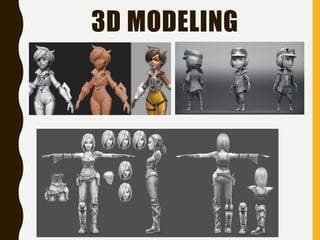
The document discusses various types of animation, including cel, 2D, 3D, motion graphics, and stop-motion animation, each with distinct techniques and characteristics. It outlines the traditional cel animation process and contrasts it with modern methods like 2D and 3D animations which utilize computer software. Additionally, the production pipeline for creating animations is detailed, encompassing stages from idea development to final rendering.