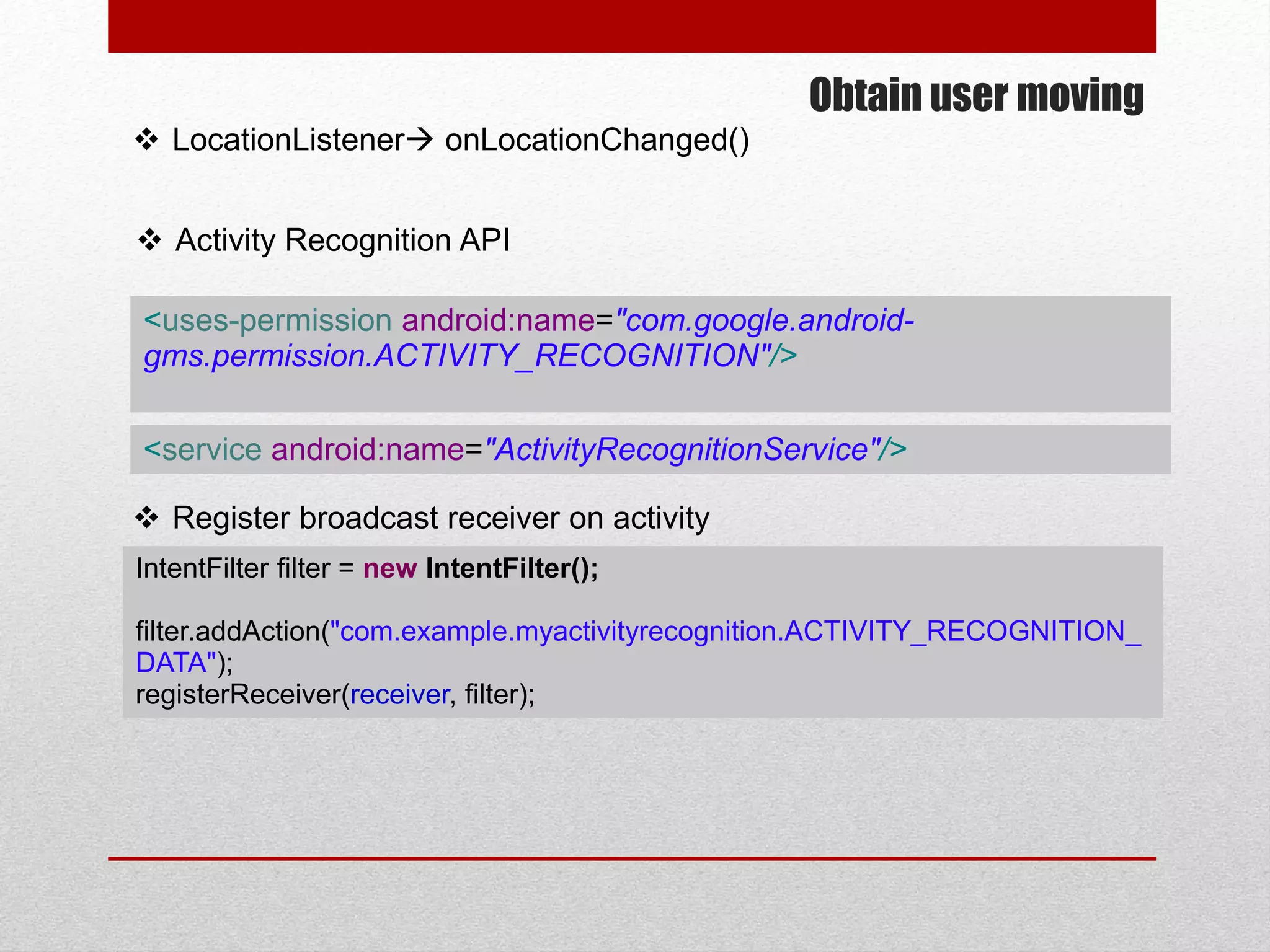
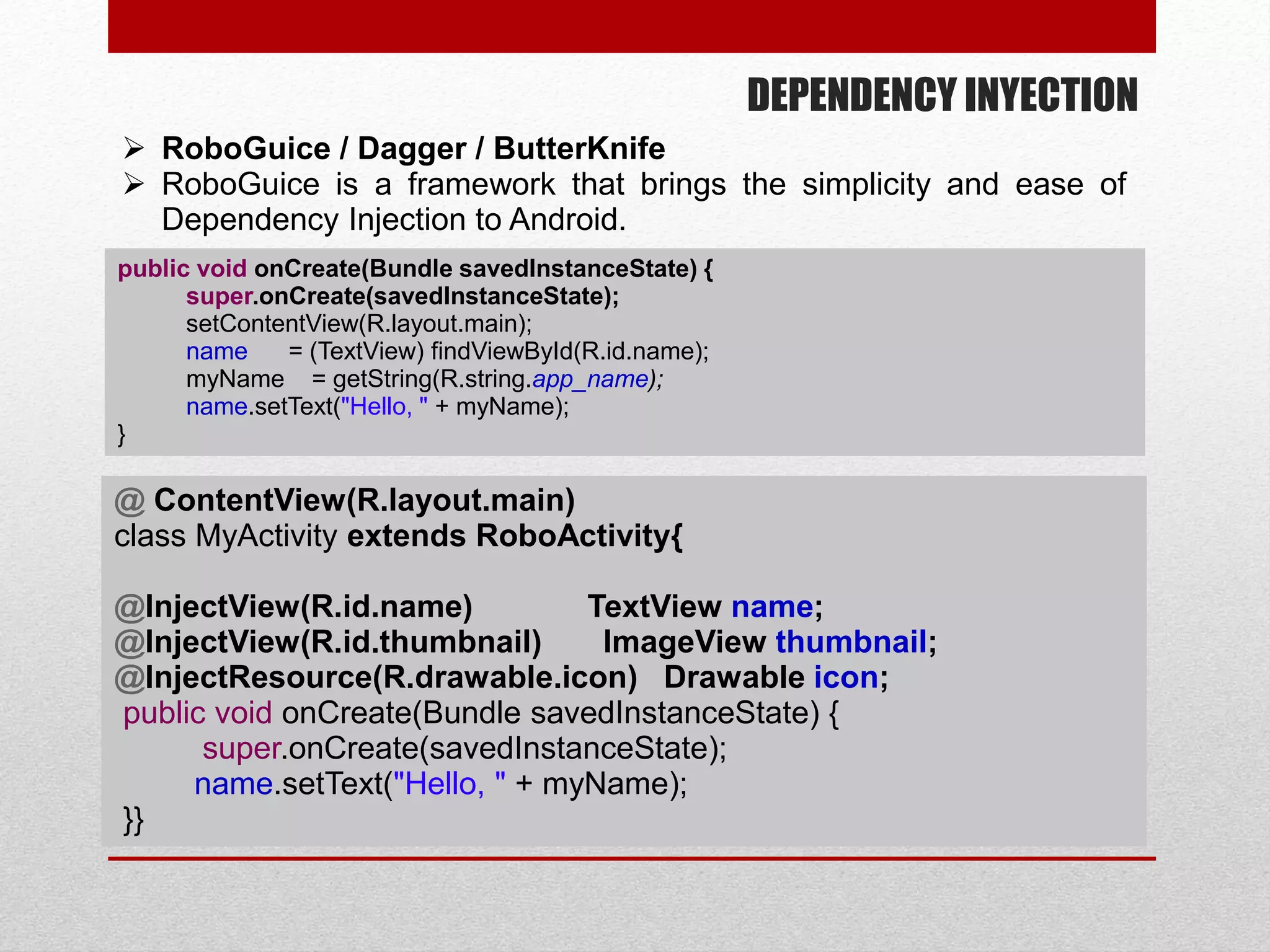
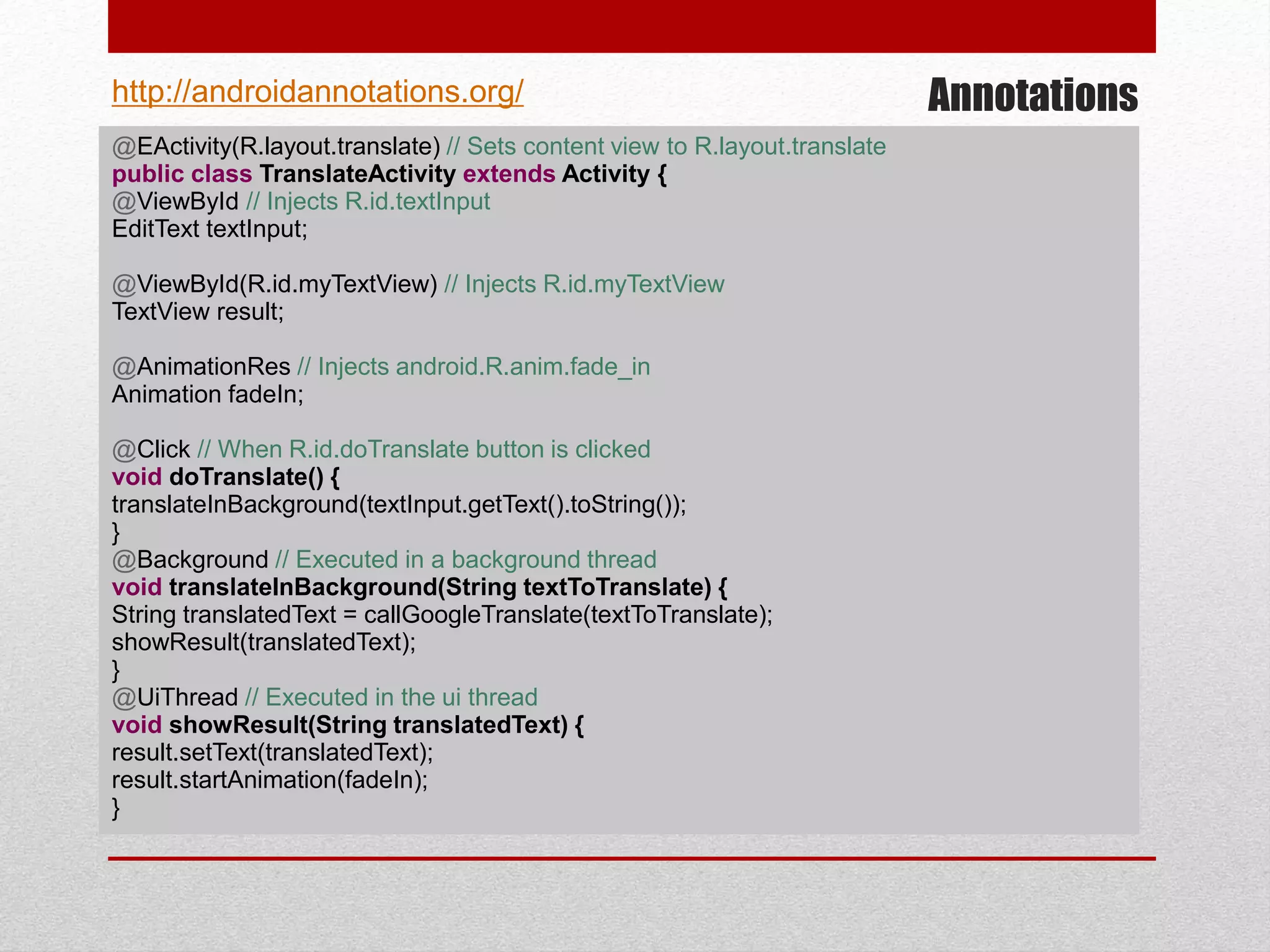
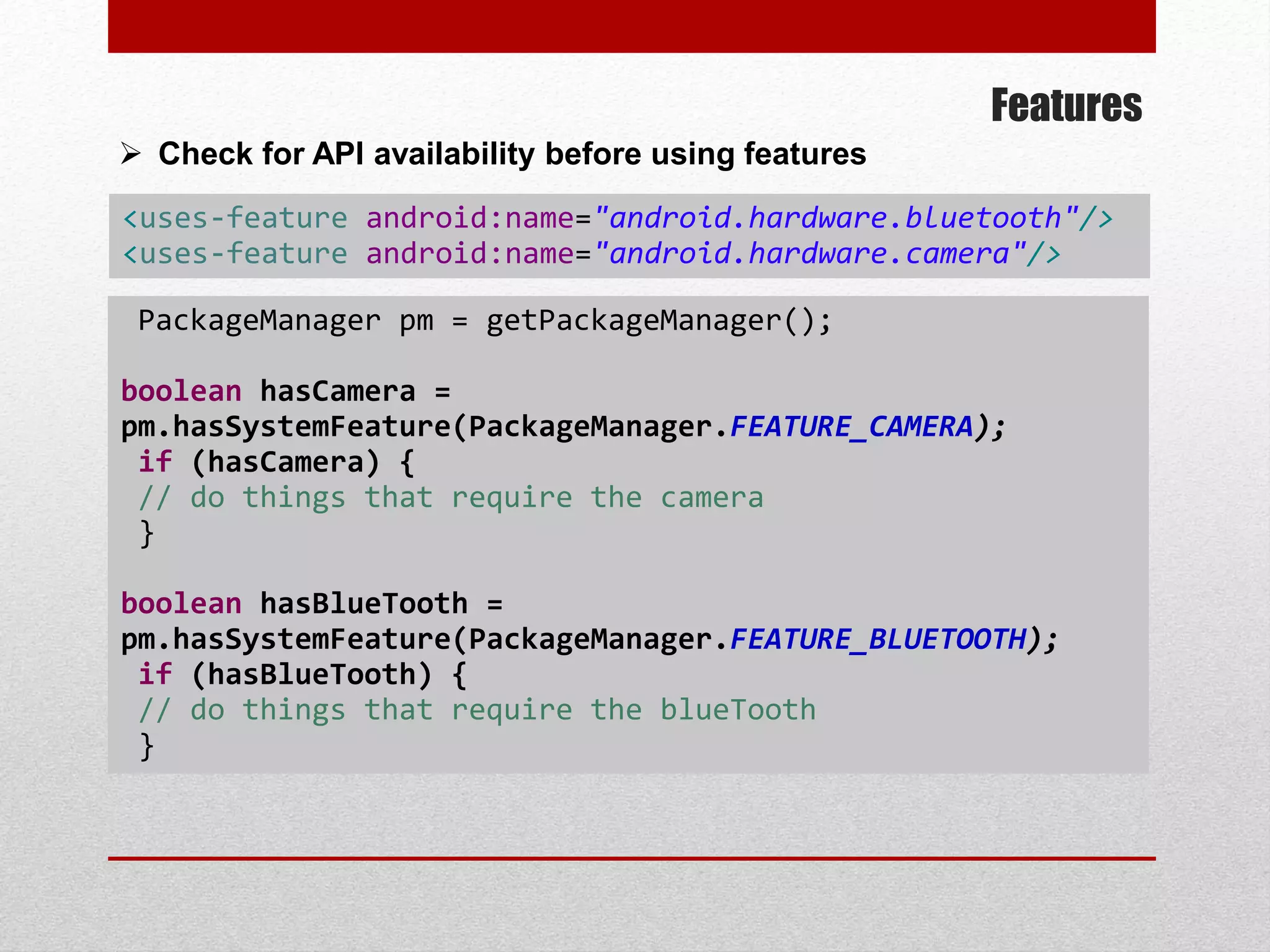
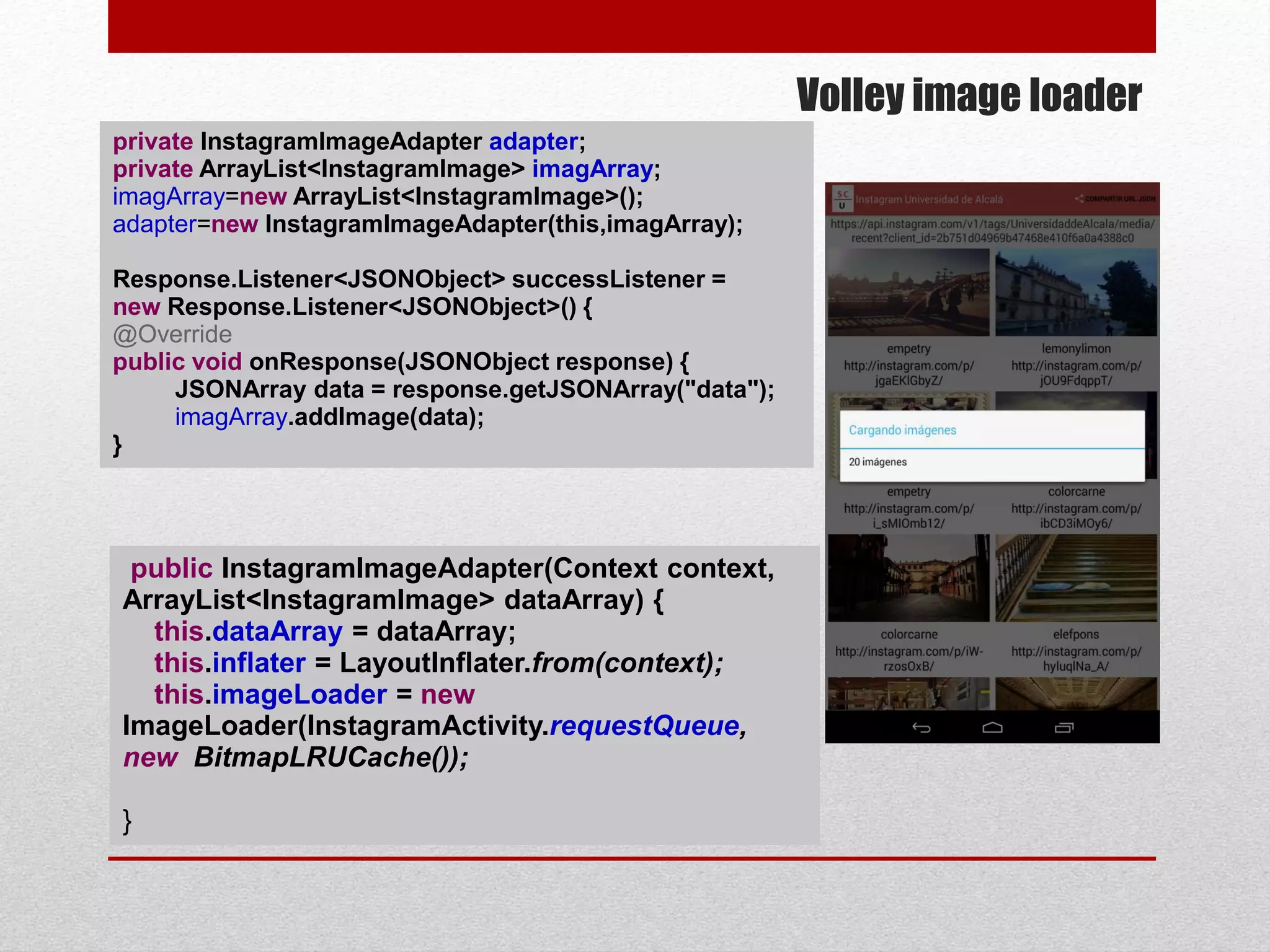
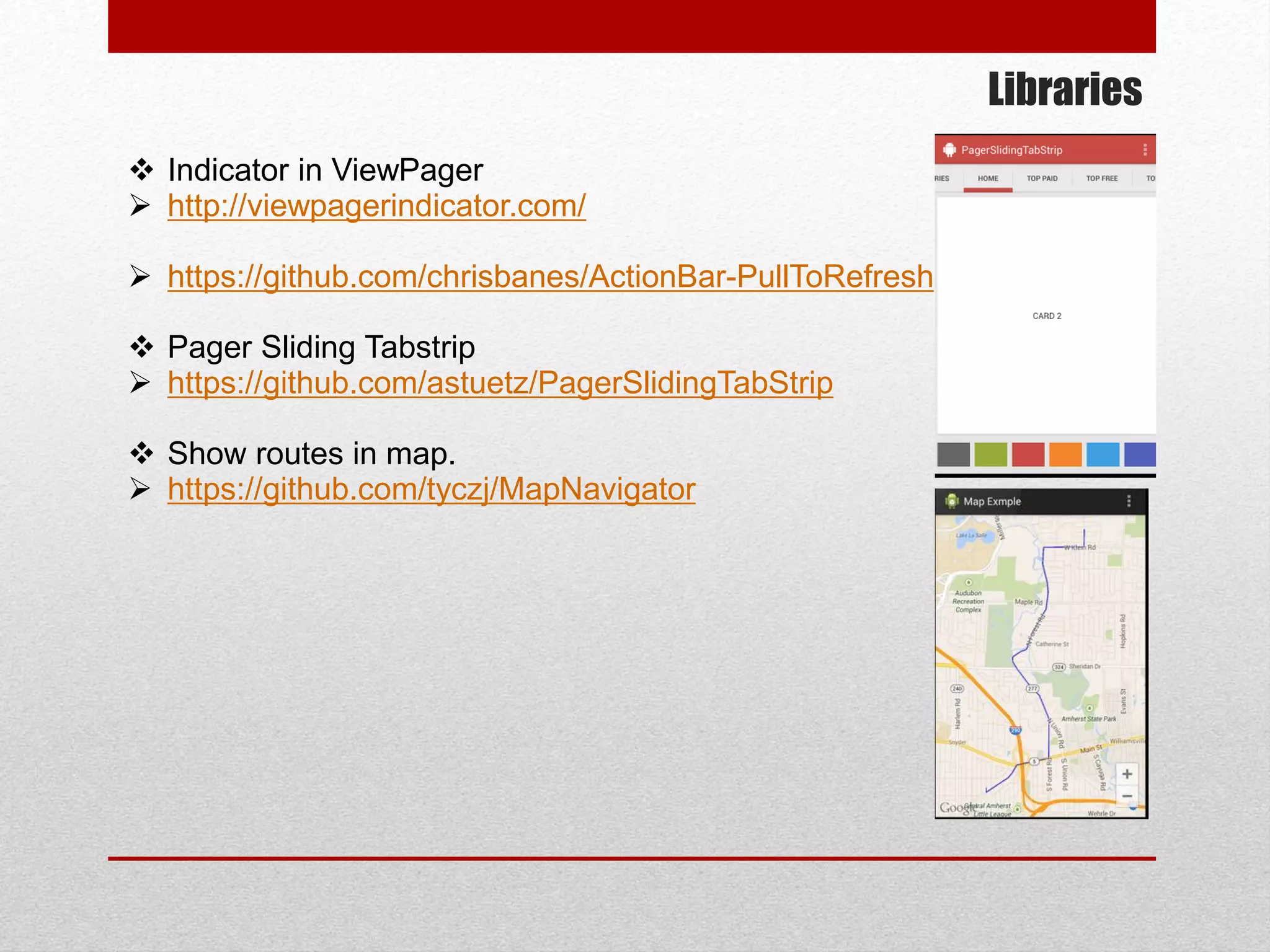
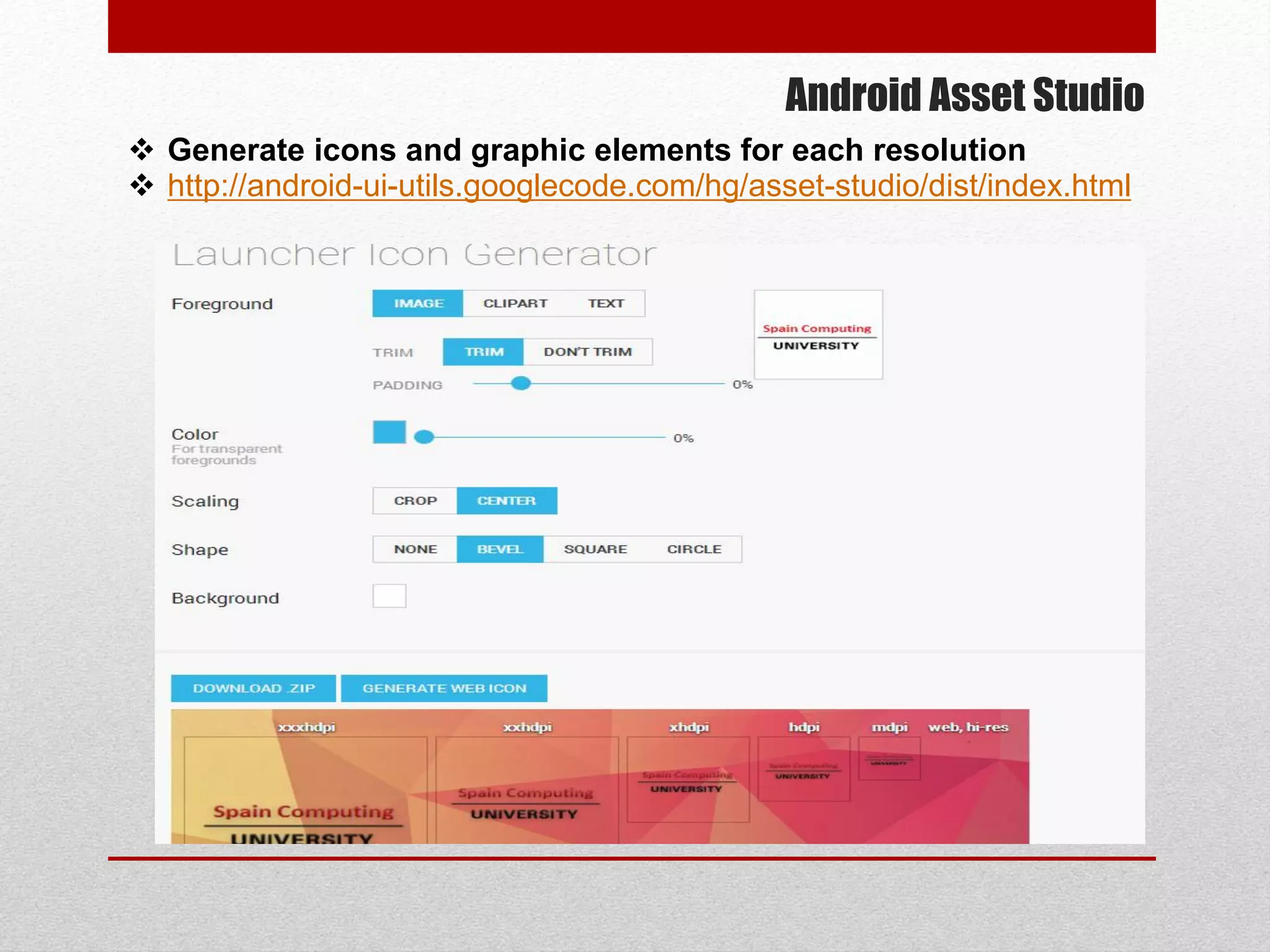
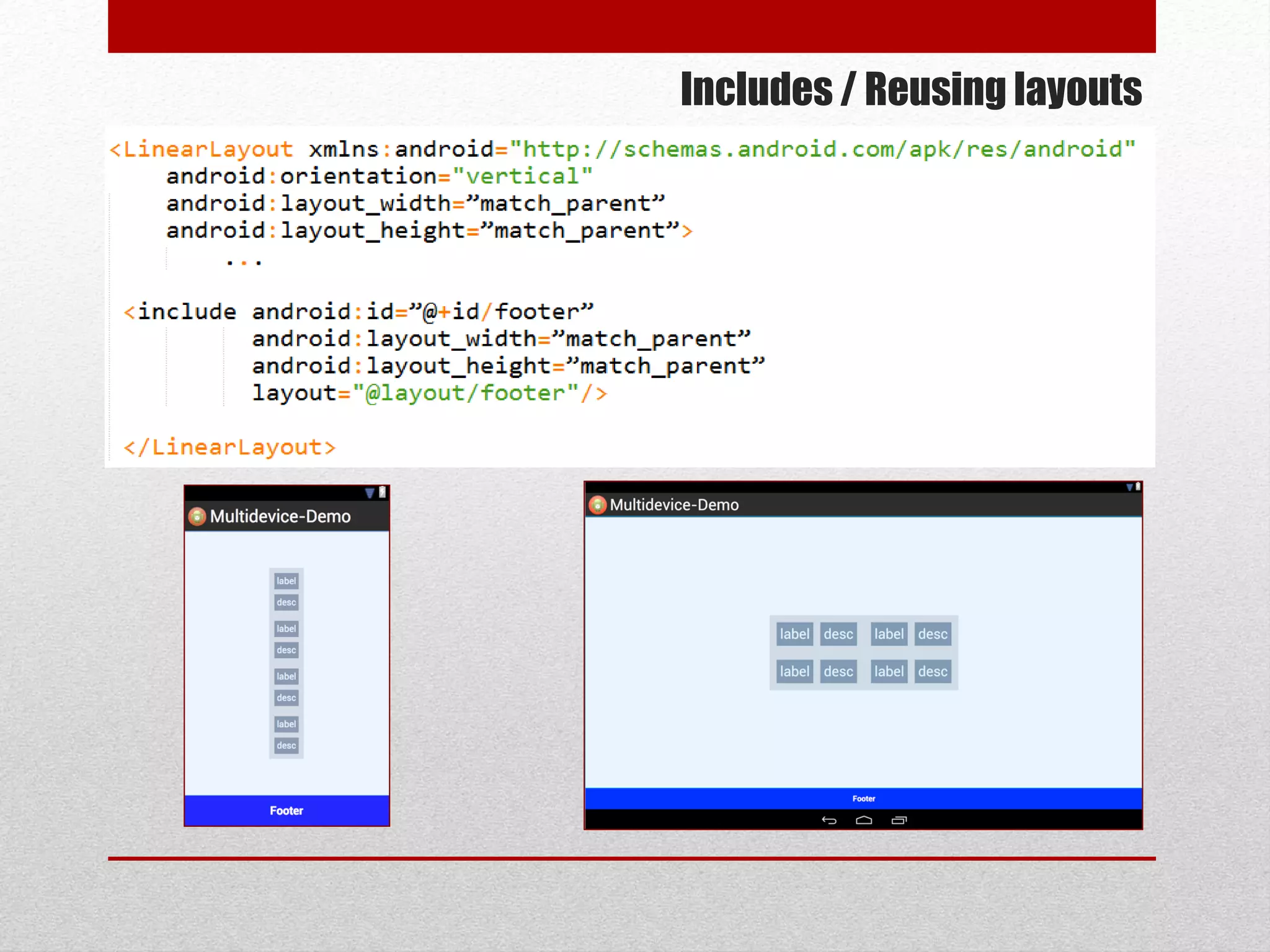
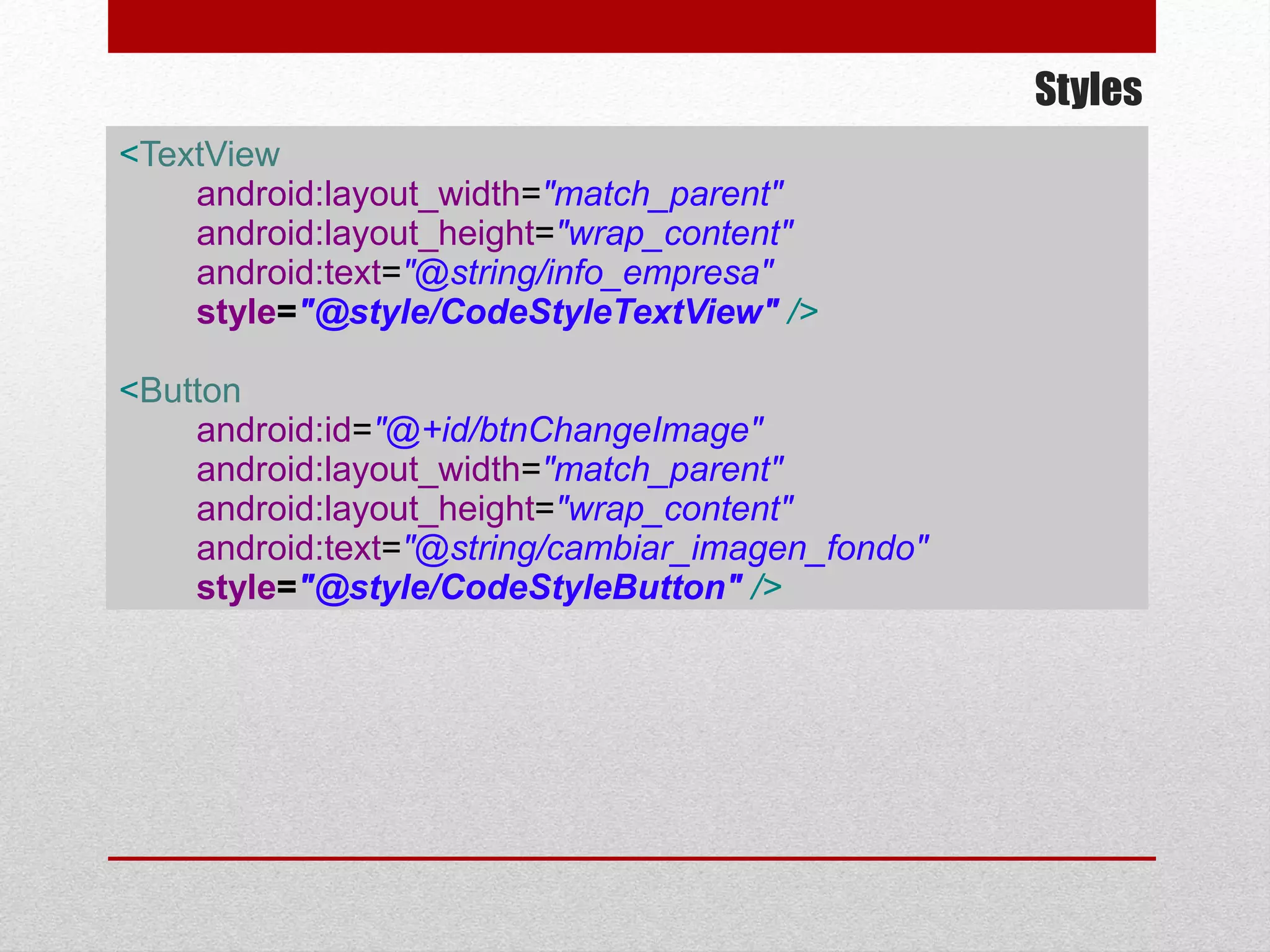
