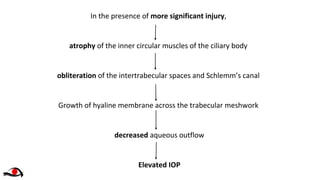
The document summarizes several studies on angle recession glaucoma following blunt ocular trauma.
The first study found that ultrasound biomicroscopy is useful for detecting angle pathology when the media is hazy. Surgical treatment resulted in more stable and normal intraocular pressure compared to medical treatment alone.
The second study in Bangladesh found that conservative treatment controlled intraocular pressure in most cases, while a small percentage required surgery.
The third study found that trabeculectomy with antimetabolic drugs was most effective for uncontrolled angle recession glaucoma, but carried a higher risk of late bleb infection.