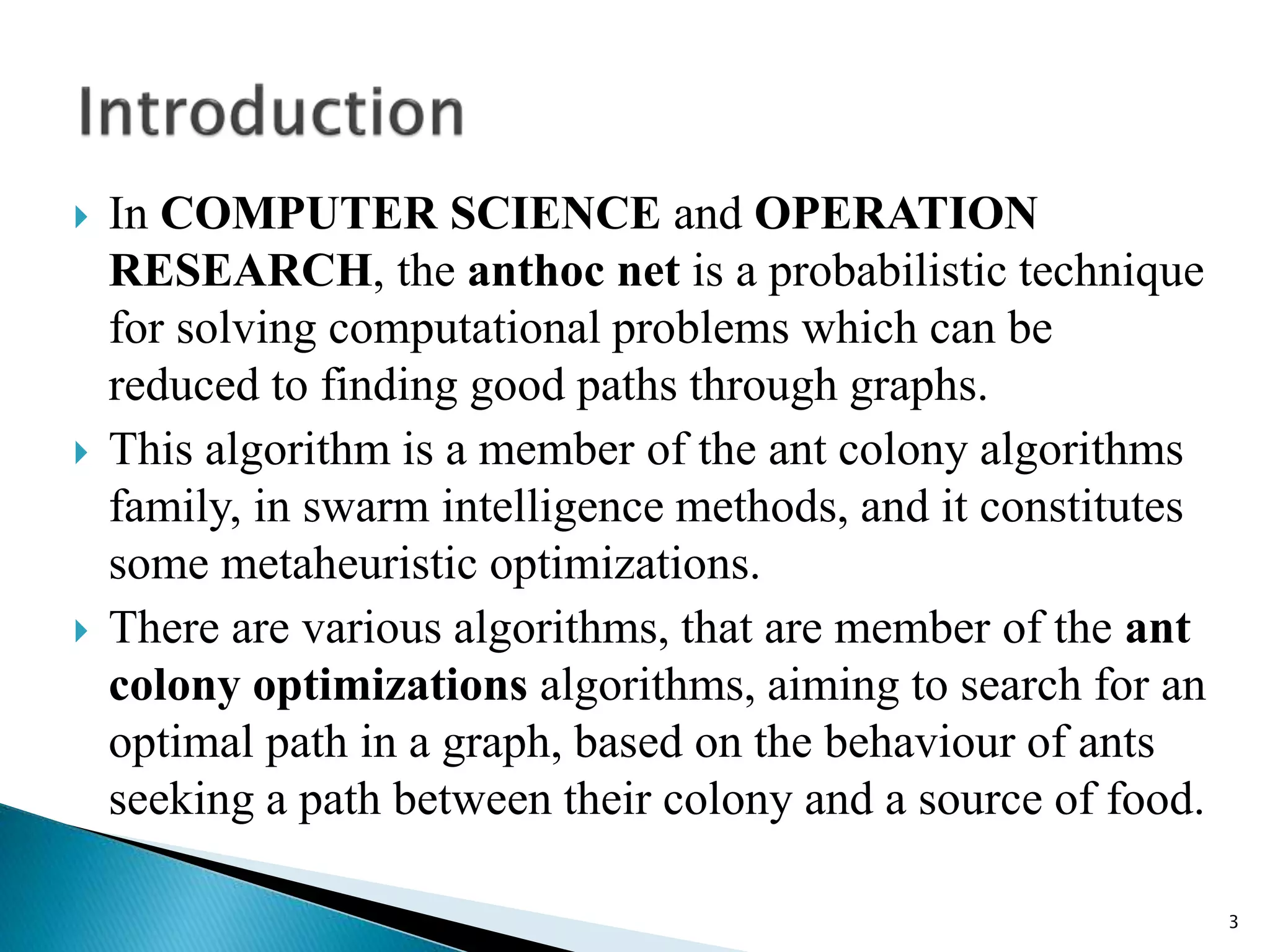
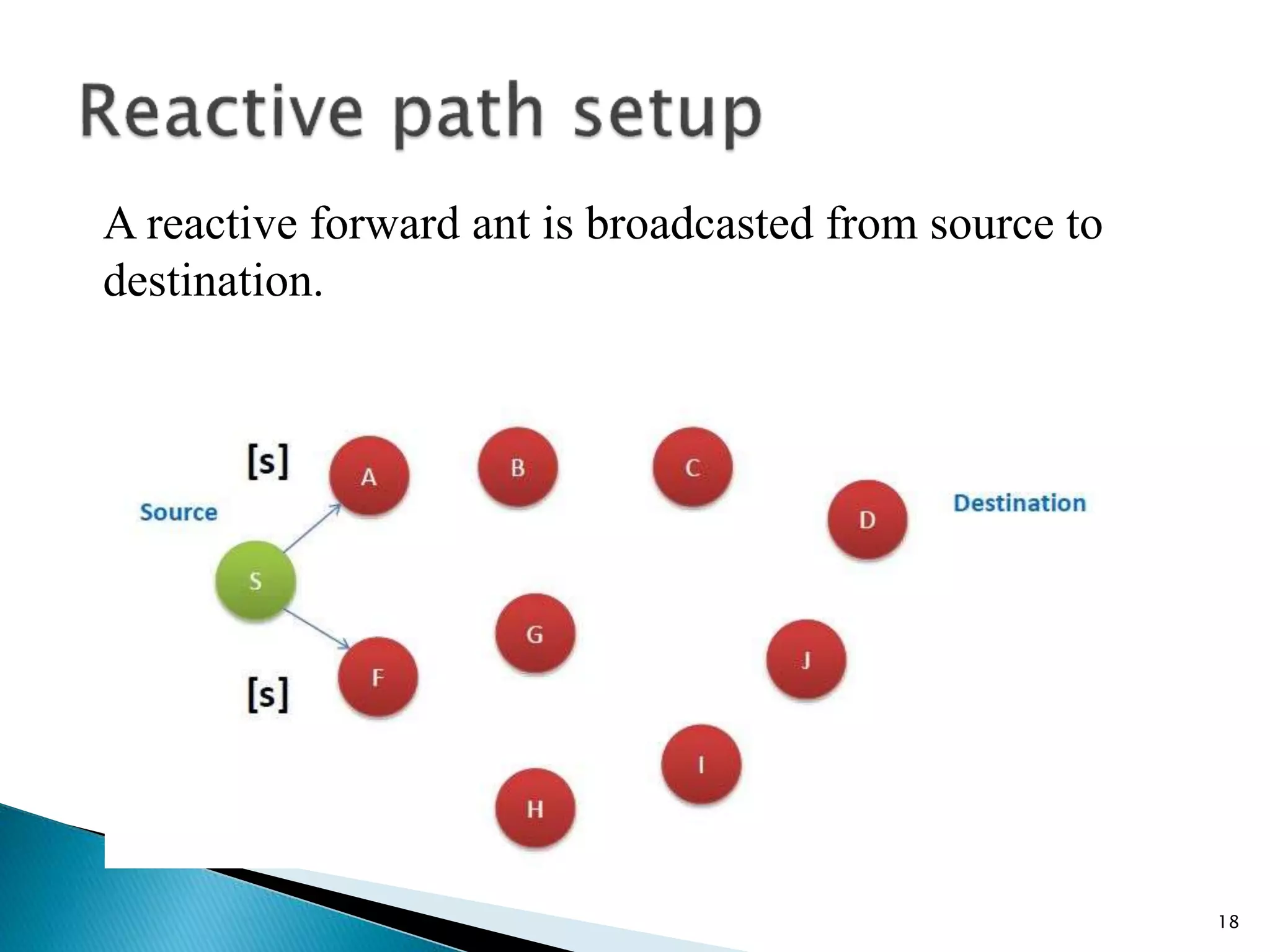
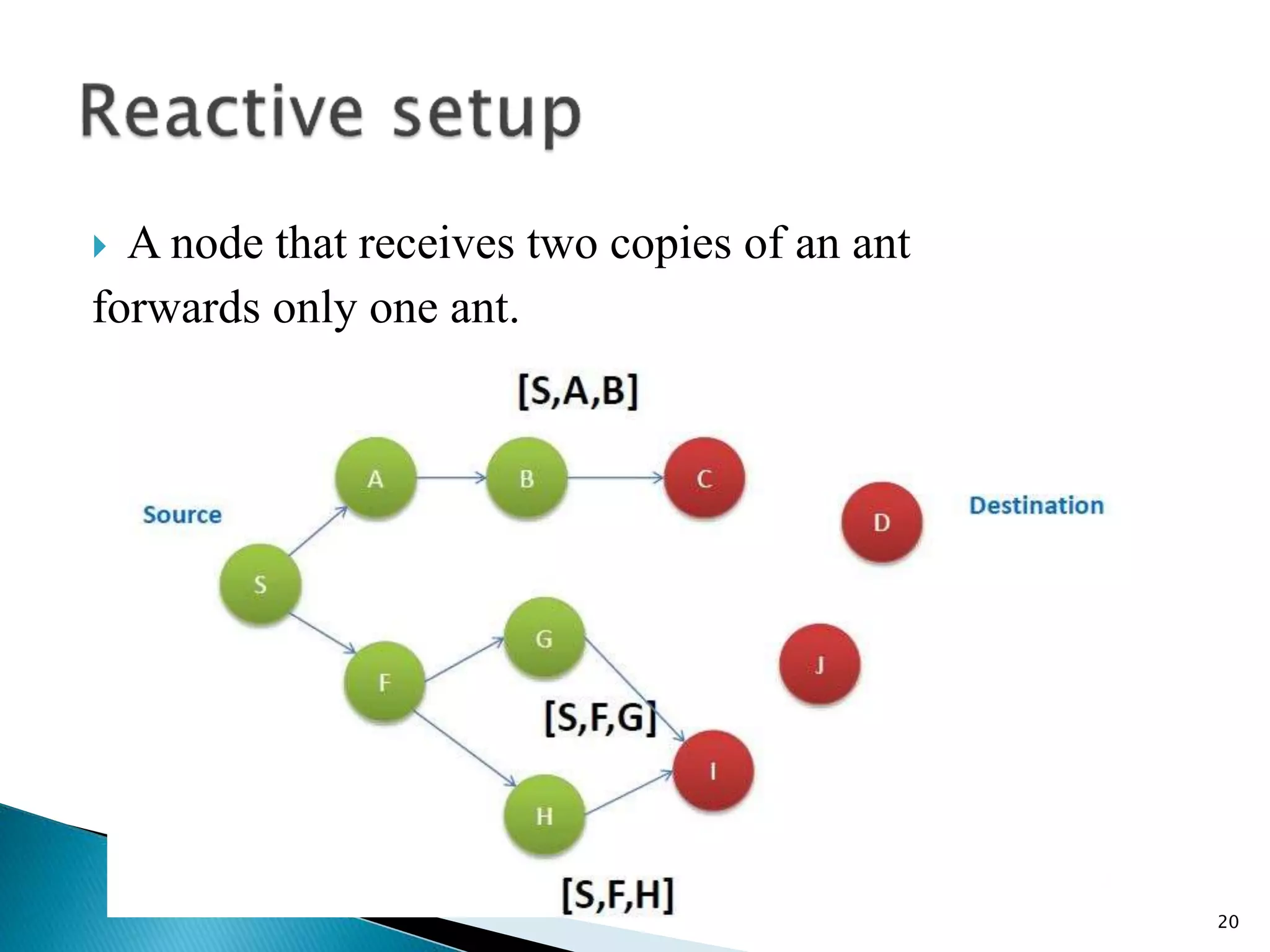
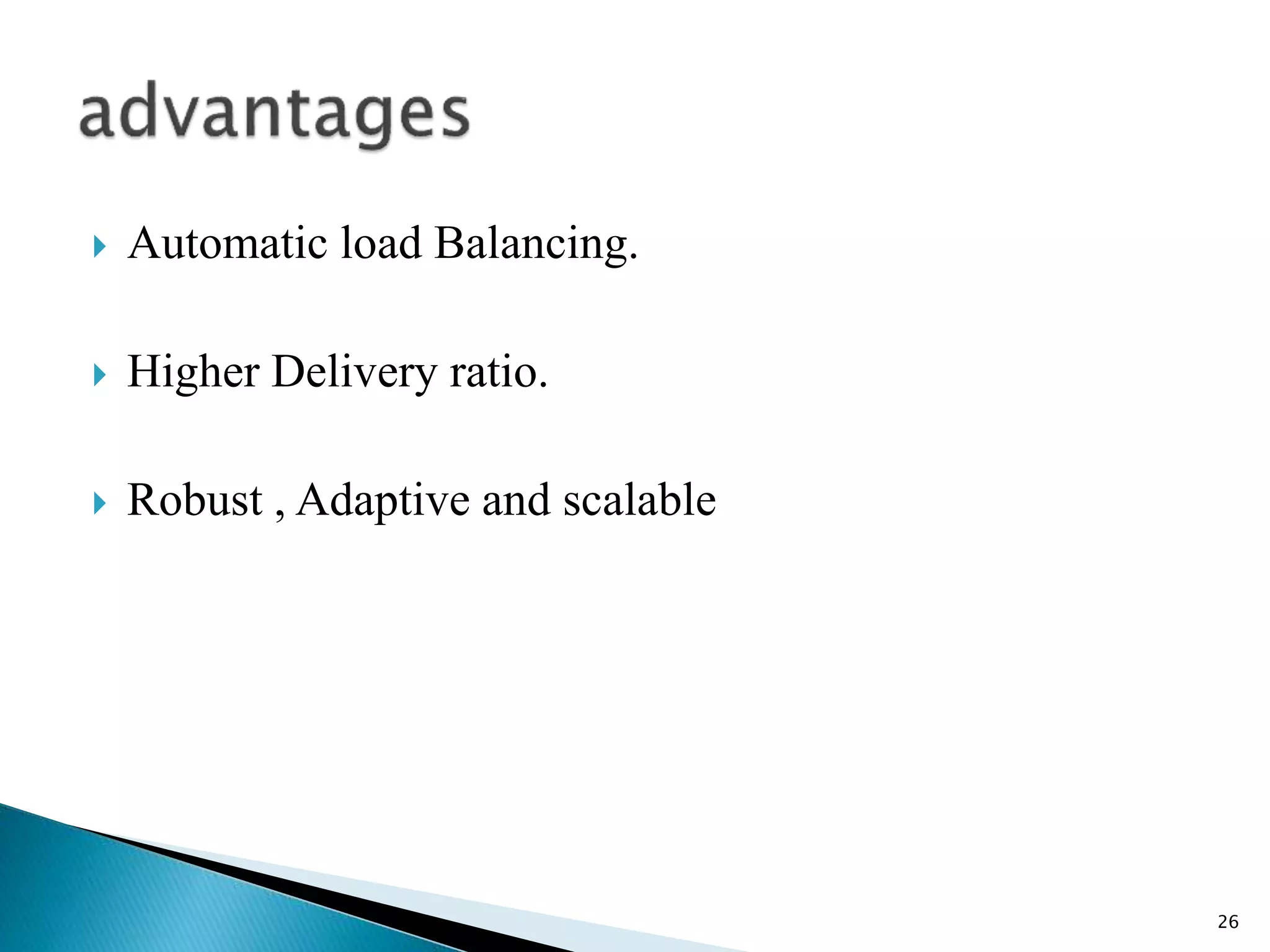
The document discusses the anthocnet routing algorithm for mobile ad-hoc networks (MANETs). It begins with an introduction to MANETs and their challenges like dynamic topology. It then discusses ant colony optimization techniques and how anthocnet is inspired by the behavior of real ants. Anthocnet uses reactive path setup, proactive path maintenance, and stochastic data forwarding. It handles link failures by allowing nodes to detect failures and update their routing tables. The key advantages of anthocnet are automatic load balancing, higher delivery ratio, and robustness to changes in the network.






















![ [1] The internet engineering task force mobile ad-hoc networking
page(MANET). Available from:
http://www.ietf.org/html.charters/
manet-charter.html.
[2] Microsoft Mesh Networks. Available from: http://research.
microsoft.com/mesh/.
[3] ANTHOCNET, Available from
http://www.idsia.ch/~frederick
/anthocnet/anthocnet.html
[4] B. Baran and R. Sosa. A new approach for AntNet routing. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer
Communications Networks, Las Vegas, USA, 2000.
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17304001-abidha-200209164746/75/ANTHOCNET-HYBRID-ROUTING-ALGORITHM-FOR-MANET-USING-SWARM-TECHNOLOGY-27-2048.jpg)
