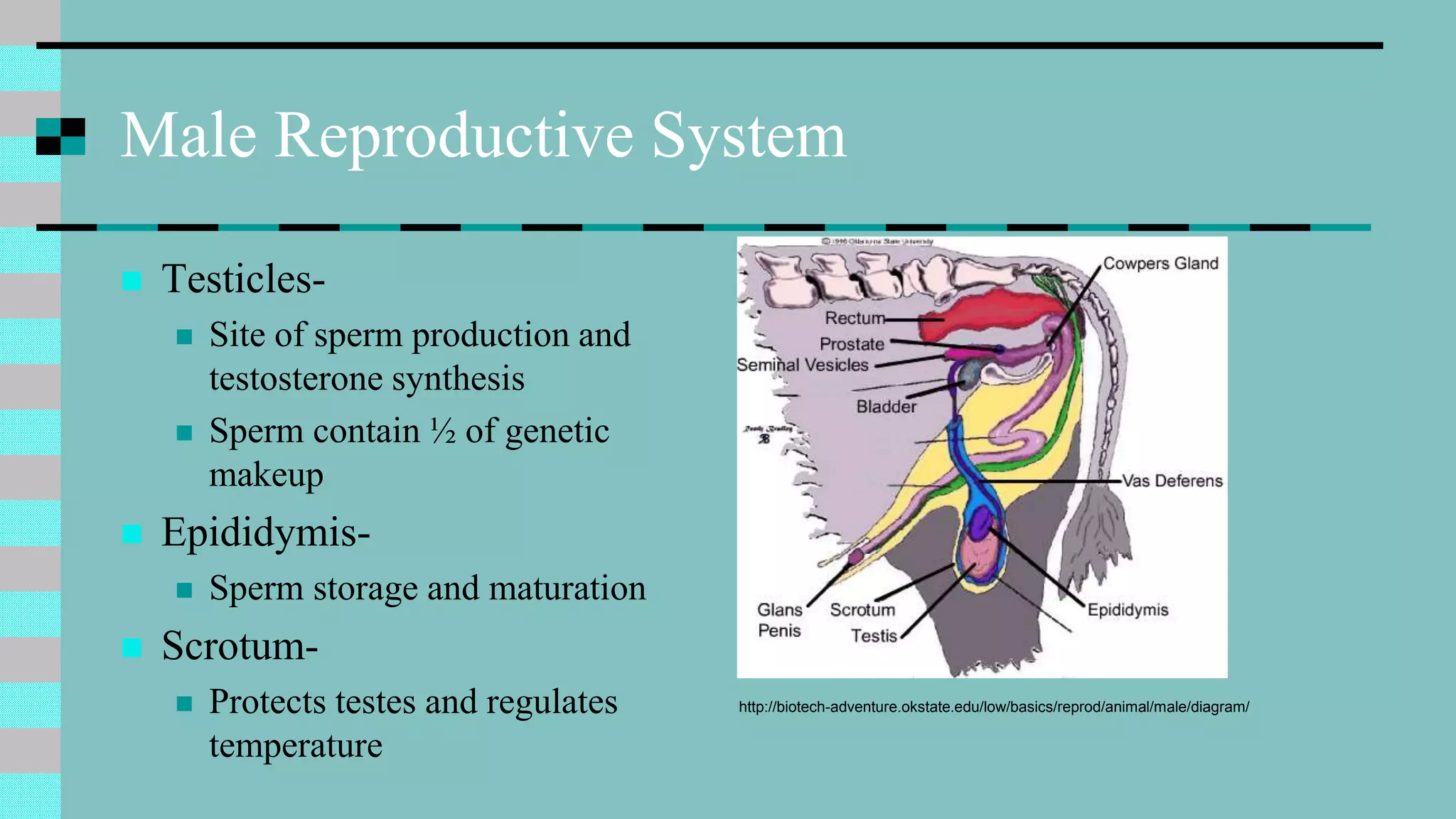
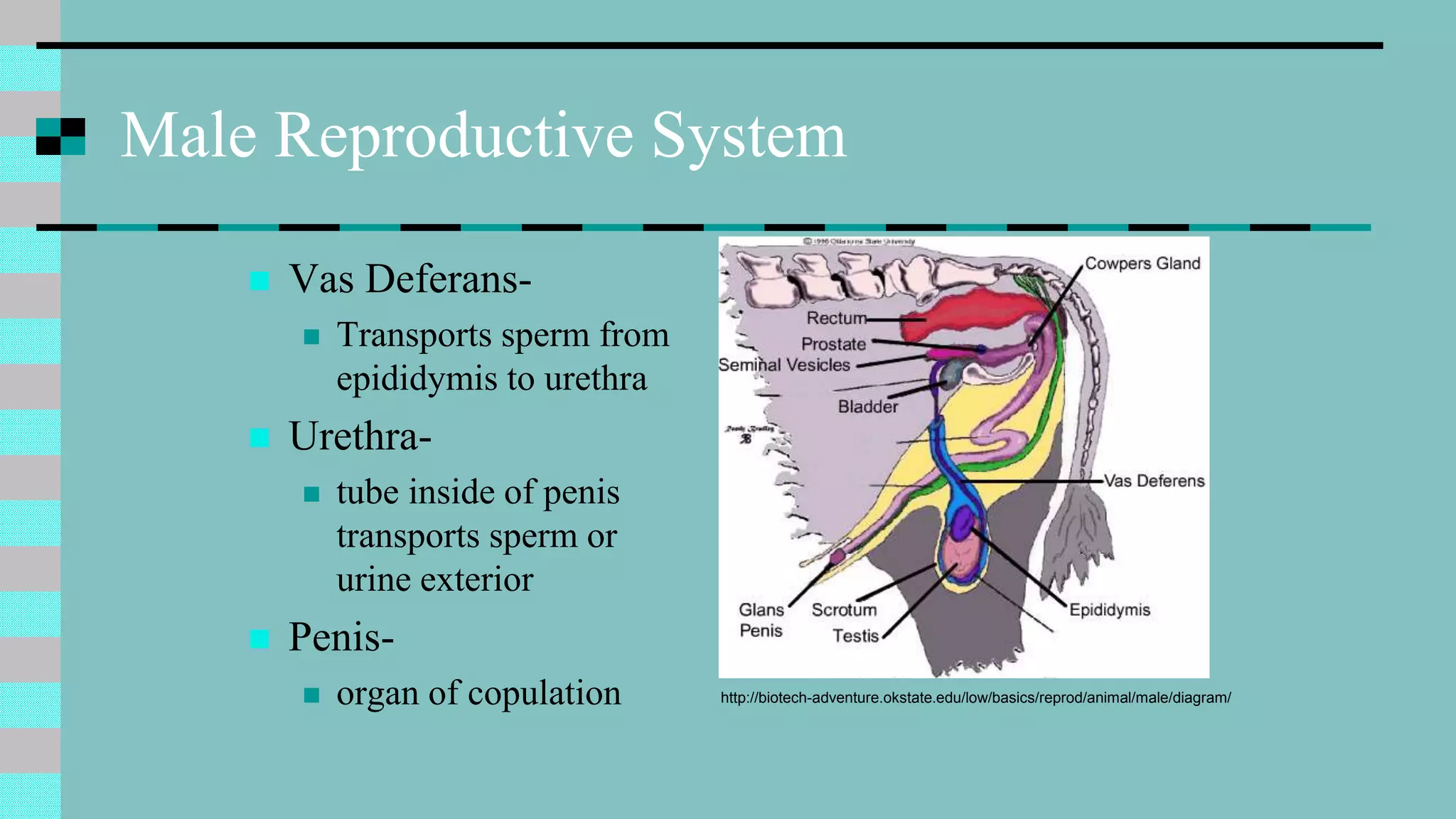
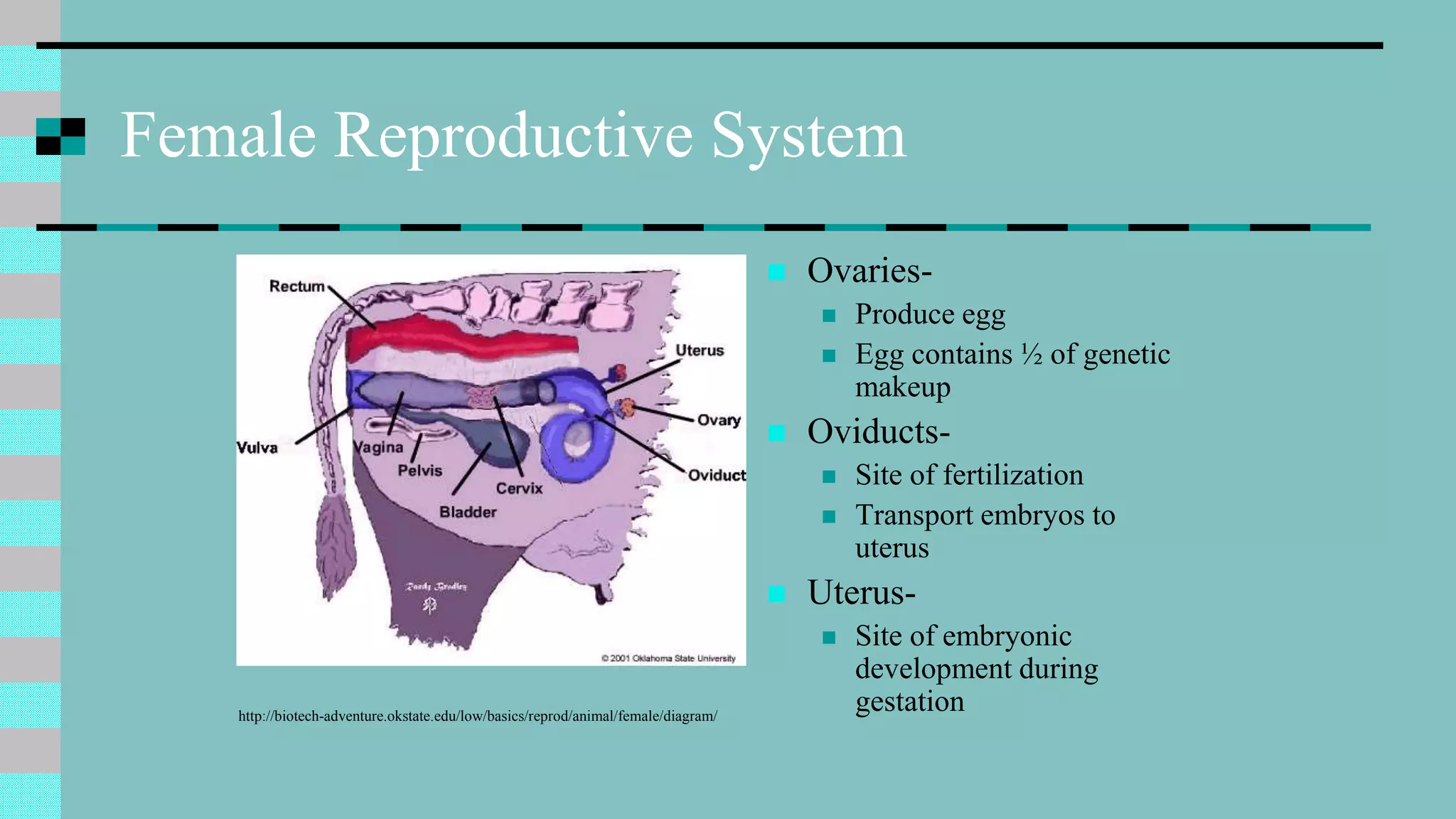
