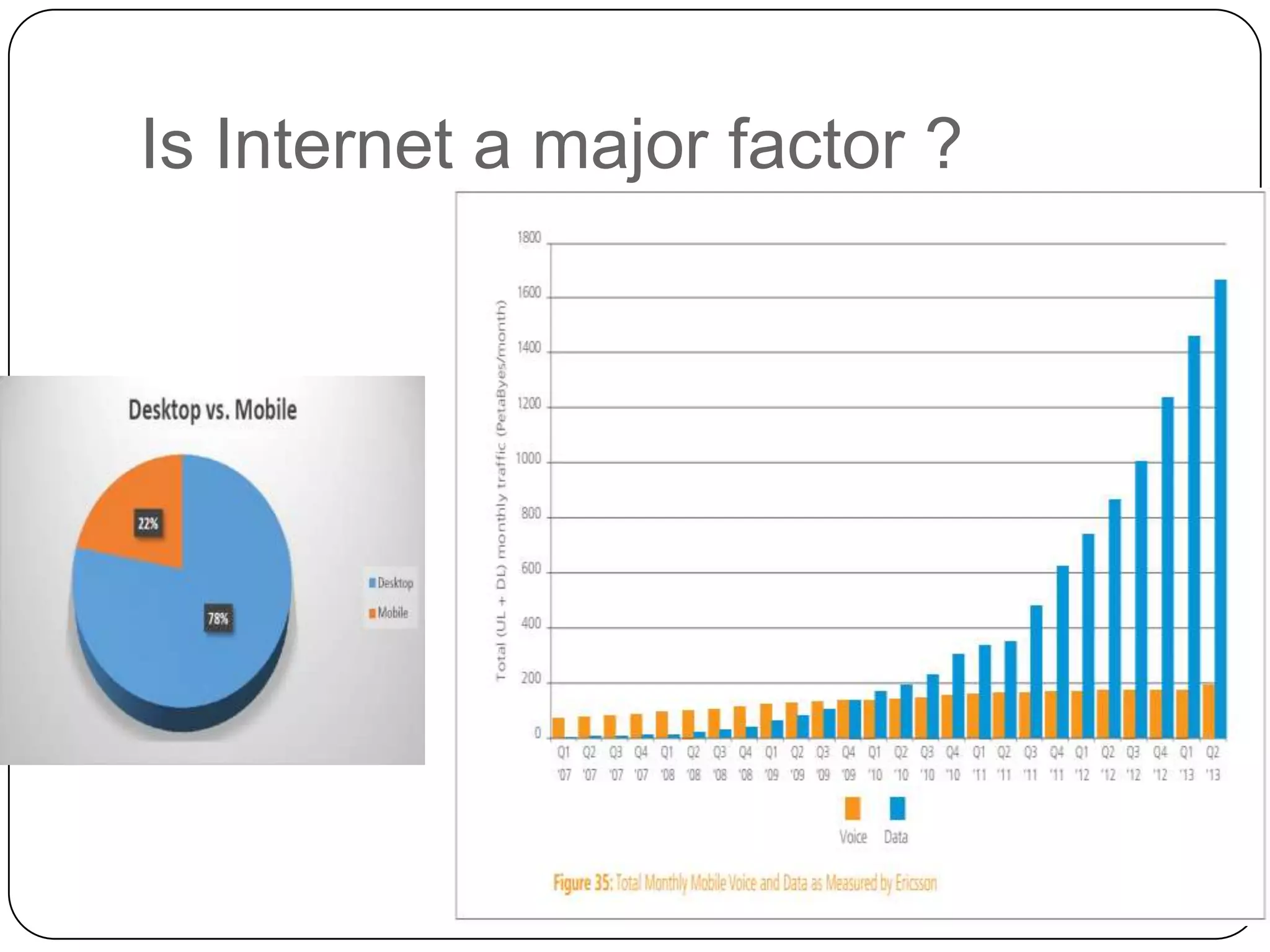
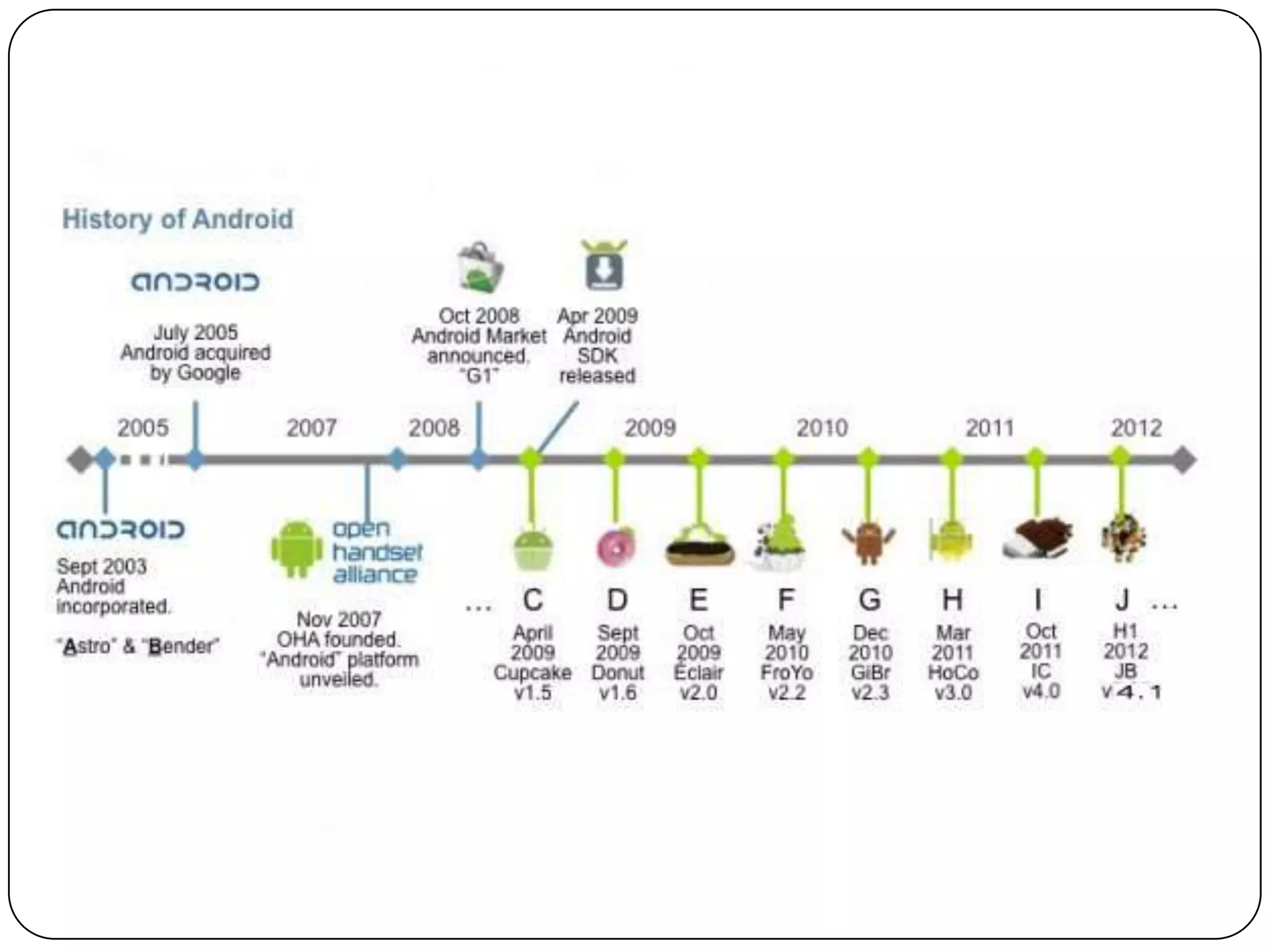
