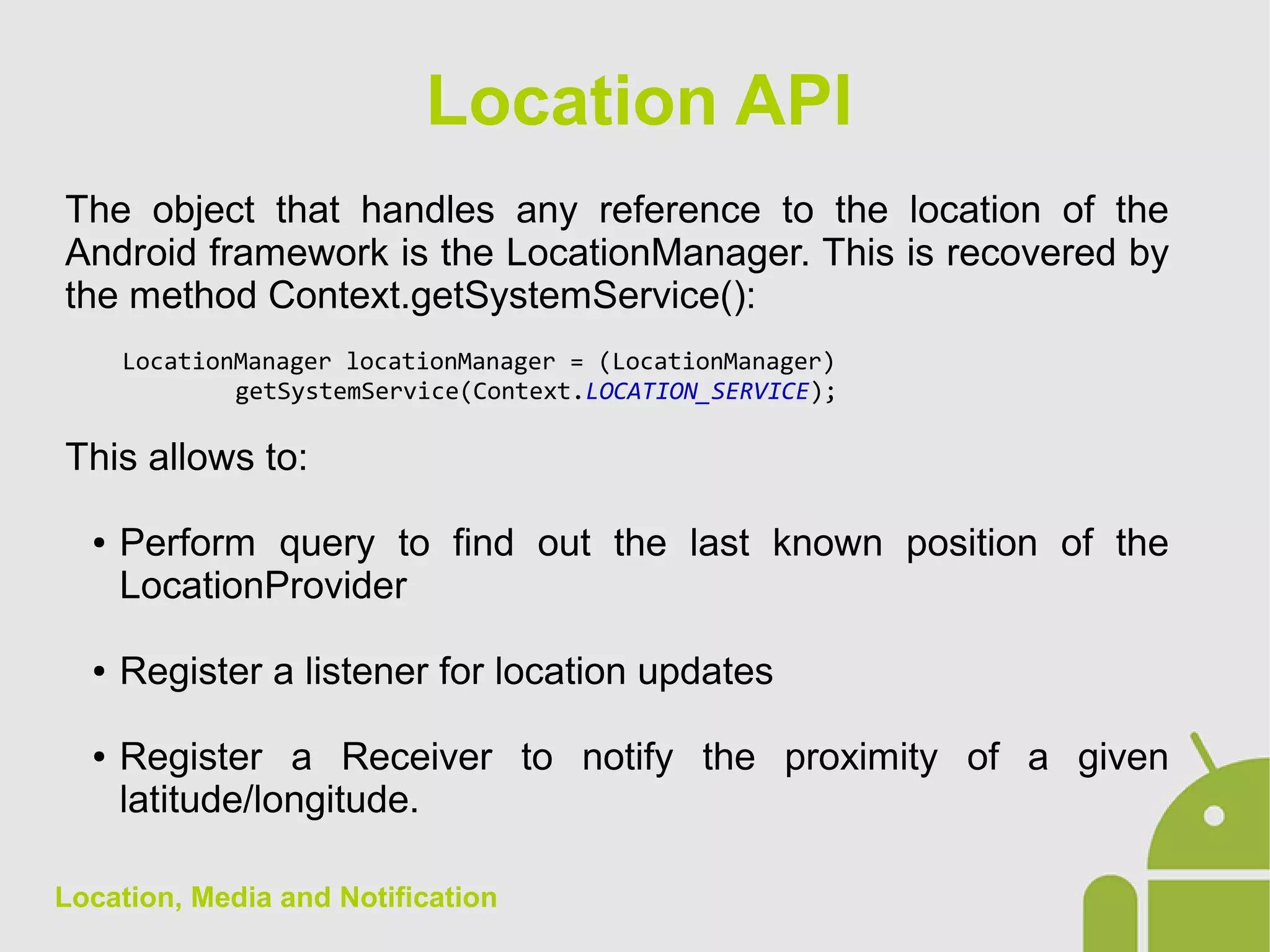
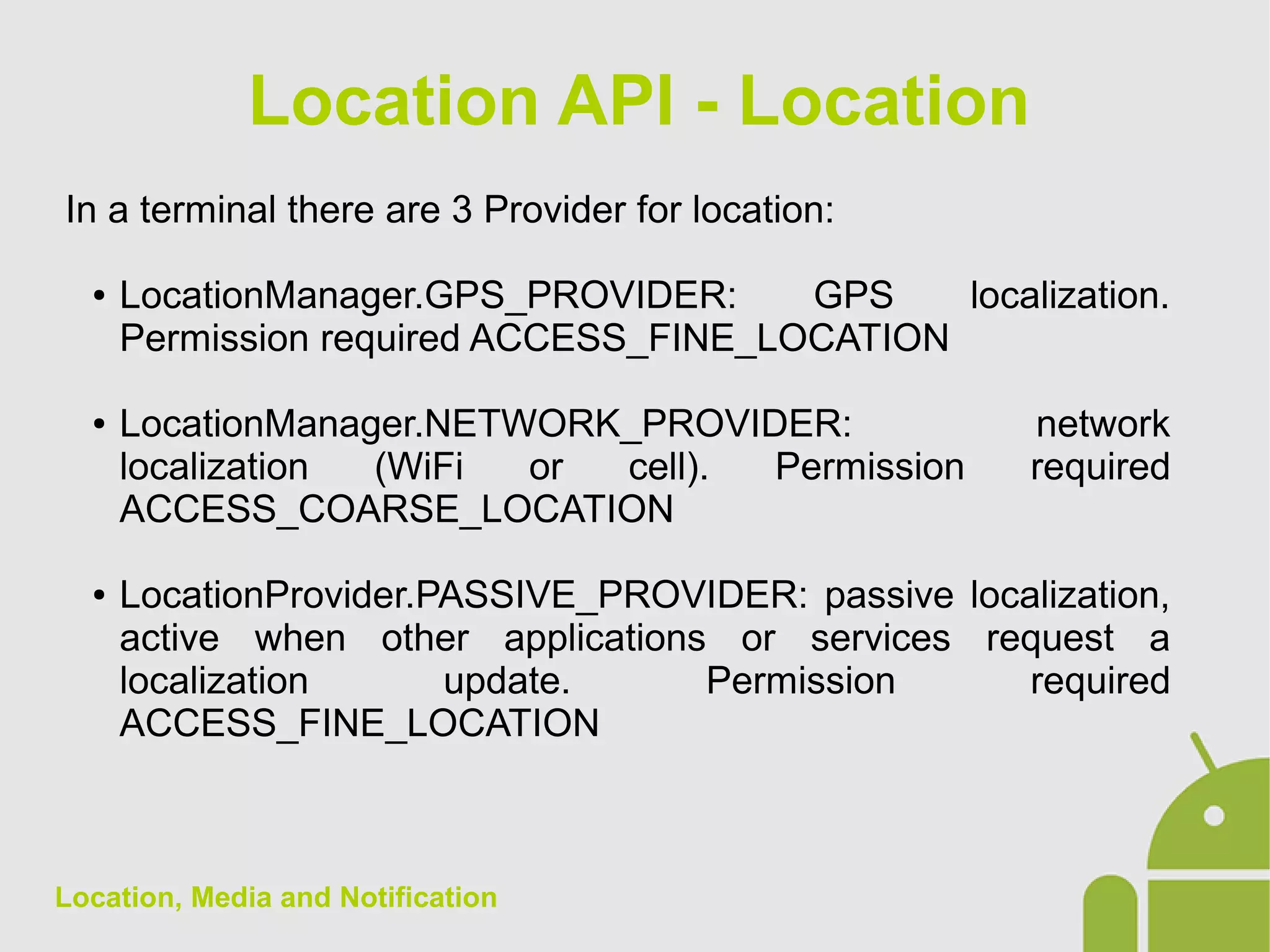
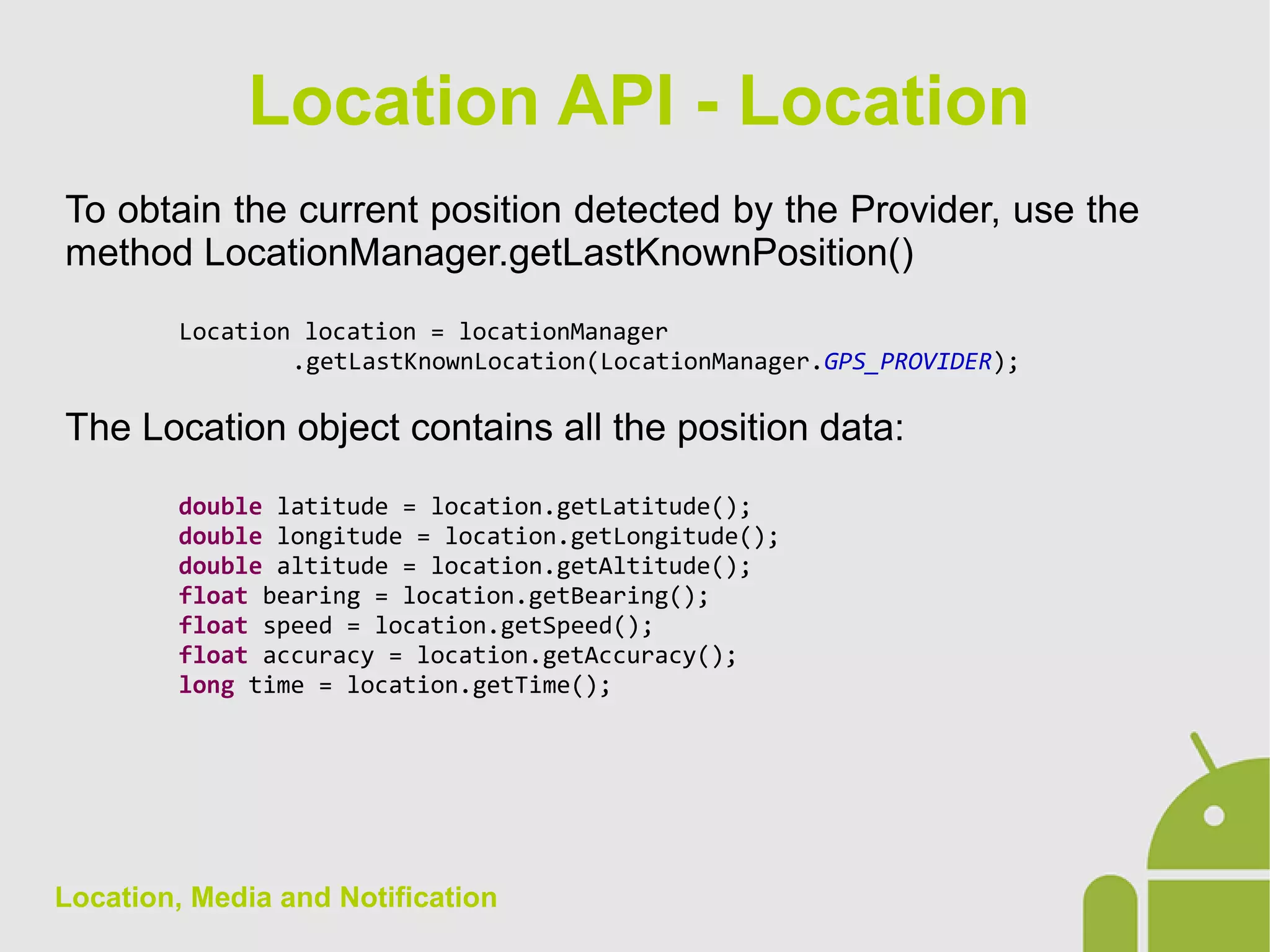
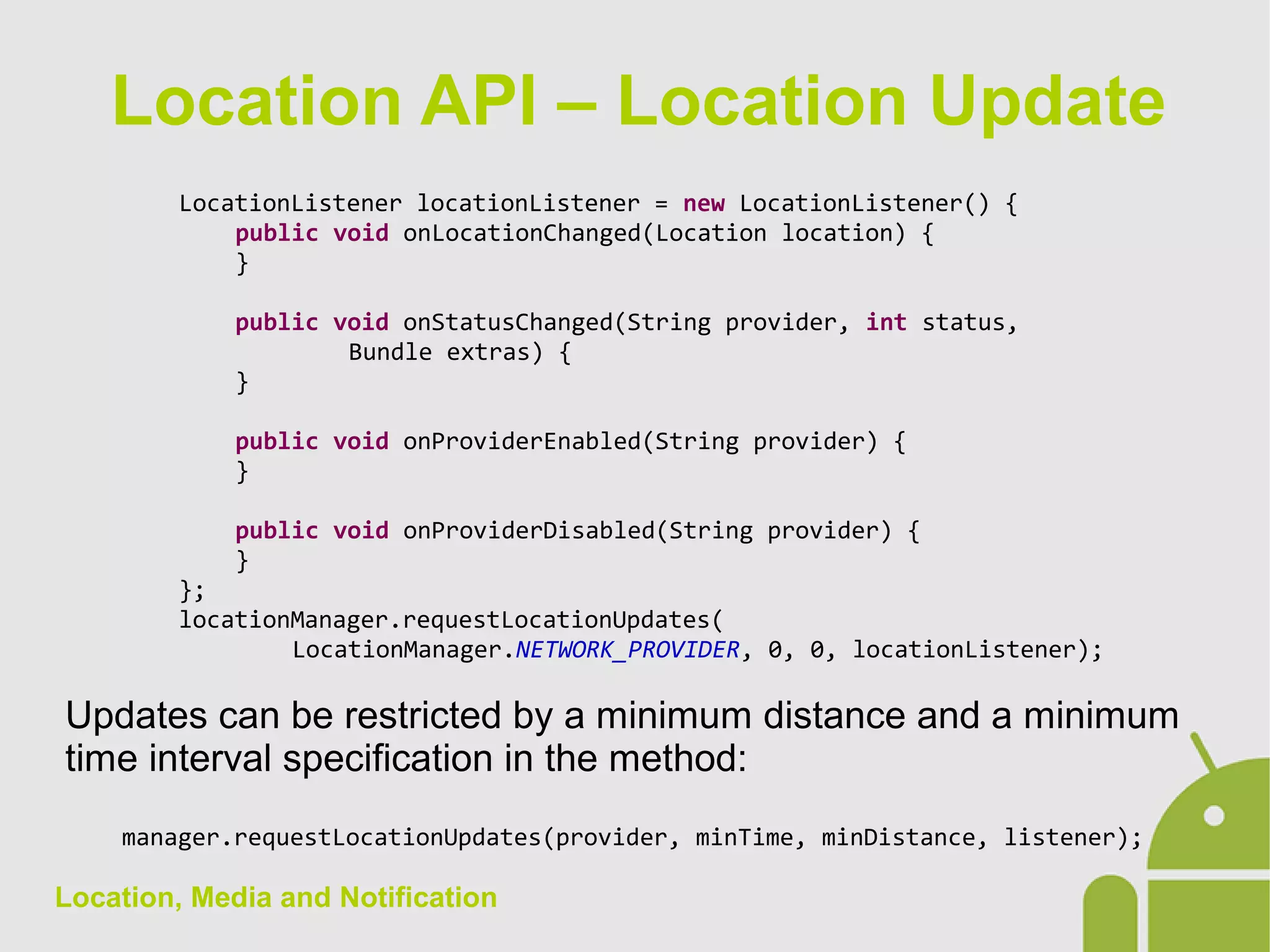
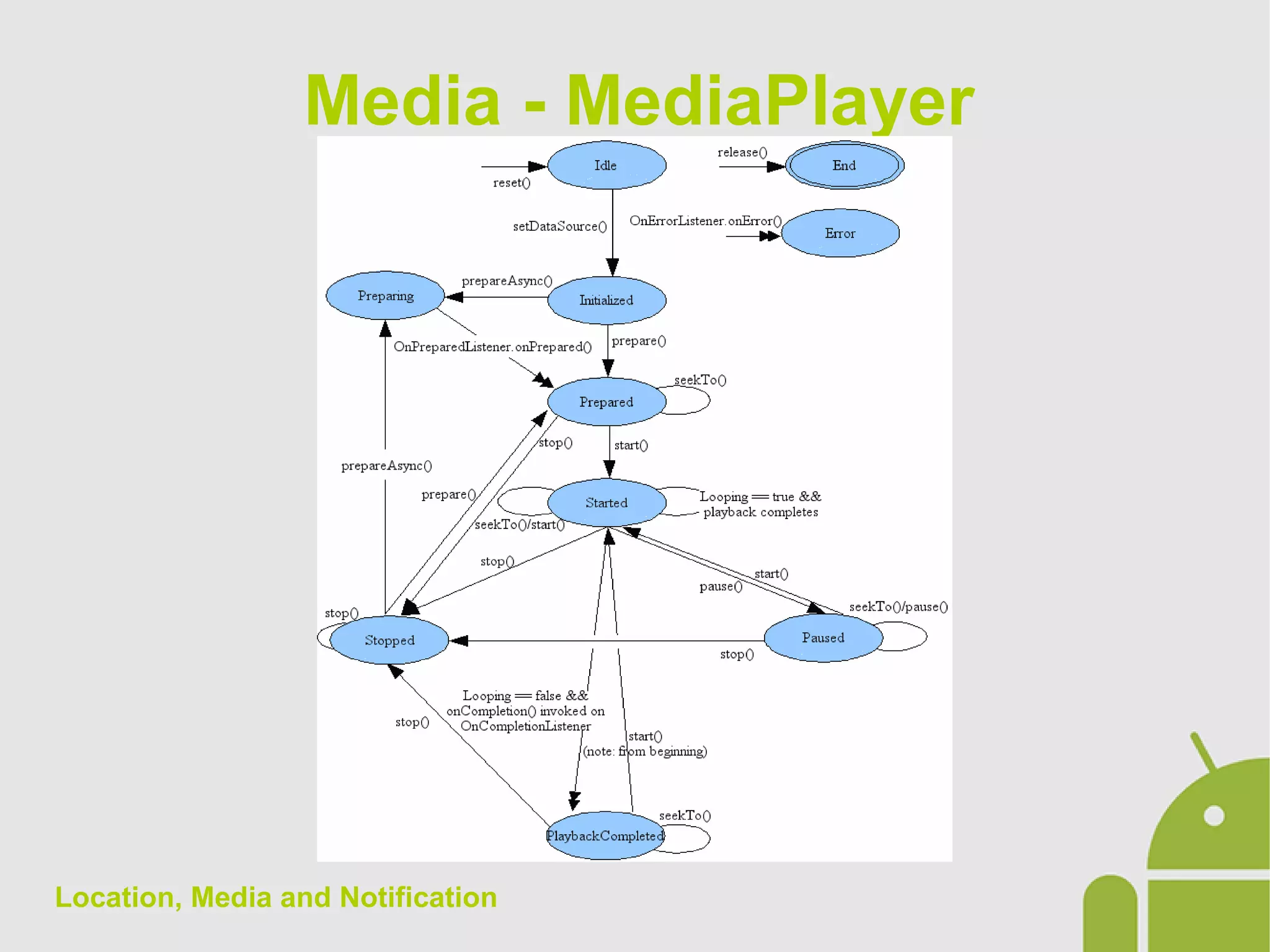
The document discusses location, media, and notifications in Android. It describes how to get the last known location using the LocationManager and register for location updates. It explains how to play audio and video using the MediaPlayer and VideoView classes. It also covers creating normal and big style notifications using the NotificationCompat builder and sending notifications via GCM.








![Location, Media and Notification
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(
this).setSmallIcon(R.drawable.notification_icon)
.setContentTitle("Event tracker")
.setContentText("Events received");
NotificationCompat.InboxStyle inboxStyle = new
NotificationCompat.InboxStyle();
String[] events = new String[6];
// Sets a title for the Inbox style big view
inboxStyle.setBigContentTitle("Event tracker details:");
// Moves events into the big view
for (int i = 0; i < events.length; i++) {
inboxStyle.addLine(events[i]);
}
// Moves the big view style object into the notification object.
mBuilder.setStyle(inBoxStyle);
Notification – Big Style](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14locationmediaandnotifications-150510062002-lva1-app6891/75/Android-App-Development-14-location-media-and-notifications-14-2048.jpg)






