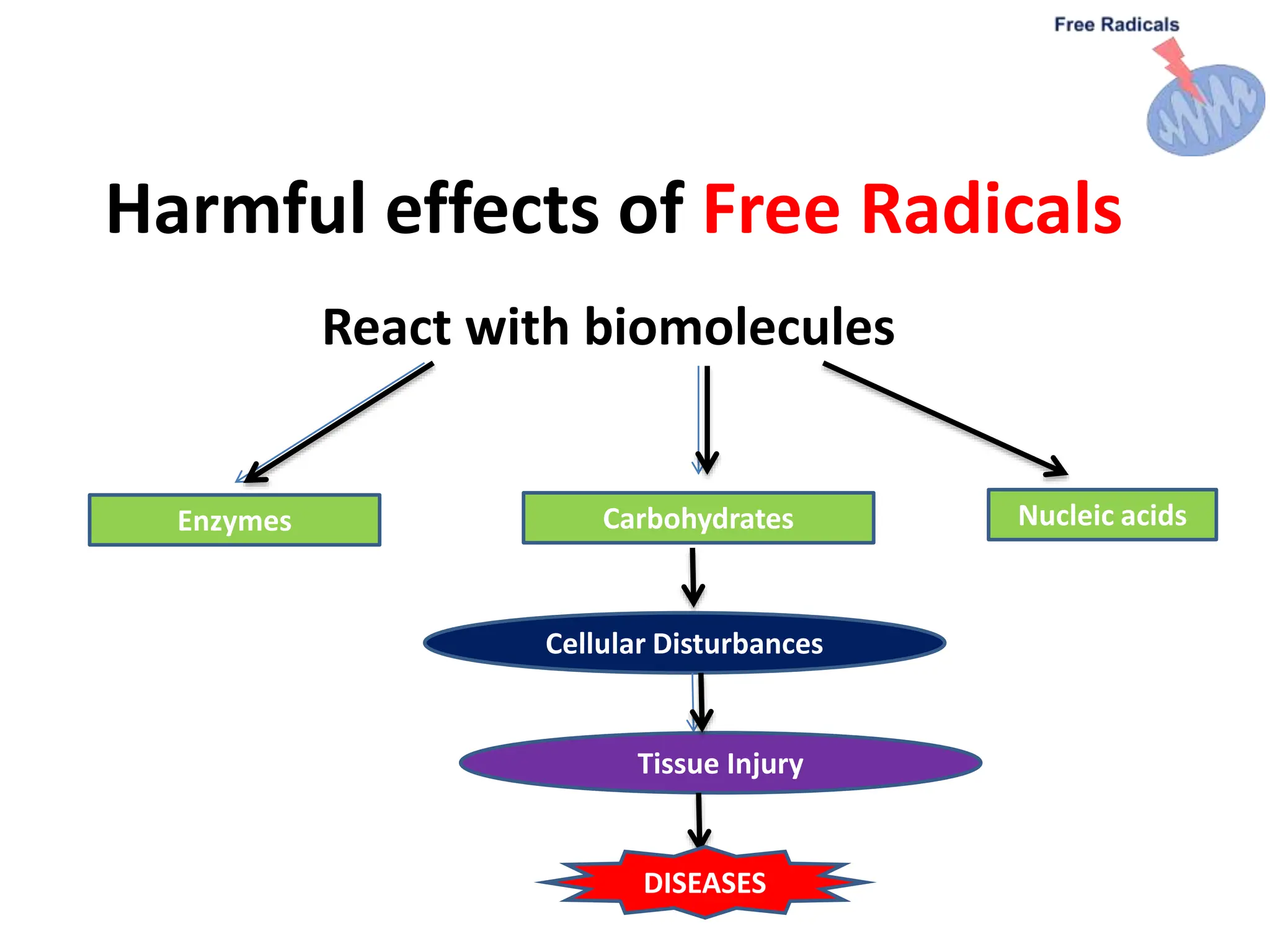
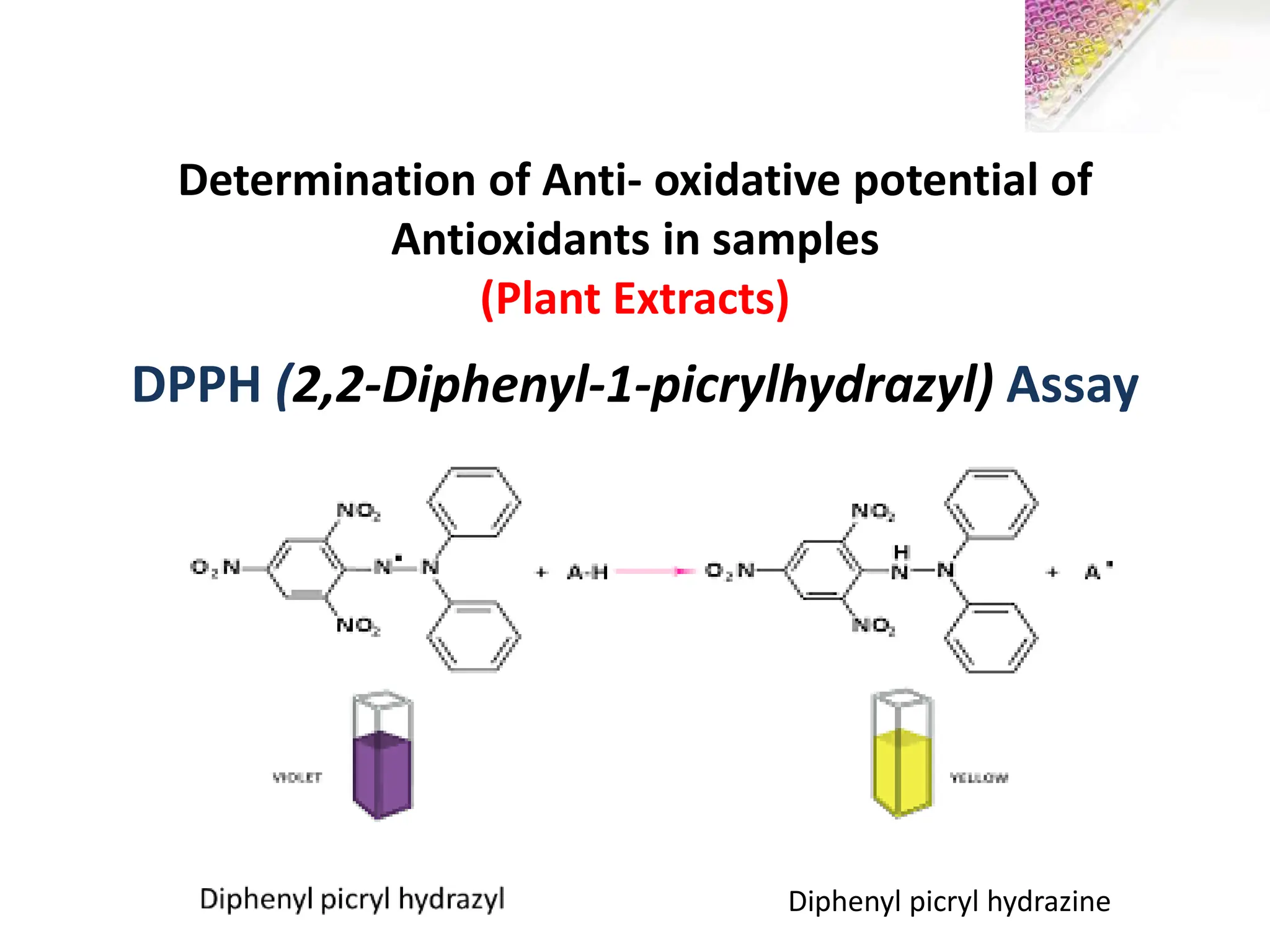
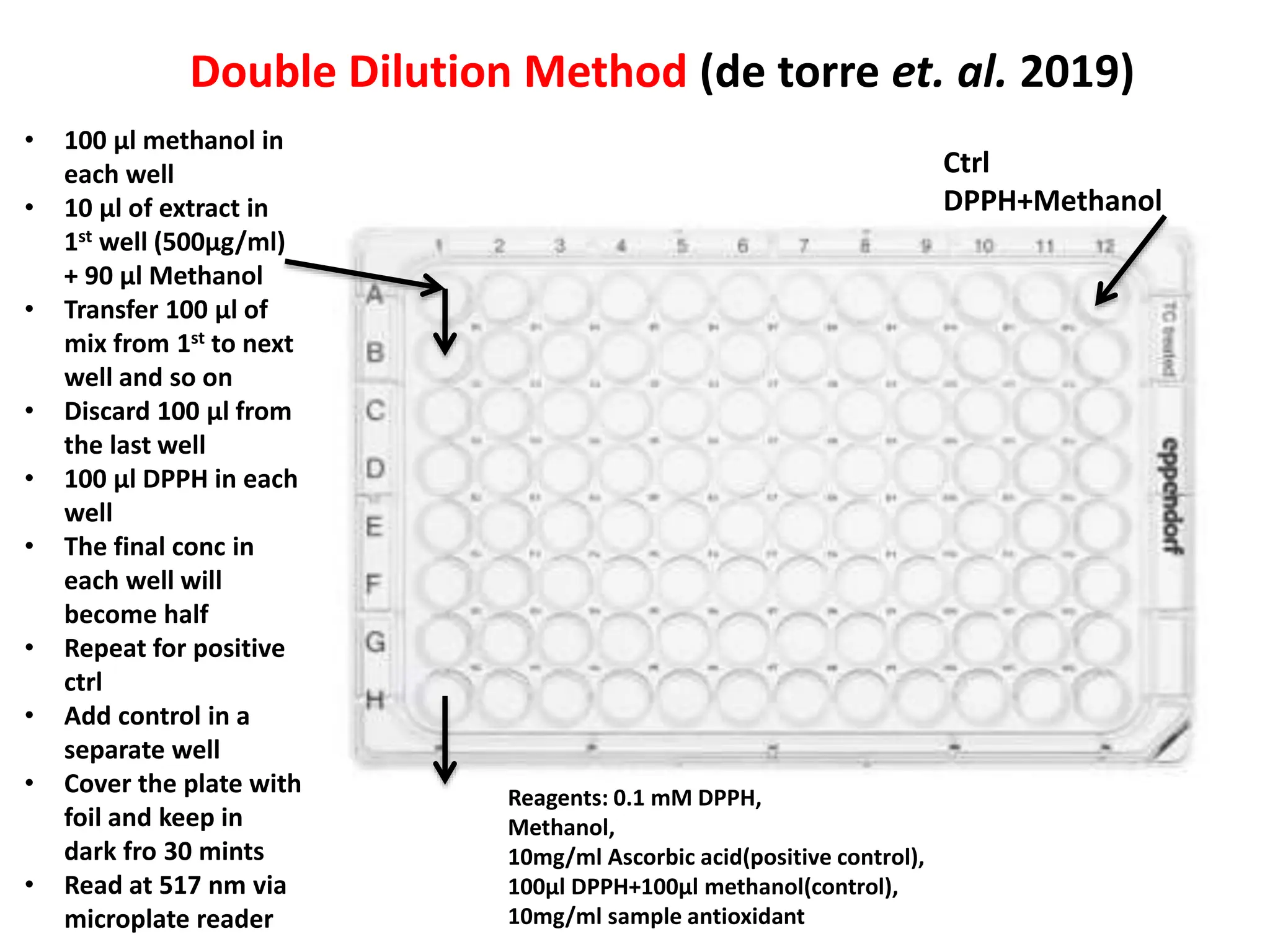
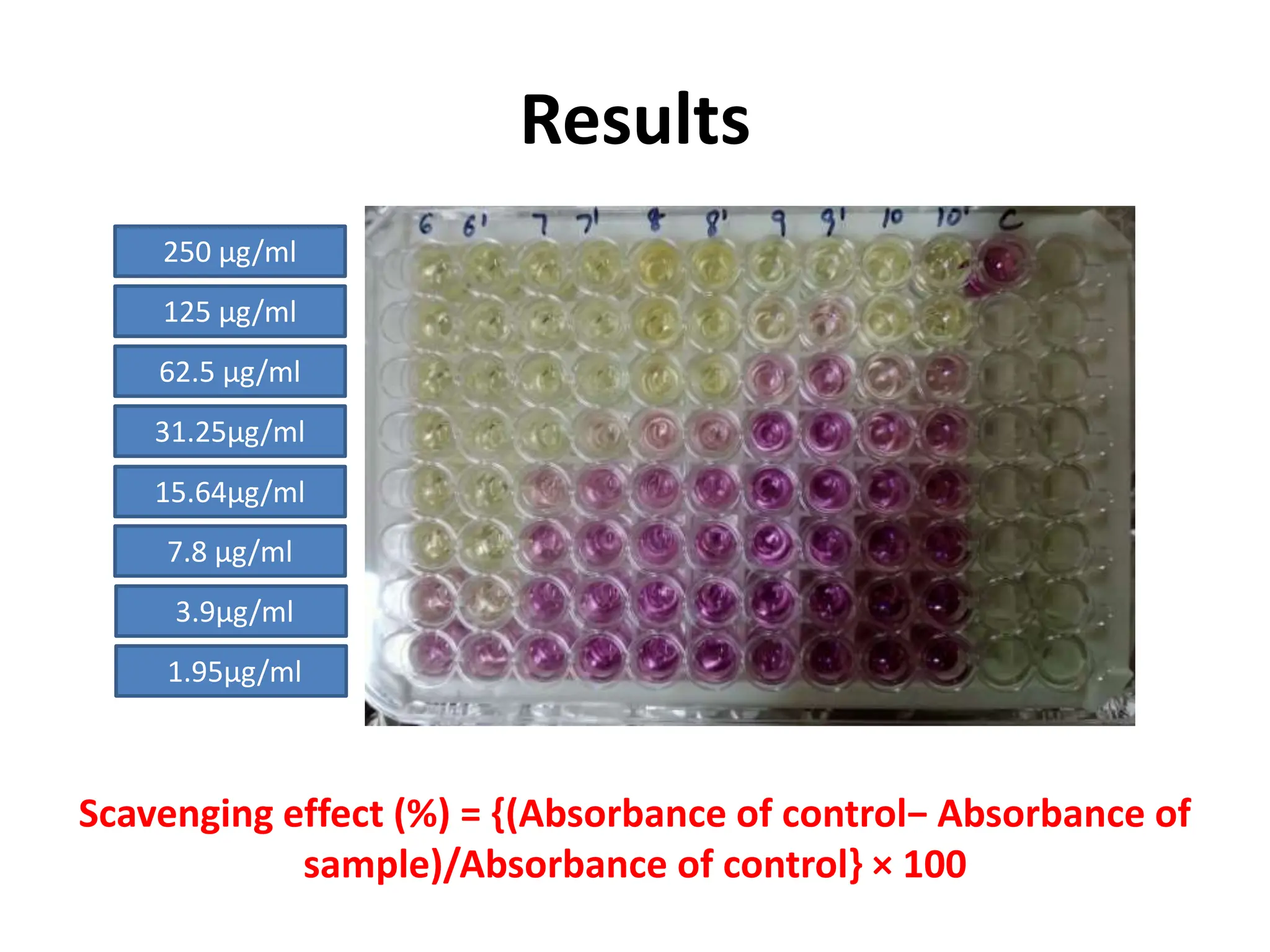
