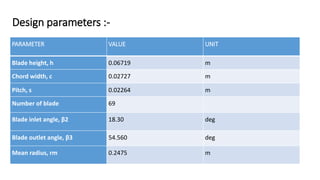
1) The document discusses the design and analysis of a turbo jet engine high pressure turbine (HPT) rotor blade. It analyzes two potential materials, Inconel 718 and Titanium T6, to achieve good performance.
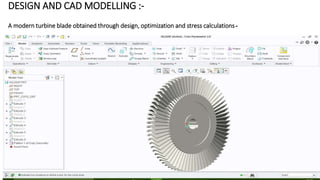
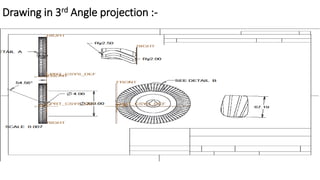
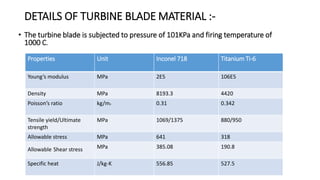
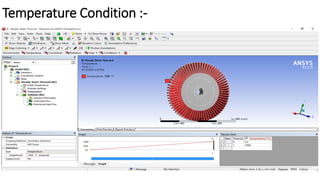
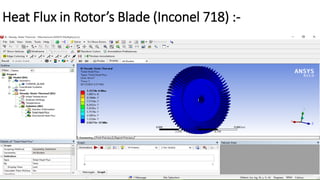
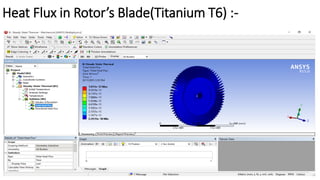
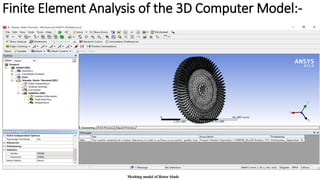
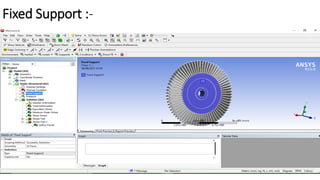
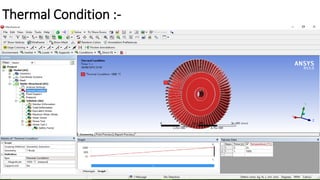
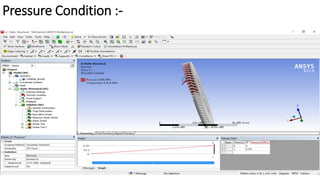
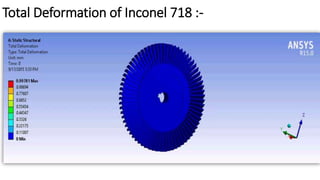
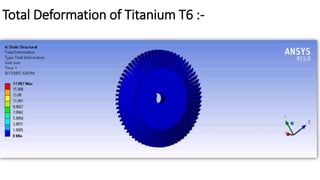
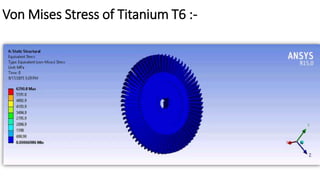
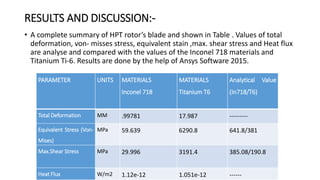
2) A CAD model and finite element analysis of the HPT blade is presented. Results show that under operating conditions of 101kPa pressure and 1000°C temperature, the blade experiences less deformation and stress when made from Inconel 718 compared to Titanium T6.
3) While Titanium T6 has better heat dissipation properties, Inconel 718 is concluded to be the better material choice as it is stronger at high temperatures and more economical.