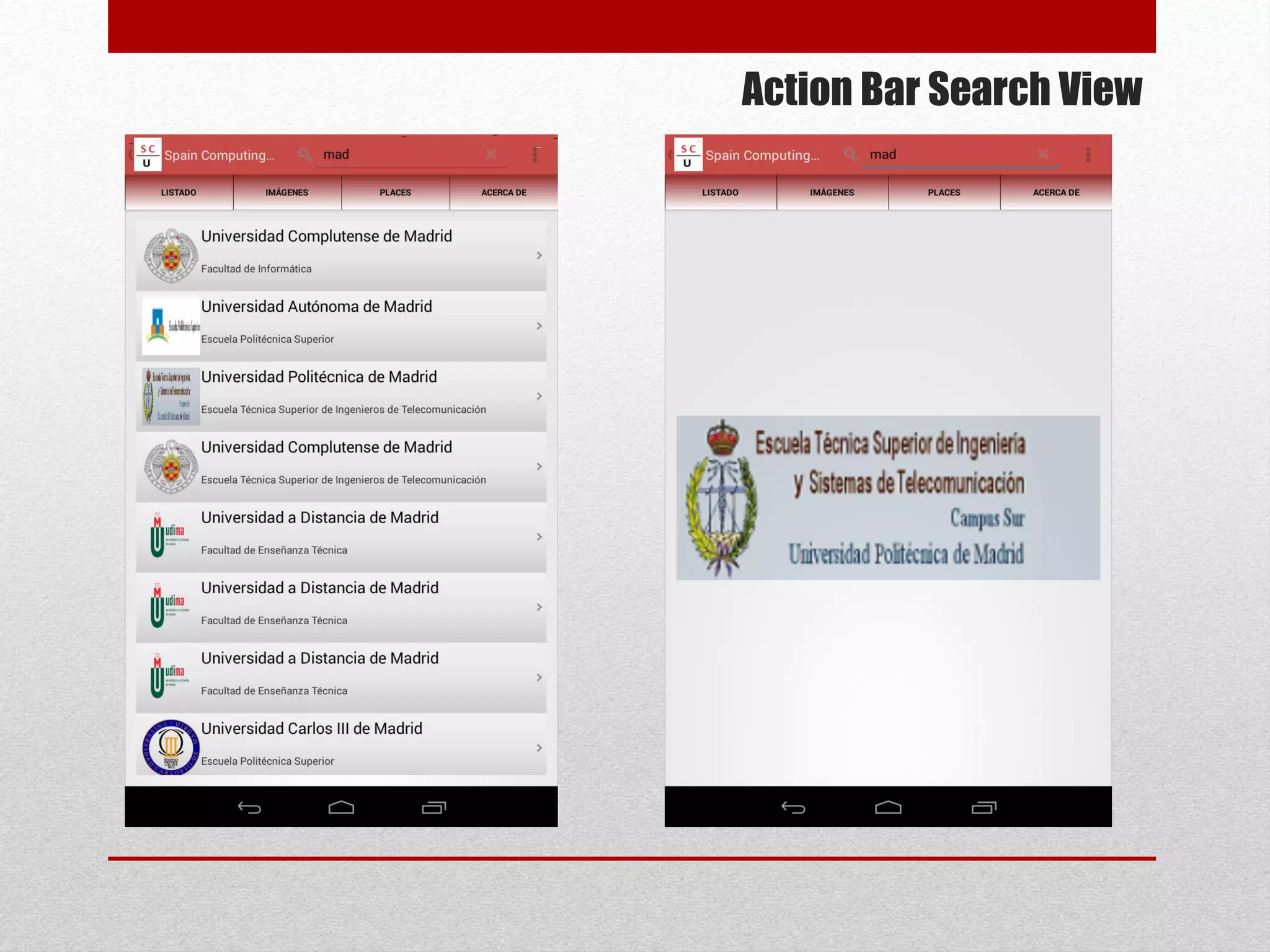
This document provides an overview of best practices for Android development. It discusses topics such as UI design, including layouts and styles; using the action bar for search and progress indicators; accessibility; network connections; asynchronous tasks and services; fragments and navigation