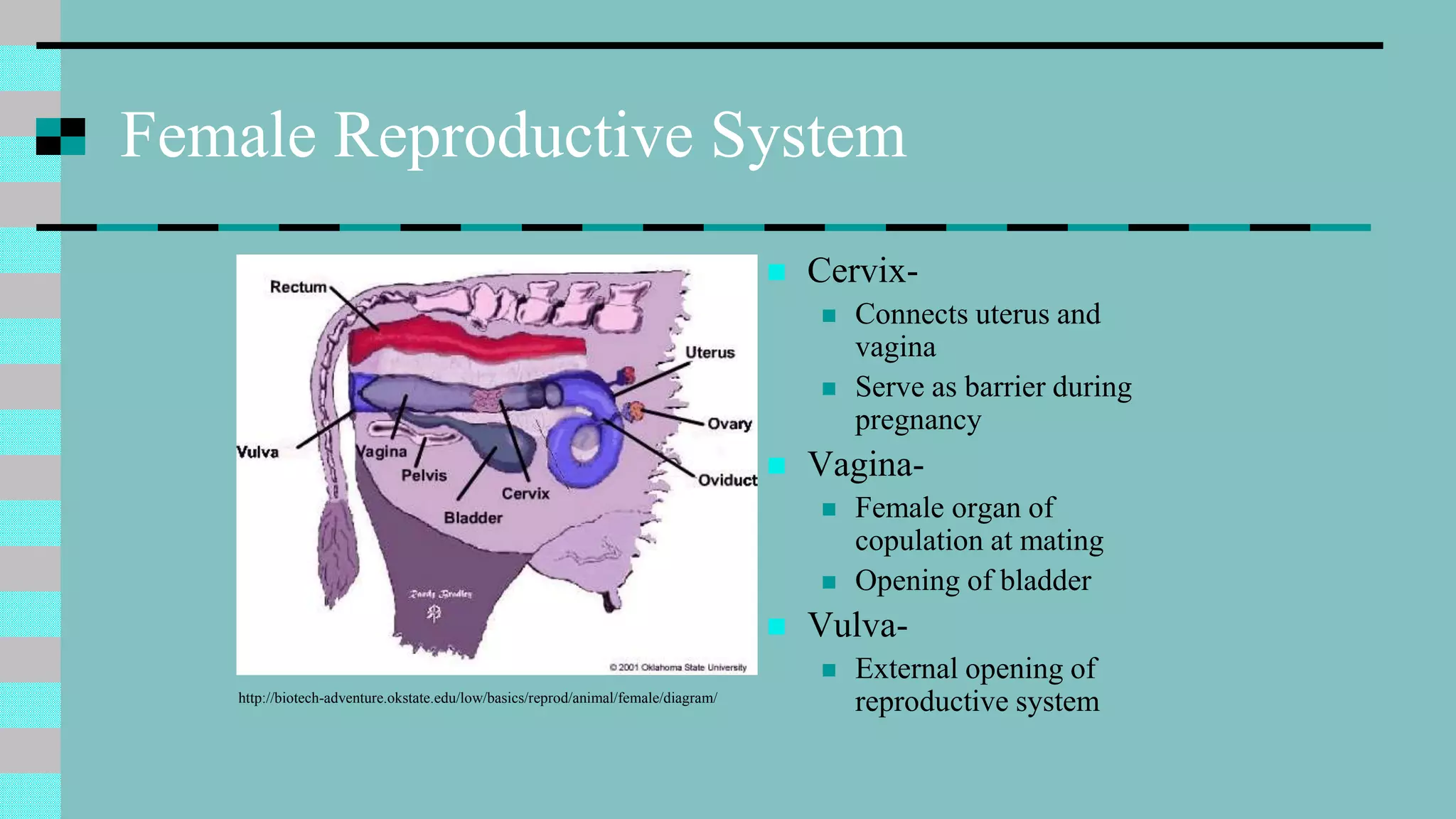
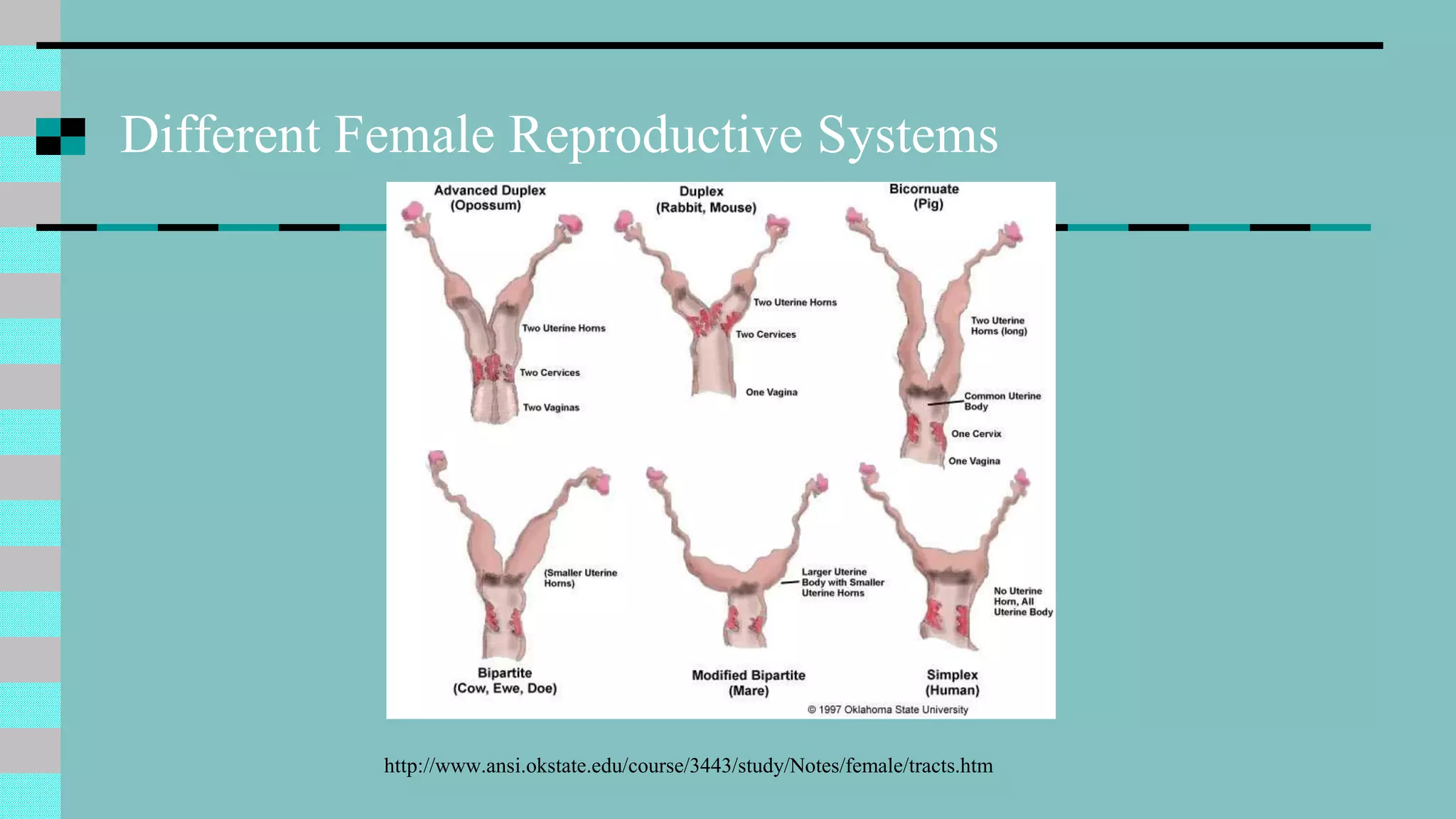
