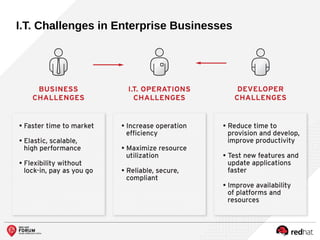
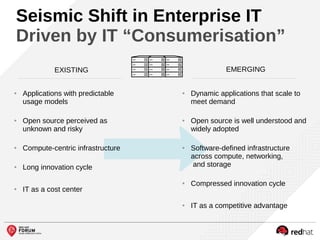
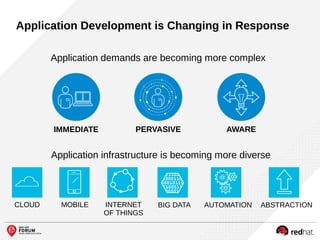
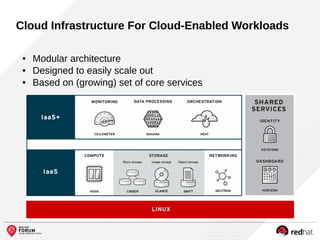
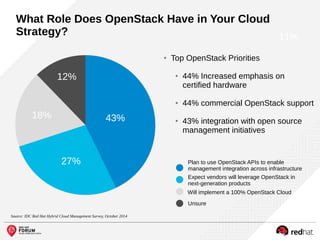
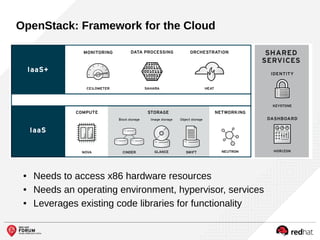
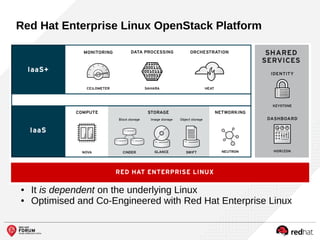
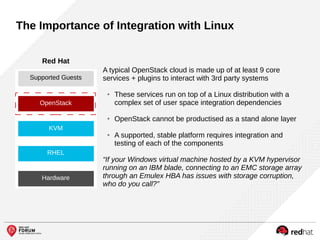
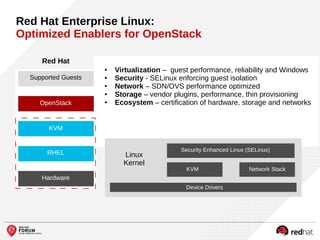
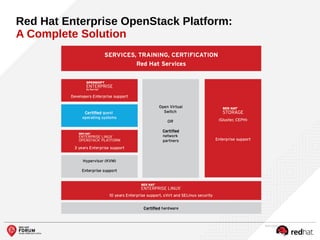
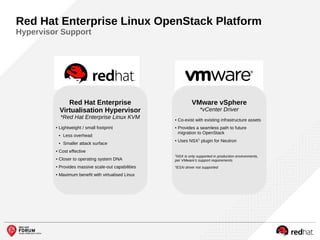
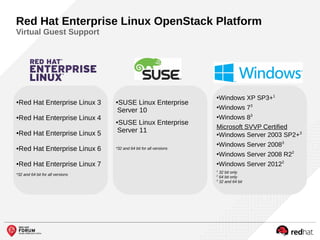
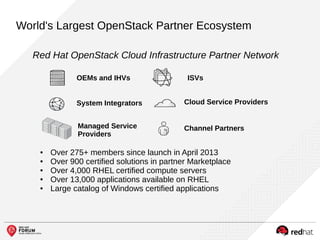
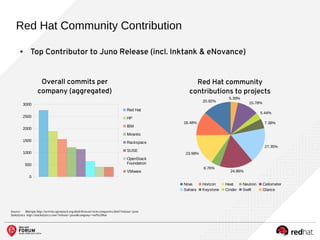
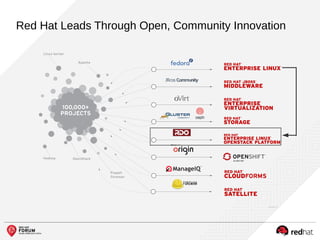
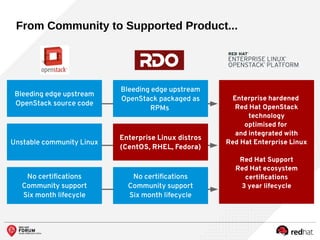
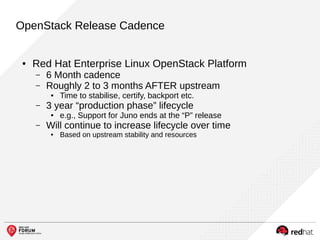
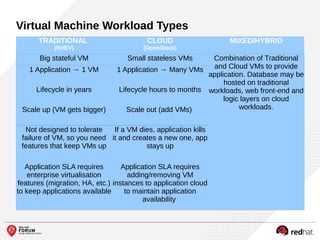
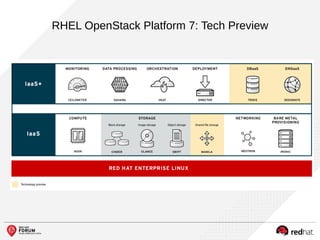
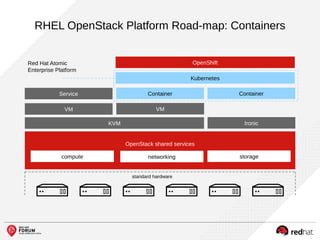
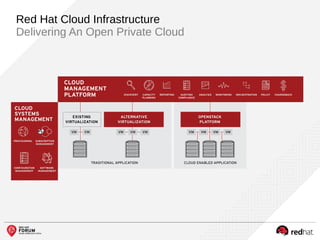
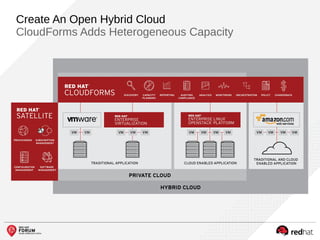
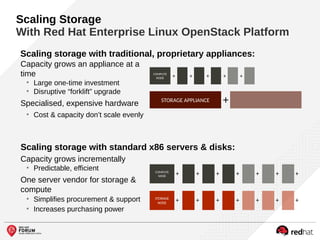
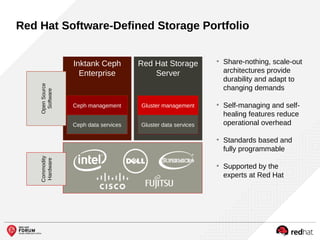
The document outlines the benefits and features of the Red Hat Enterprise OpenStack Platform for creating a scalable cloud infrastructure in enterprise IT. It addresses various IT challenges, explains the OpenStack framework, and highlights Red Hat's contributions to the OpenStack community, emphasizing its integration with Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Additionally, it discusses future developments and next steps for implementing OpenStack solutions.