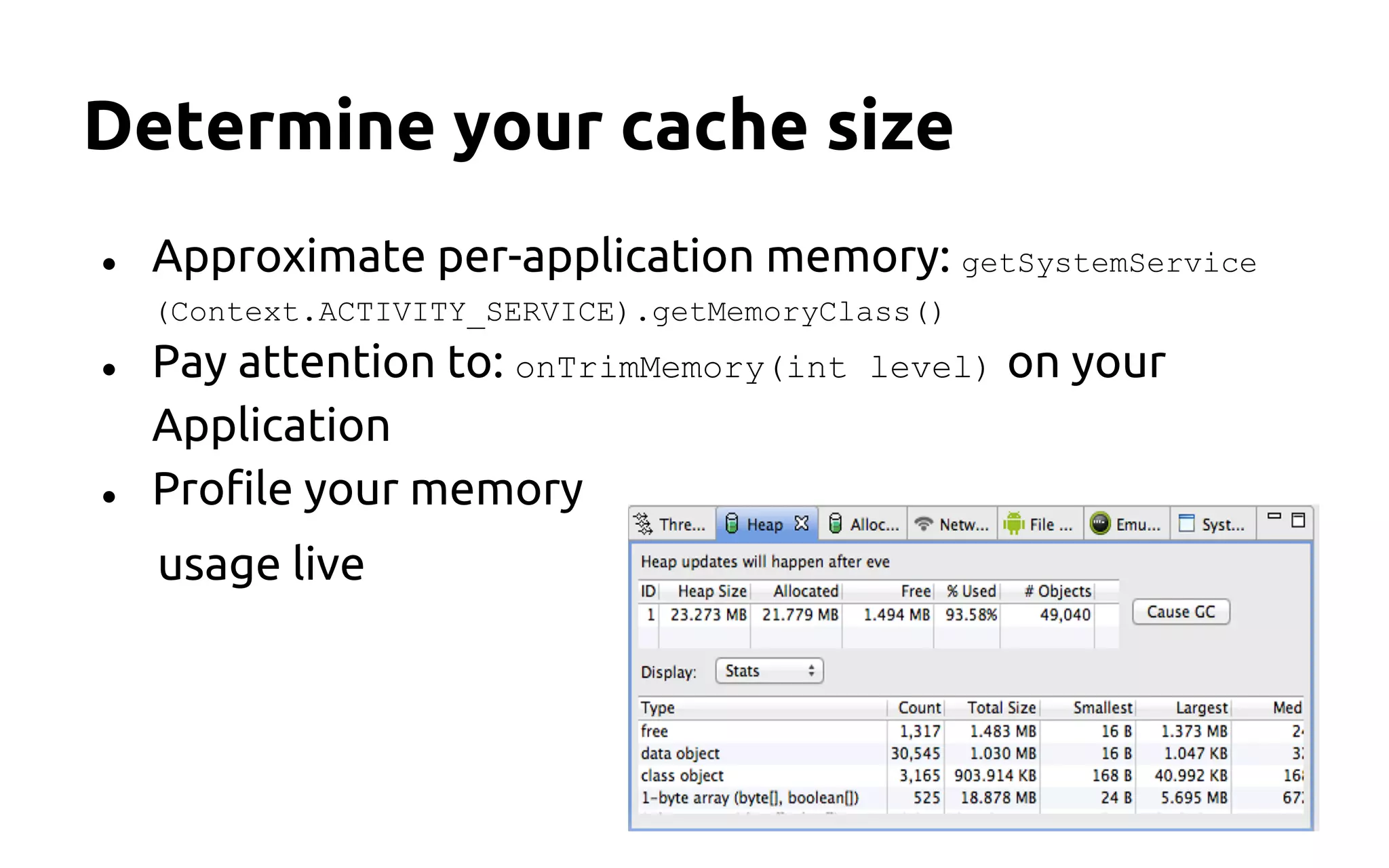
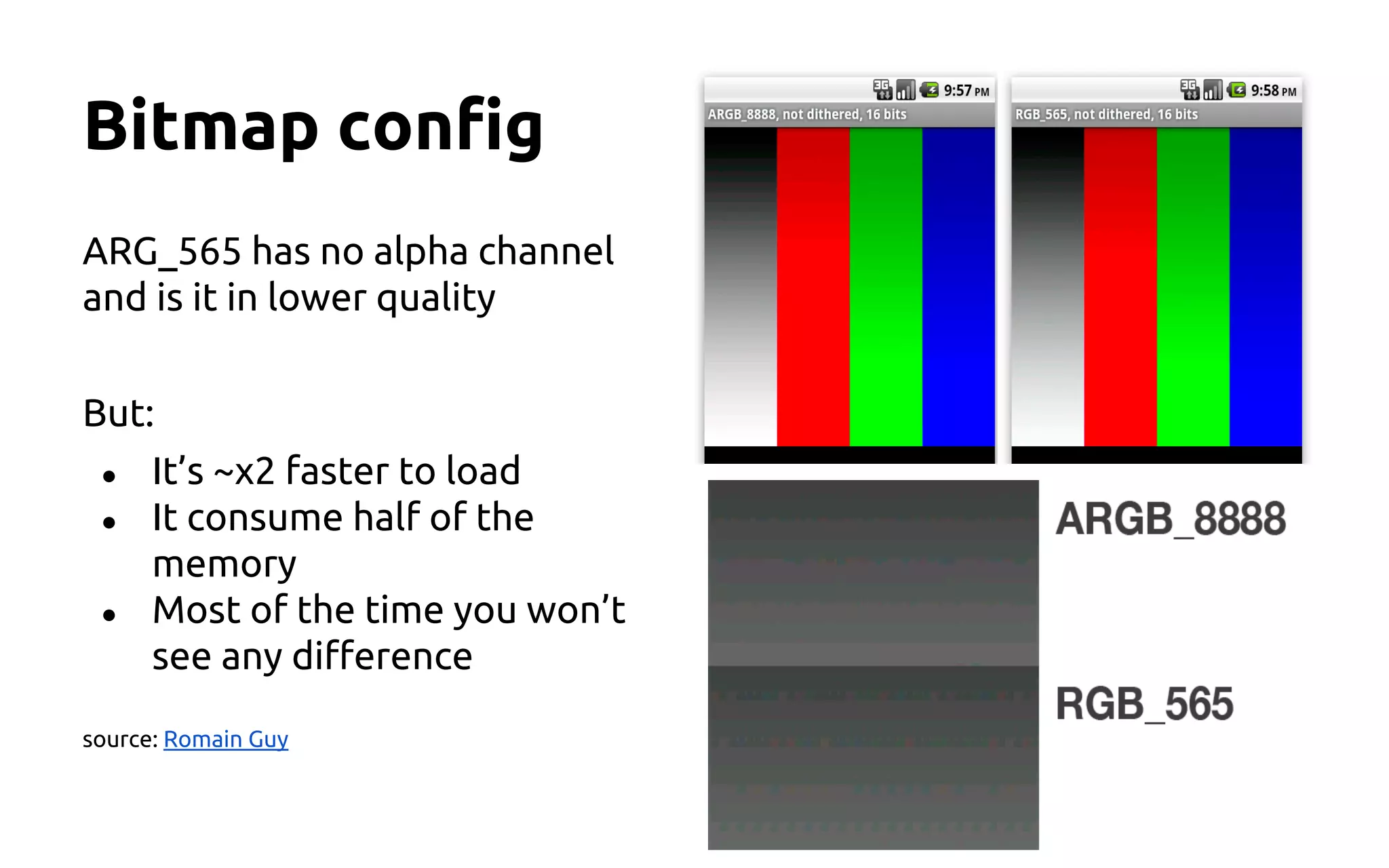
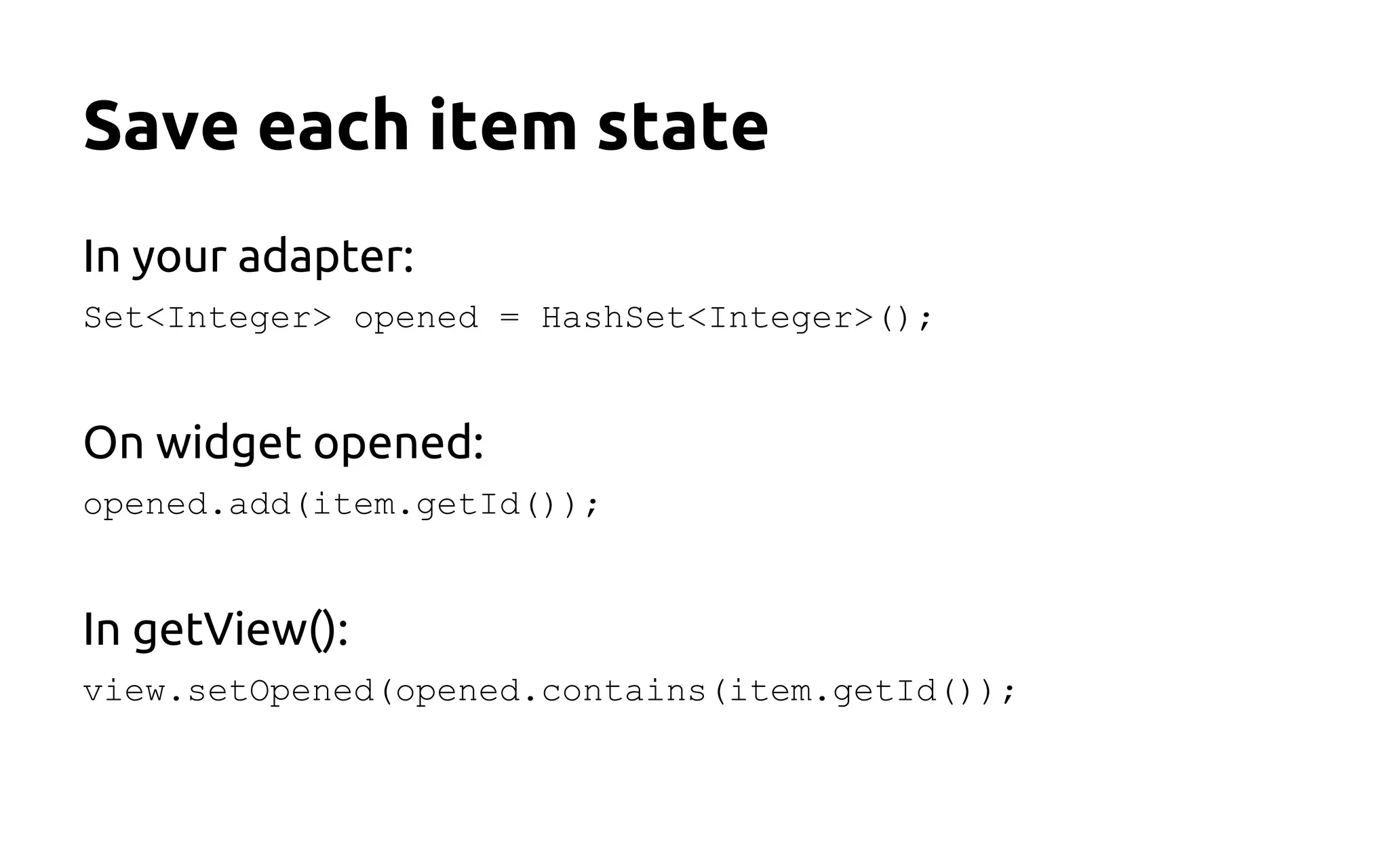
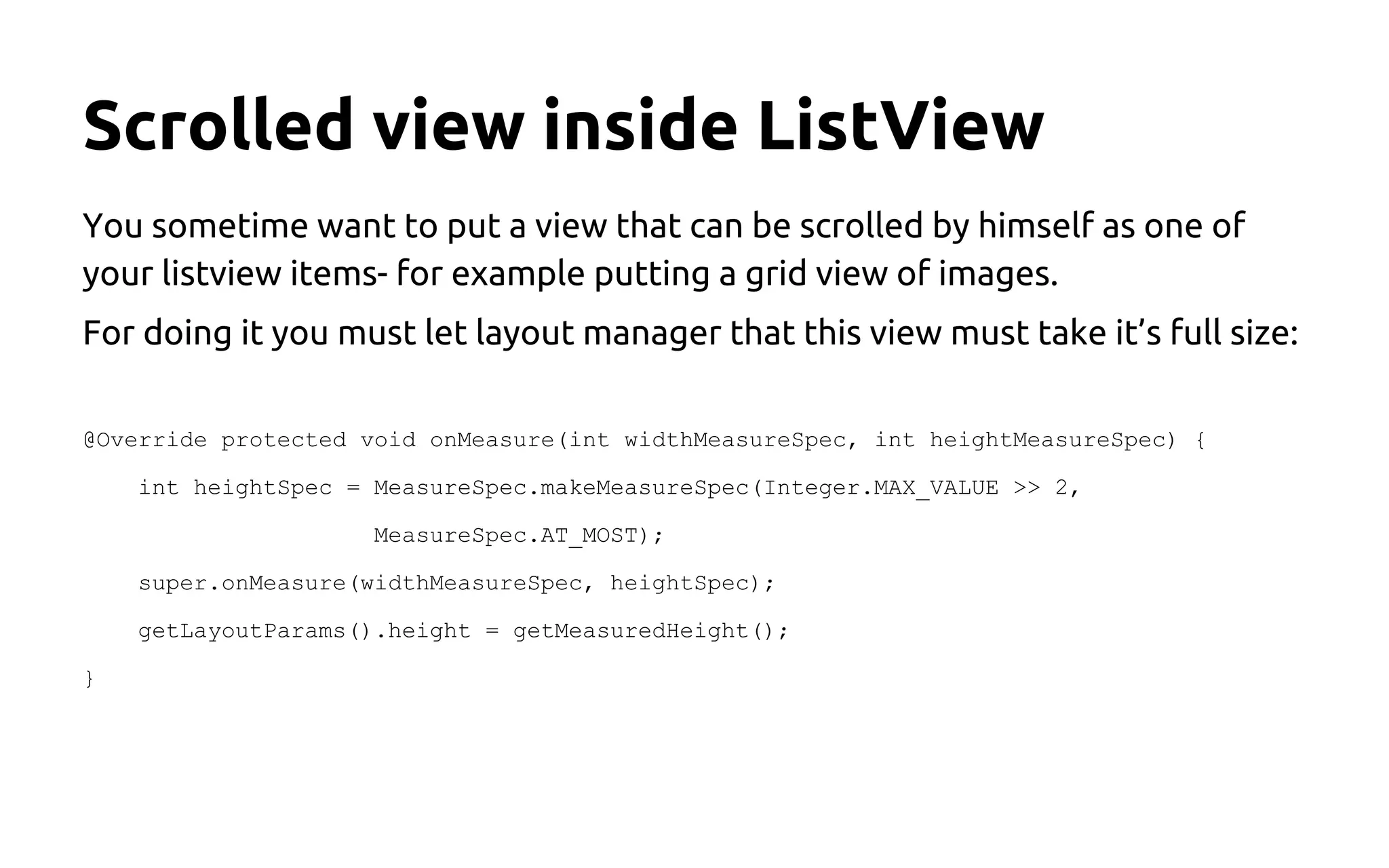
This document provides Android UI tips and tricks focused on performance and aesthetics, covering image handling, animations, and list management. Key recommendations include using caching for images, implementing animations thoughtfully to enhance user experience, and optimizing lists with the ViewHolder pattern and async tasks. It emphasizes the importance of memory management and measuring layouts to avoid UI lag and improve overall app performance.