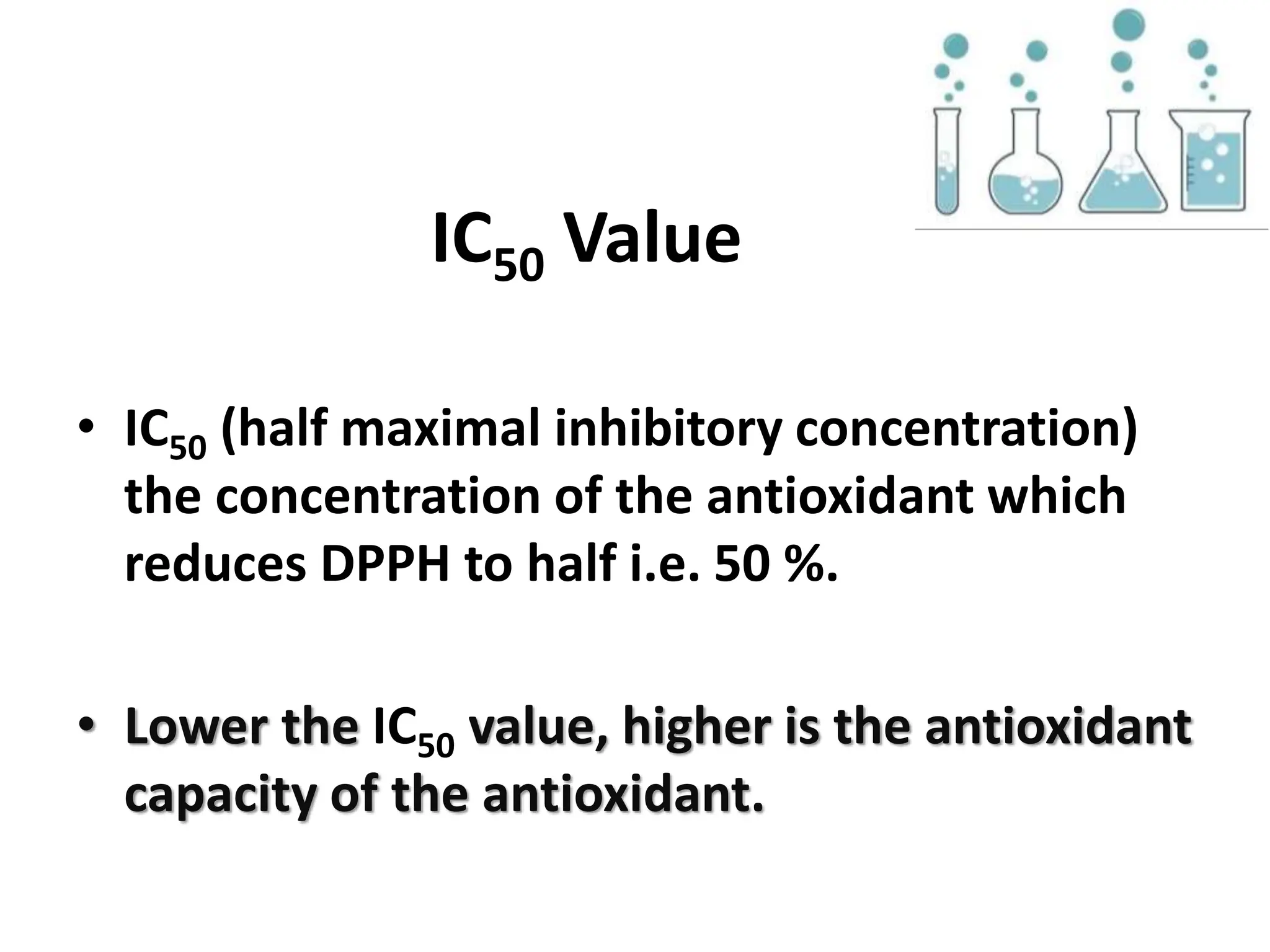
This document describes the DPPH radical scavenging assay method for determining the antioxidant potential of plant extracts. The DPPH assay involves adding varying concentrations of a test sample to the stable DPPH radical. Antioxidants in the sample will scavenge DPPH, reducing the purple color. The amount of color reduction is measured spectrophotometrically and used to calculate the sample's antioxidant capacity. A double dilution method is used to serially dilute the sample in microplate wells from 500 μg/ml to 1.95 μg/ml. The IC50 value, the concentration that causes 50% inhibition of DPPH, indicates the sample's antioxidant strength, with a lower IC50 reflecting higher antioxidant capacity.