patterns; geolocation and performance; dependency injection; and recommended tools and libraries. The document provides code snippets and links to the Android developer documentation for further information on these topics.










![Fragments
Add a fragment to view
By code
//Fragments array
Fragment[] fragments = new Fragment[]{new PortadaFragment(),
new UniversityListFragment(),new
UniversidadesImagesFragment()};
FragmentManager manager = getSupportFragmentManager();
manager.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.contentFrame, fragments[0])
.add(R.id.contentFrame, fragments[1])
.add(R.id.contentFrame, fragments[2])
.commit();
//show/hide
manager.beginTransaction().show(fragments[0]).commit();
manager.beginTransaction().hide(fragments[1]).commit();
manager.beginTransaction().hide(fragments[2]).commit();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidbestpractices-140728114150-phpapp01/75/Android-best-practices-25-2048.jpg)
![Criteria Geolocation
LocationManager / android.location package
ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION/ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
//Obtain Location Manager
LocationManager locationManager = (LocationManager)this.getSystemService
(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
Criteria criteria = new Criteria();
//criteria.setAccuracy(Criteria.ACCURACY_FINE); //GPS
criteria.setAccuracy(Criteria.ACCURACY_COARSE); // WIFI
criteria.setPowerRequirement(Criteria.POWER_LOW);
criteria.setAltitudeRequired(false);
criteria.setBearingRequired(false);
criteria.setSpeedRequired(false);
criteria.setCostAllowed(false);
String provider = locationManager.getBestProvider(criteria, true);
// In order to make sure the device is getting the location, request
// updates [wakeup after changes of: 5 sec. or 10 meter]
locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(provider, 5, 10, this);
locationBridge.setNewLocation(locationManager.getLastKnownLocation(provider
));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidbestpractices-140728114150-phpapp01/75/Android-best-practices-42-2048.jpg)