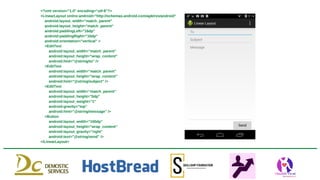
The document outlines a workshop on Android application development conducted by the Department of Information Technology at Priyadarshini Bhagwati College of Engineering, detailing Android's history, application components, and XML design. Key topics include activities, services, intents, and content providers, alongside fundamental UI components like TextView and EditText. The document provides XML code examples for various layouts, demonstrating how to create user interfaces for Android applications.