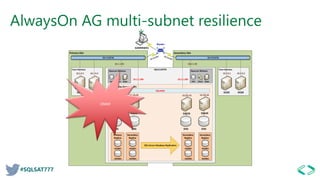
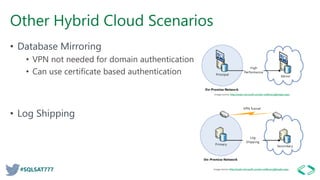
This document discusses AlwaysOn availability in SQL Server 2017. It provides an overview of AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) and AlwaysOn Availability Groups (AG), including how they provide high availability and disaster recovery. It describes features like multi-subnet support, read-only access to secondary replicas, and enhancements in SQL Server 2014-2017 like increased synchronous replicas and secondary replica seeding.