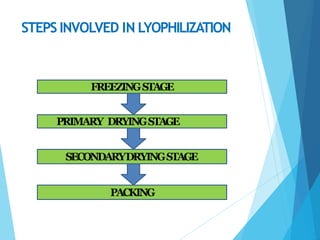
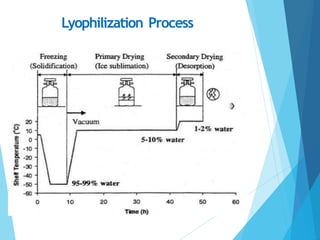
This document discusses various methods for preserving bacteria, including periodic transfer to fresh media, refrigeration, cryopreservation, storage in water, agar slant culture, porcelain bead technique, storage in silica gel, preservation in soil, and lyophilization. Lyophilization, or freeze drying, is described as one of the best preservation methods as it reduces the risk of intracellular ice crystallization by removing water from specimens, effectively preventing damage and allowing bacteria to remain viable for up to 30 years. The lyophilization process involves freezing, primary drying, secondary drying, and packaging stages.

















![STORAGE IN SOIL
Storing organisms in soil fall into two groups;
[1]sterile soil infested with small amount of inoculum,immediately
dried and stored in refrigerator.
[2]Soil infested with the organism,than incubated allowing
The organism to grow;thus the mycelium and propagative unit of
second generation are preserved.
The soil preservation method is useful for fungi,and by this method
actinomycetes are maintained in soil for 4 to 5 years,and there are
several bacterial spp which are also maintained in soi for several
years.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalankiitppt-190426115740/85/ANKIT-PPT-ON-BACTERIAL-PRESERVATION-20-320.jpg)