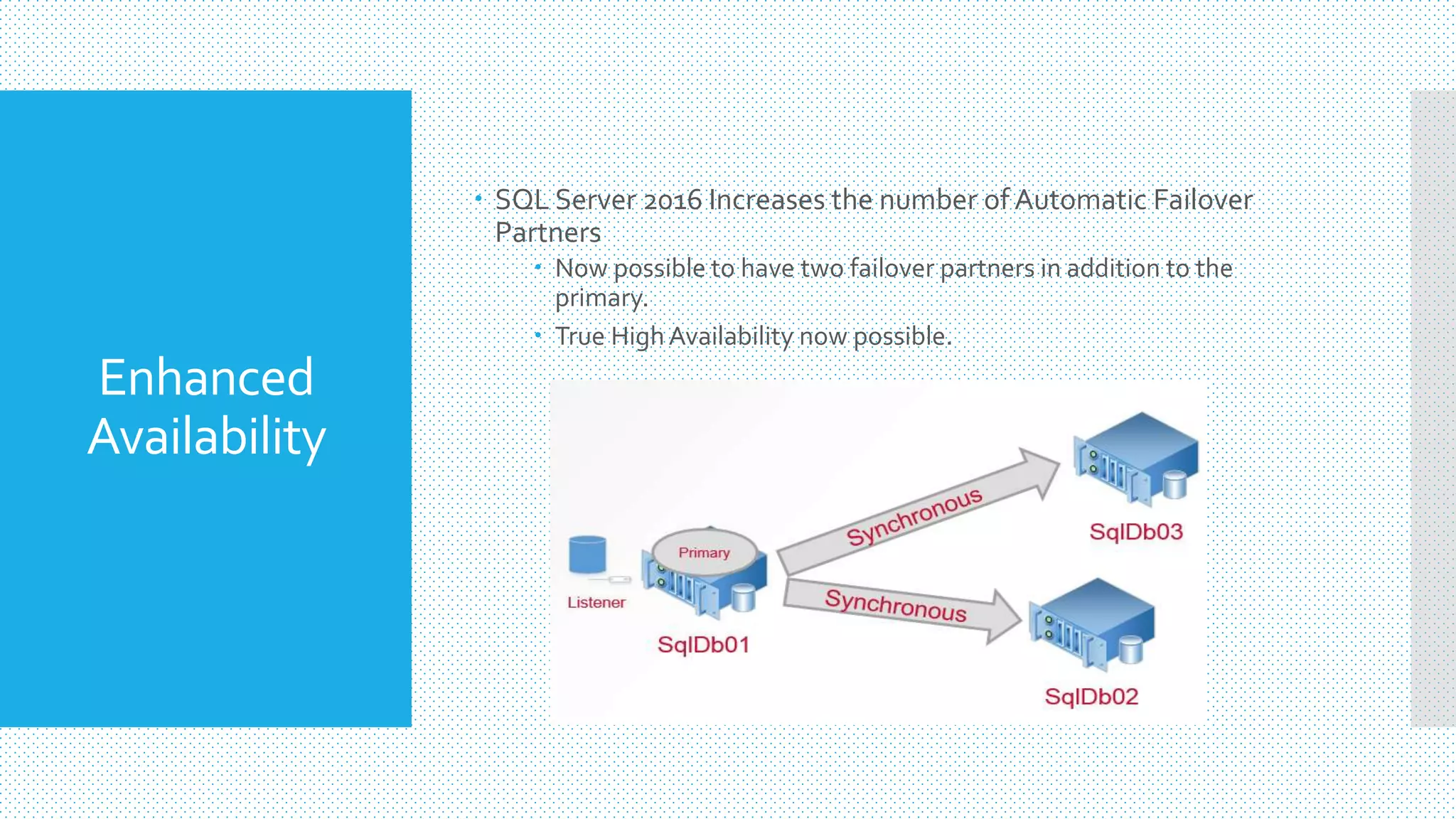
- SQL Server 2016 enhances AlwaysOn availability groups by allowing up to two additional secondary replicas for failover purposes, improving high availability.
- It introduces load-balanced read-only replicas that can distribute read-only workloads across multiple secondaries in a round-robin fashion.
- Distributed transaction support is now provided for AlwaysOn when using Windows Server 2016 and SQL Server 2016.











![Load Balanced
Read-only
Replica
Read-only routing refers to the ability of SQL Server to route
qualifying read-only connection requests to an availableAlwaysOn
readable secondary replica.
Read-only clients must direct their connection requests to this
listener, and the client's connection strings must specify the
application intent as "read-only"
SQL Server 2014 routing lists were the order of the secondaries that
you wanted to access in a failure precedent order.
alter availability group [sqlLabAg01]
modify replica on 'sqlLabDb01'
with
(
primary_role(read_only_routing_list =
)
;
go
('sqlLabDb02','sqlLabDb03','sqlLabDb01'))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alwaysonenhancements-160118130951/75/Alwayson-AG-enhancements-13-2048.jpg)
![Load Balanced
Read-only
Replica
SQL Server 2016 allows for groups of replicas to be specified to
accessed in a round robin order.
Configure load-balancing across a set of read-only replicas
Note the additional parentheses in the routing list.
alter availability group [sqlLabAg01]
modify replica on 'sqlLabDb01'
with
(
primary_role(read_only_routing_list =
)
;
go
(('sqlLabDb02','sqlLabDb03‘),'sqlLabDb01')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alwaysonenhancements-160118130951/75/Alwayson-AG-enhancements-14-2048.jpg)