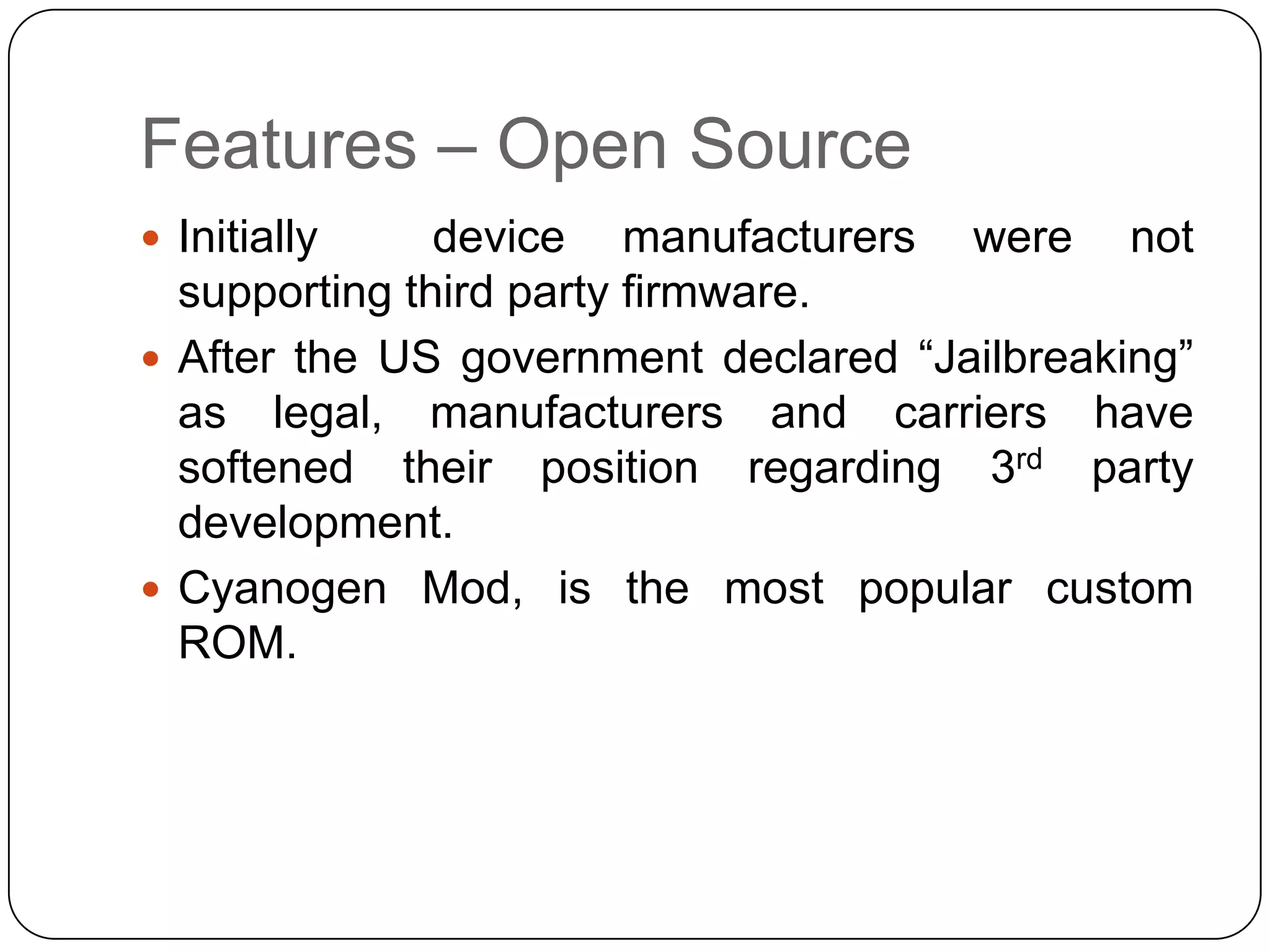
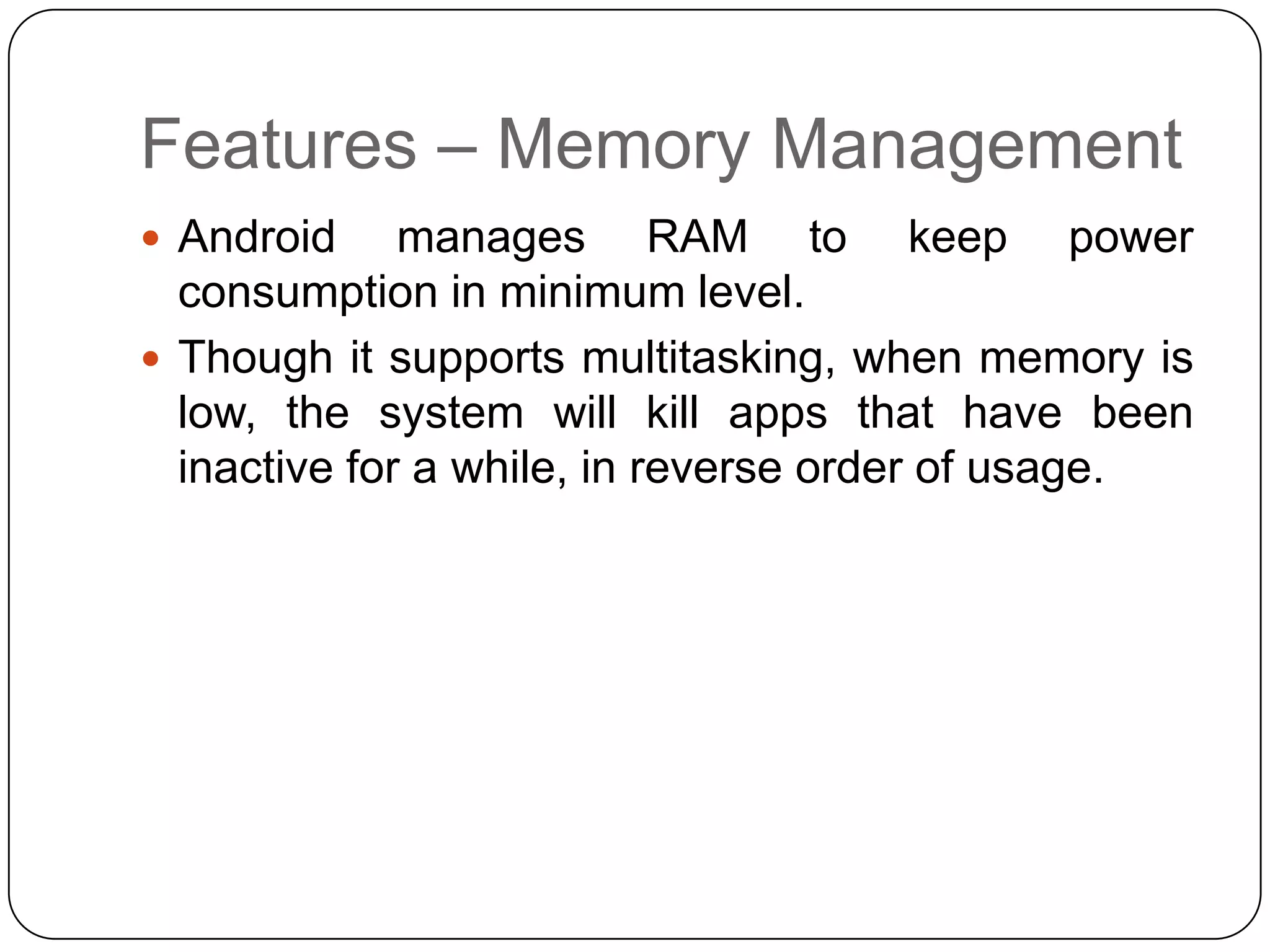
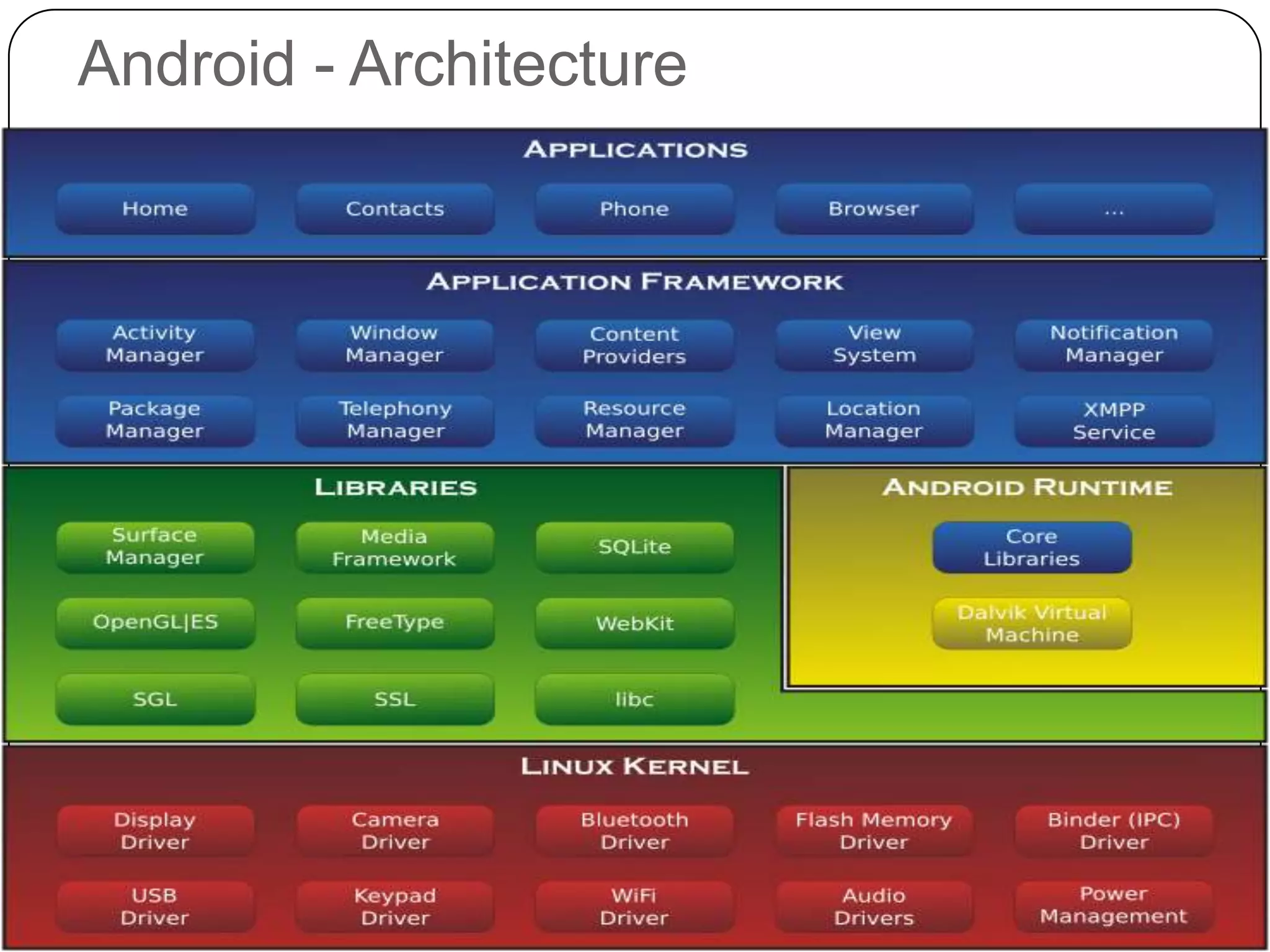
