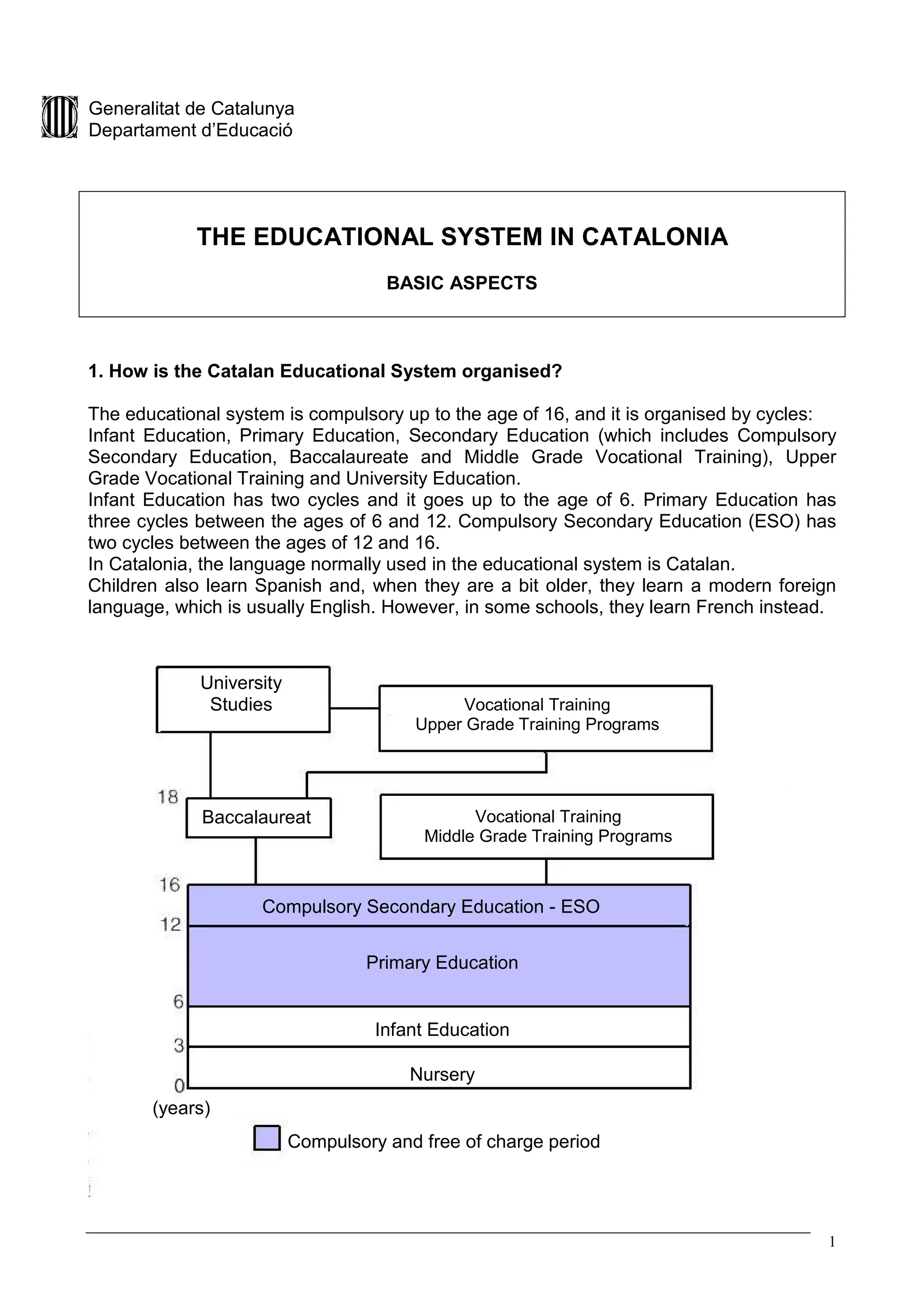
The educational system in Catalonia is organized into cycles from infant education up through university level. It is compulsory through age 16 and is commonly taught in Catalan, though Spanish and English are also taught. Schools can be public, public but subsidized, or private. Registration requires completing an application and submitting documentation by certain deadlines. Schools are staffed by directors, tutors, teachers and other personnel. Students and families have both rights like to education and duties like attending school. Financial assistance is available, and the school year runs September through June divided into quarters.