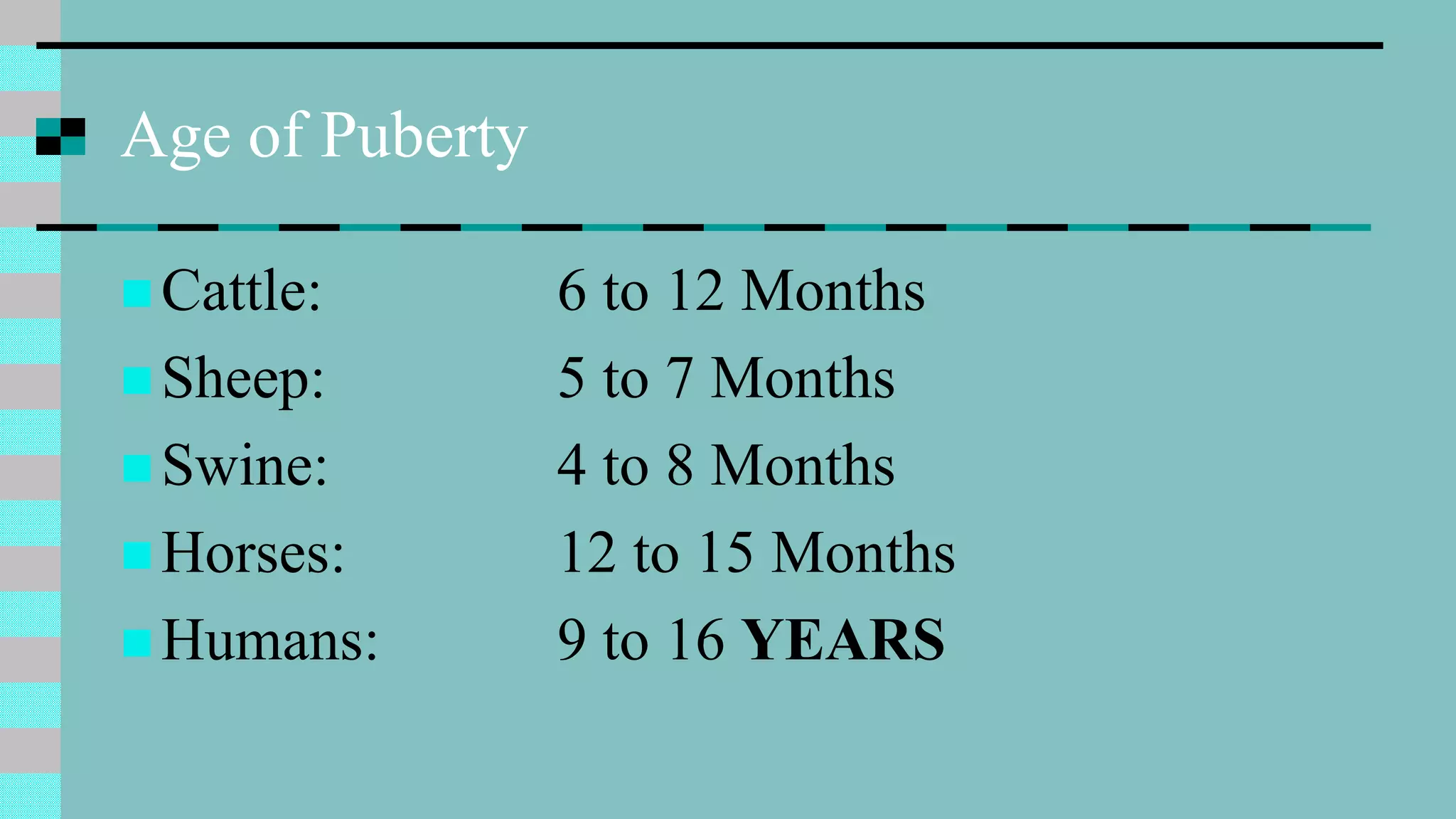
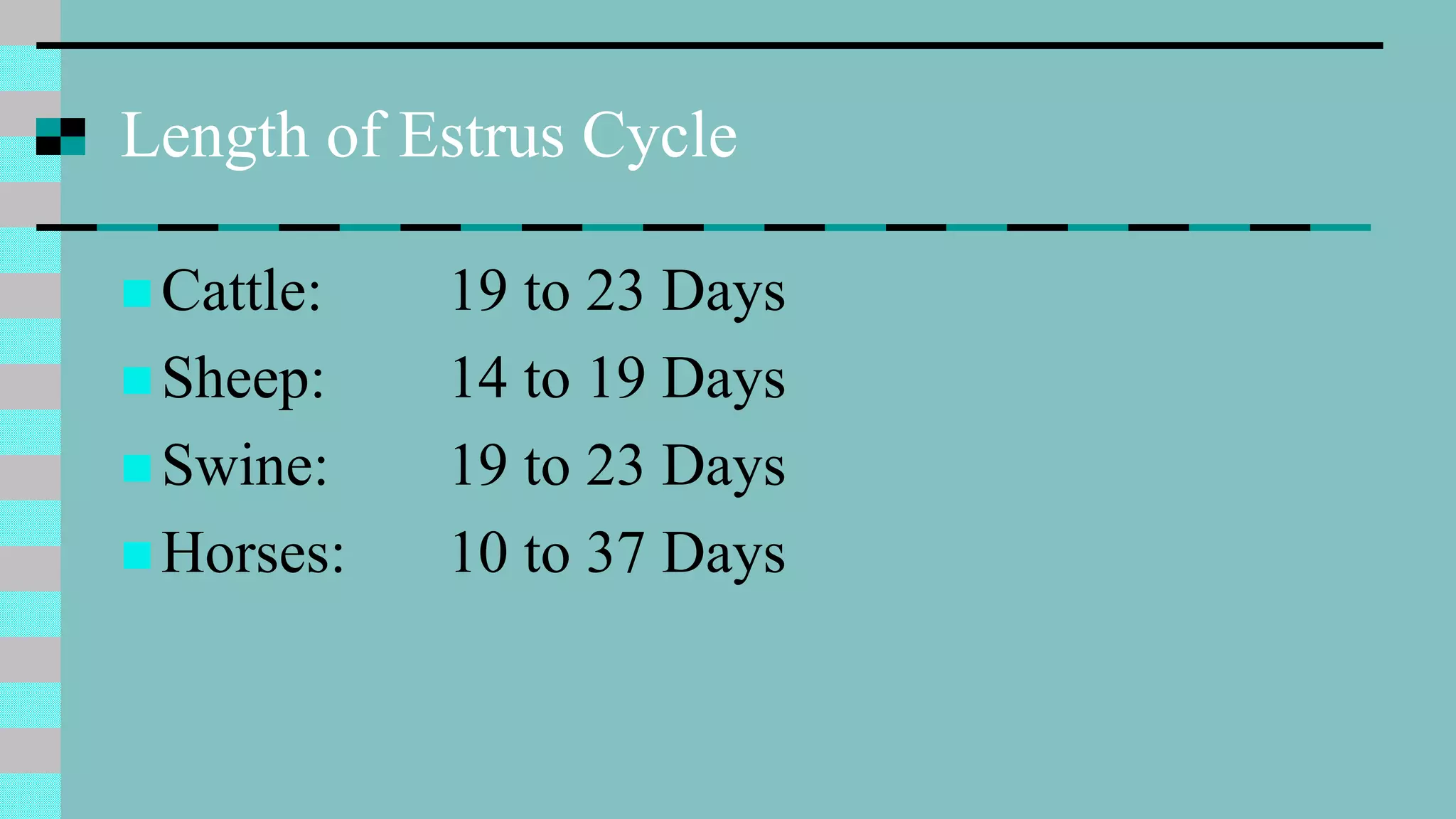
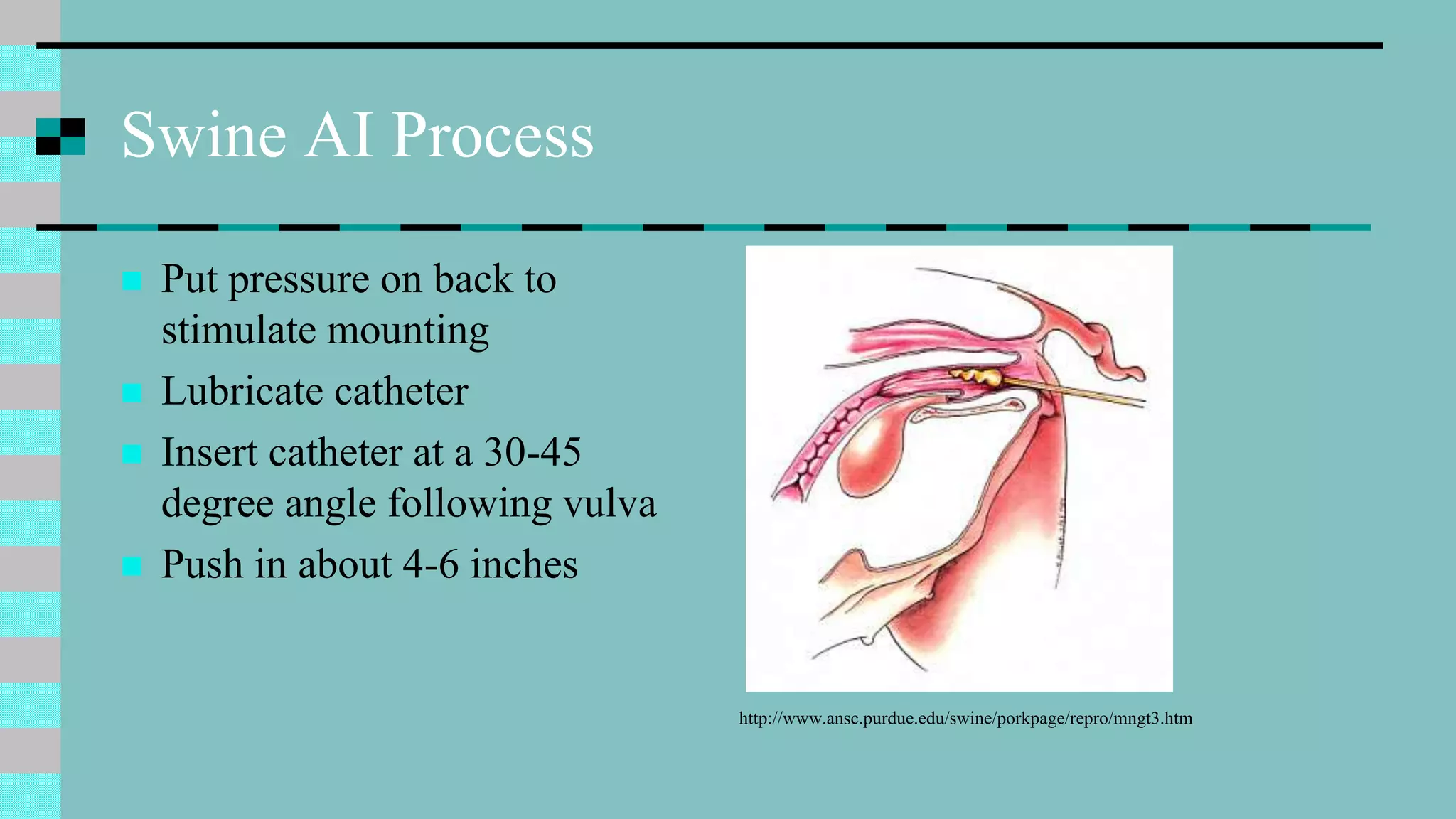
This document discusses animal reproduction, including the hormones involved, male and female reproductive systems, the estrous cycle, signs of estrus, gestation length, signs of parturition, artificial insemination, and differences between species. Key points include testosterone and estrogen roles, ovarian and uterine cycle phases, estrus duration times varying between species, gestation length differences, signs of impending birth, and the process of artificial insemination including checking for heat and proper insertion technique.