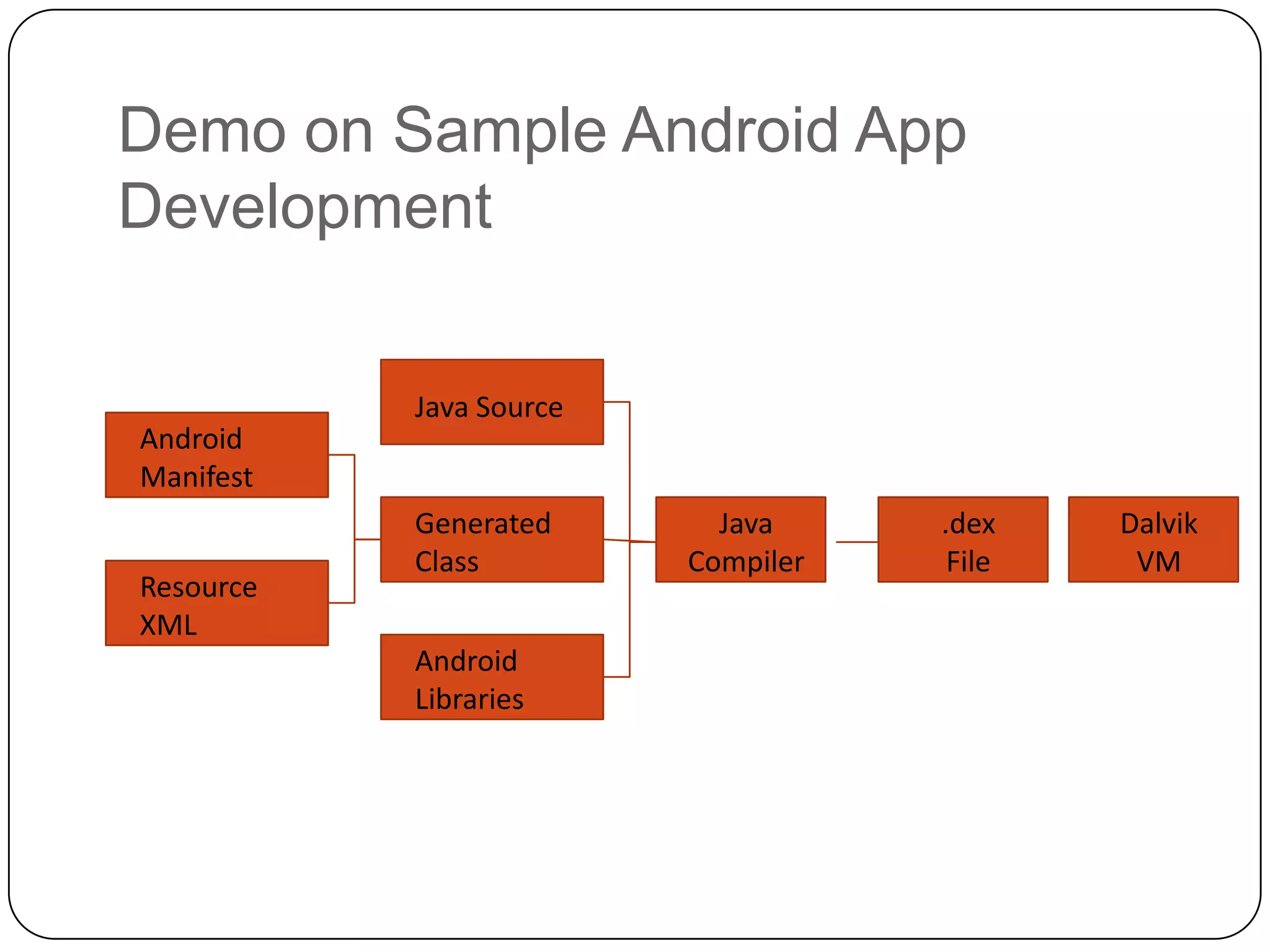
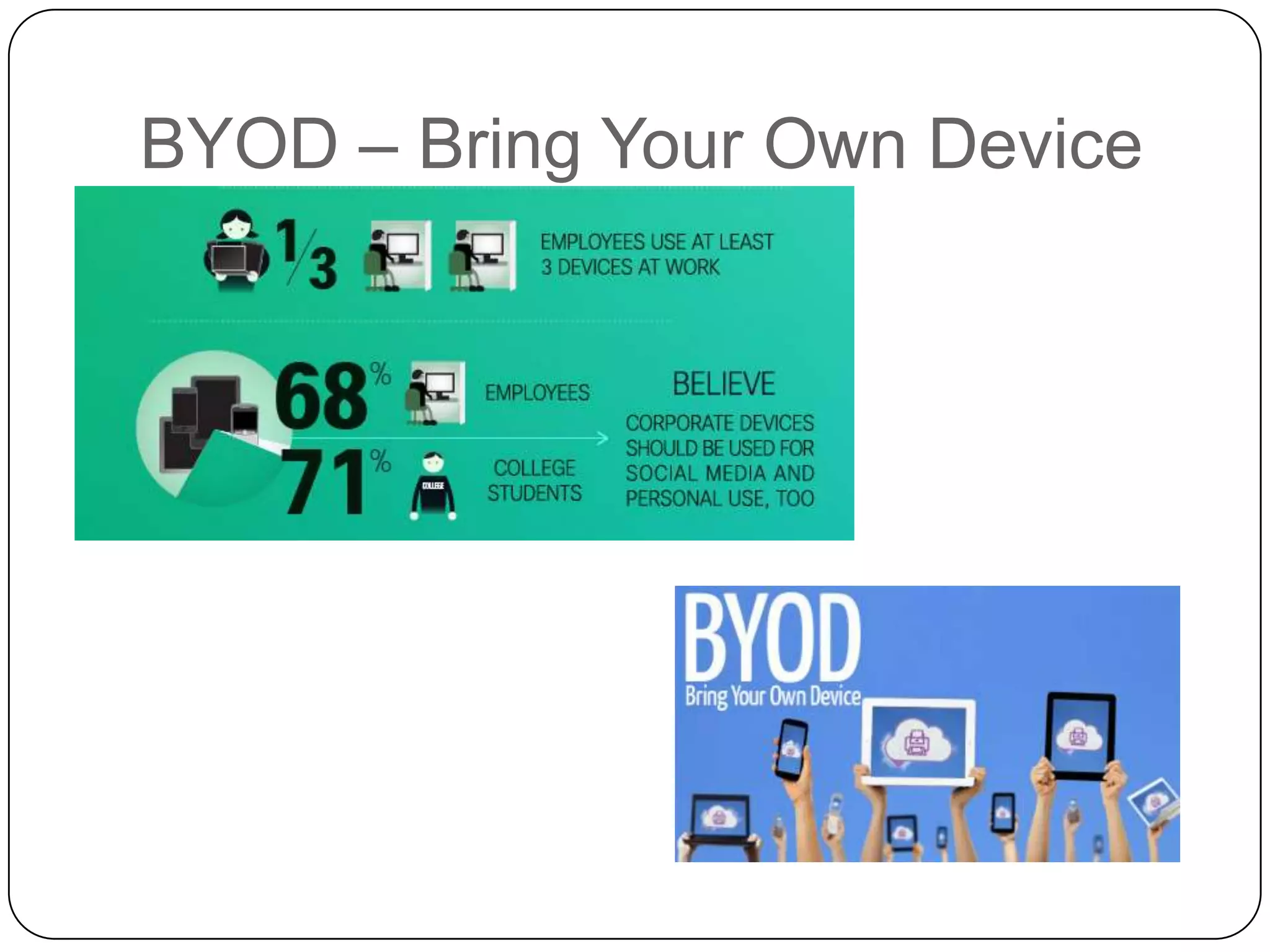
