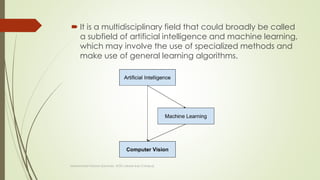
This document provides an overview of computer vision (CV). It discusses the desire for computers to understand visual content like humans. Computer vision seeks to develop techniques to help computers understand digital images and videos by recognizing objects and scenes. While humans can easily recognize and understand visual content, computer vision remains challenging due to the complexity of visual data and infinite possibilities in images. The document outlines some applications of computer vision like optical character recognition, face detection, medical imaging, and surveillance.