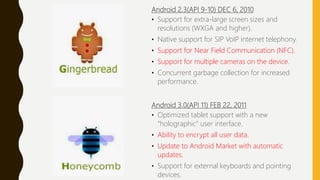
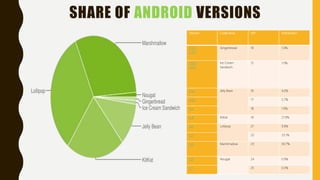
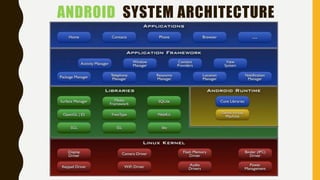
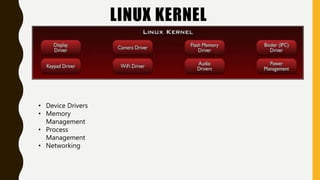
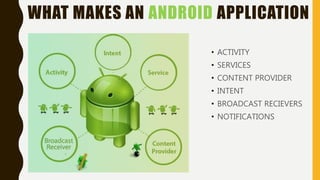
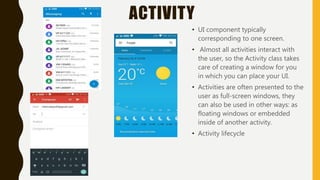
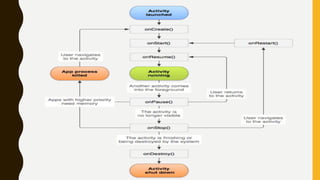
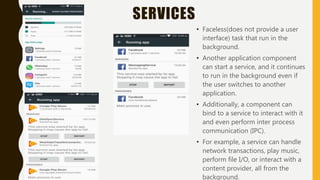
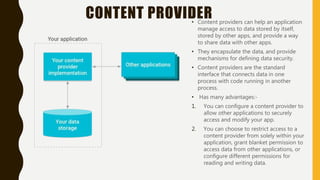
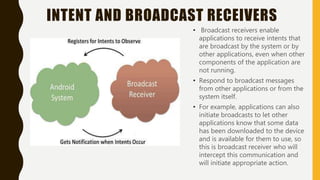
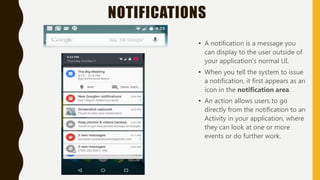
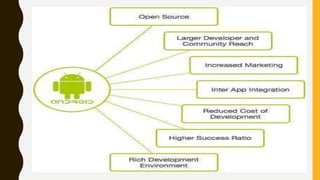
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Android, including its history, features, architecture, and application development. Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google based on the Linux kernel, with significant market dominance. It covers aspects such as the evolution of Android versions, application components, and the process for publishing apps on the Google Play Store, while also addressing drawbacks like storage limitations and battery issues.