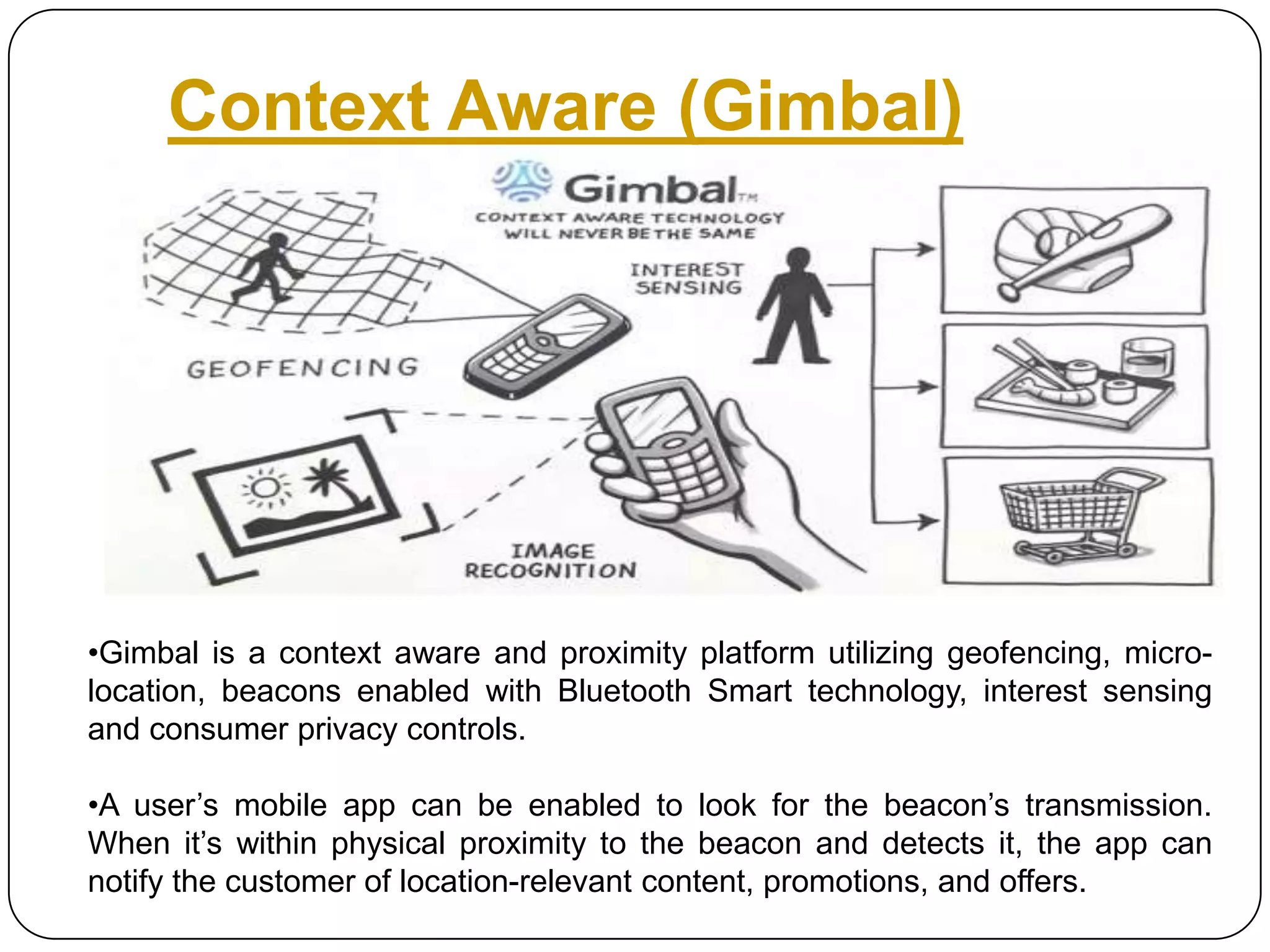
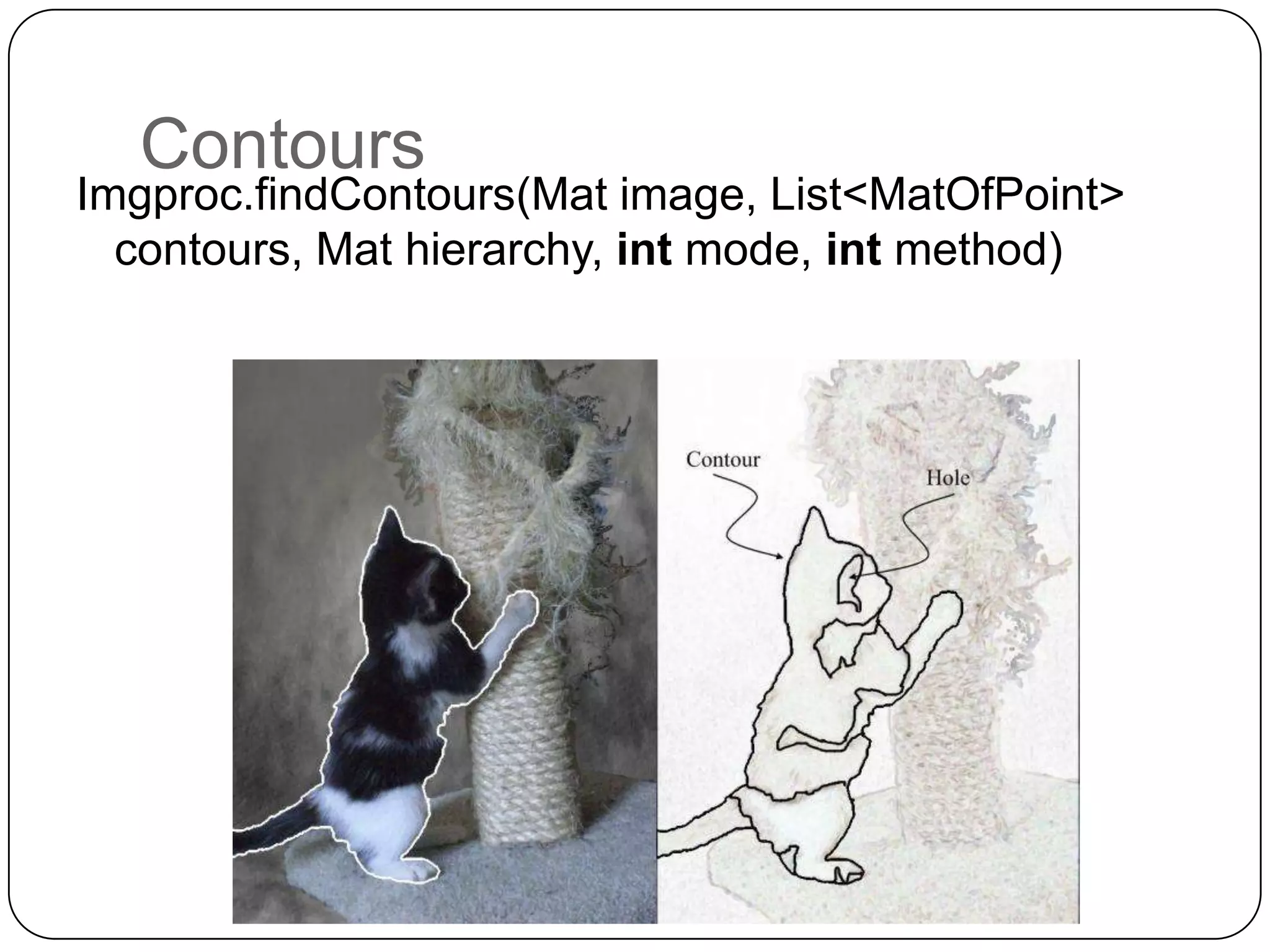
The document discusses Android operating system and its features. It provides an overview of Android OS, its architecture, development framework and tools like Open Handset Alliance, Dalvik VM, ART, OpenCV etc. that make application development easier. It also summarizes key features of Android including security, hardware support, open source nature, memory management and how latest technologies are supported.