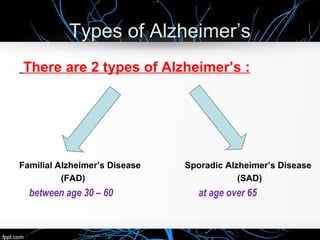
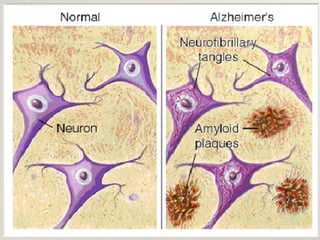
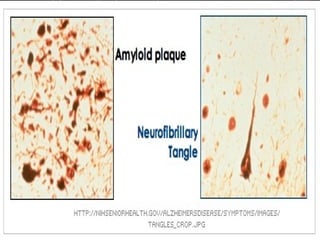
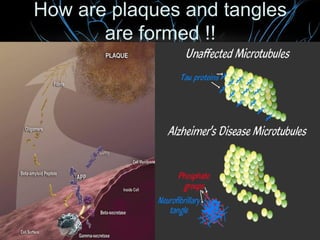
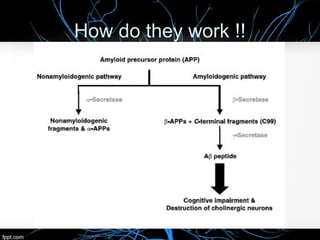
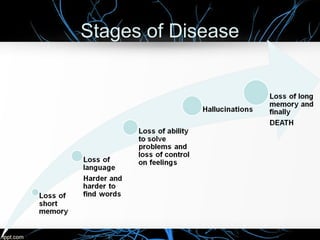
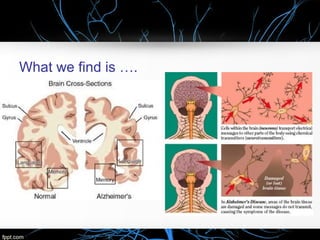
Alzheimer's disease, named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer, is a progressive disorder that leads to memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes due to neuron damage. There are two types of Alzheimer's: familial (affecting ages 30-60) and sporadic (occurring after age 65), characterized by beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. While there is no cure, the FDA has approved medications to slow its progression and improve quality of life.